
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecule is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
The given molecule A is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
![]()
The given molecule is in trans form. The directions of the vectors of both the C-F bonds are equal but opposite to each other. Hence the dipole moments of both the C-F bonds get cancelled out with each other. Therefore, there is no net dipole moment.
Dipole moment on this molecule is symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule A is nonpolar.
(b)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecule is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
The given molecule B is polar.
Explanation of Solution
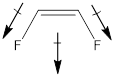
The given molecule is in cis form. The direction of vectors of both the C-F bonds is in the same direction, giving a net permanent dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule B is polar.
(c)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule C is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
![]()
In this molecule, both the C-Cl bonds are opposite to each other, so the dipole moments are cancelled out with each other. Therefore, there is no net dipole moment in this molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule C is nonpolar.
(d)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
The given molecule D is polar.
Explanation of Solution
![]()
In this molecule, chlorine is more electronegative than the carbon atom; hence the direction of the vector of dipole moment is more towards C-Cl bond, giving a net dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule D is polar.
(e)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule E is polar.
Explanation of Solution
![]()
In this molecule, Chlorine is more electronegative than bromine; hence the direction of the vector of dipole moment is more towards C-Cl bond, giving a net dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule E is polar.
(f)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule F is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
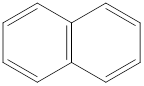
In this molecule, there is no electronegative atom present since no charge separation is taking place. So there is no net dipole moment.
Dipole moment on this molecule is symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule F is nonpolar.
(g)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule G is polar.
Explanation of Solution
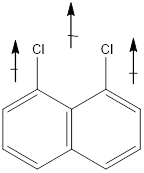
In this molecule, Chlorine is an electronegative atom, and both the C-Cl bonds are in the same direction. Therefore, the direction of the vector of dipole is moment is upward, giving a net dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule G is polar.
(h)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule H is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
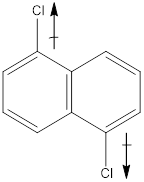
In the molecule, chlorine is an electronegative atom, and both the C-Cl bonds are in opposite direction. Therefore, the directions of the vectors of dipole moment of two C-Cl bonds get cancelled out with each other. Hence there is no net dipole moment.
Dipole moment on this molecule is symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule H is nonpolar.
(i)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule I is polar.
Explanation of Solution
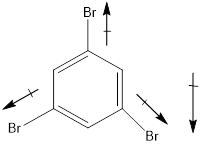
In this molecule, bromine is an electronegative atom, but one C-Br bond is in upward direction, and two C-Br bonds are in downward direction. Therefore, the net dipole moment acts in downward direction.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule I is polar.
(j)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule J is polar.
Explanation of Solution
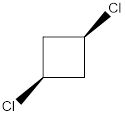
In this molecule, both the C-Cl bonds are present above the plane (that is wedge notation). Therefore, the directions of the vectors of dipole moment of both the C-Cl bonds are in the same direction, giving net dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule J is polar.
(k)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule K is polar.
Explanation of Solution
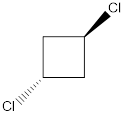
In this molecule, one C-Cl bond is present above the plane (that is, the wedge notation), and another C-Cl bond is present below the plane (that is, the dotted notation). Therefore, the directions of the vectors of dipole moment of both the C-Cl bonds are in opposite direction, which get cancelled out with each other, giving no net dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule K is nonpolar.
(l)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule L is polar.
Explanation of Solution
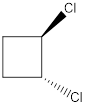
In this molecule, though both the C-Cl bonds are in opposite direction, both the chlorines are present on carbon
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule L is polar.
(m)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule M is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
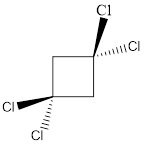
In this molecule, two C-Cl bonds are above the plane, and two C-Cl bonds are below the plane; hence the molecule has symmetry. The directions of the vectors of dipole moment of all the four C-Cl bonds are cancelled with each other, giving no net dipole moment to the molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule M is nonpolar.
(n)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the given molecules is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the magnitude of its dipole. A dipole moment is a vector, which has both magnitude and direction. Bond polarity originates from bonds between atoms of different electronegativity. Symmetry of molecules also predicts the polarity of a molecule.
Answer to Problem 2.41P
Molecule N is polar.
Explanation of Solution
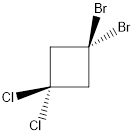
In this molecule, two C-Cl and two C-Br bonds are present. Since chlorine is more electronegative than bromine, the direction of the vector of dipole moment is towards C-Cl bonds. Therefore, there is a net dipole moment present in this molecule.
Dipole moment on this molecule is not symmetrically distributed; hence the given molecule N is polar.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- What reactant would transform the molecule from the top left to the top right. Given the same molecule, what would the given reactants transform it into below?arrow_forwardIndicate which of the following molecules is polar because it possesses a net dipole. Show the direction of the net dipole if one exists.arrow_forwardWhat is the most polar area/functionality for this compound?arrow_forward
- Please draw a more stable resonance structure for the following molecule. Use a curved arrow to show how to transform the original structure to the new one and please specify charges.arrow_forwardCircle the most basic atom or group of atoms in each of the following molecules:arrow_forwardThe instructions are to draw the resonance hybrid structure of the molecule on the left. My answer is circled , which is wrong. Can someone explain why?arrow_forward
- could you please help me redraw this molecule and indicate all the bonds that have a dipole and the net dipole moment of the molecule, if one exists? Thank youarrow_forwardHow can you tell whether a lone pair is localized or delocalized?arrow_forwardplease answer this spec question! answer choices are given except toluene and tetrahydrofuran!arrow_forward
- match the following to its compound name. *First row only from upper to bottomarrow_forwardFor each of the following compounds, identify any polar covalent bonds by indicate δ+ and δ- symbols in the appropriate locations.arrow_forward4)On the following molecules, draw the curved arrows to convert the left-hand resonance structure form to the right-hand resonance structure formarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

