
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction between
Concept introduction:
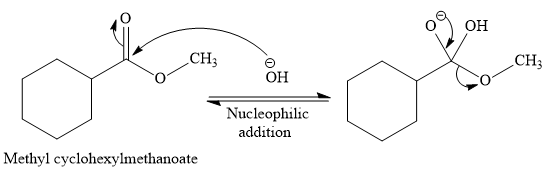
The reaction in which one form of an ester is converted to another form by changing the carbon skeleton of the alkoxide part (OR) of the ester is called transesterification. The transesterification reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction. In the first step, the nucleophile adds the electro-poor carbonyl carbon of the ester, which forces the bonding pair of carbonyl p bond onto the O atom. A negative charge is produced on that O, and a tetrahedral intermediate is formed. In the second step, tetrahedral intermediate undergoes nucleophilic elimination to form the transesterification product. The transesterification is a reversible reaction. The base hydrolysis of an ester to produce corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol is called a saponification reaction. Saponification also involves a reversible nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction. The first step in saponification is the same as in the transesterification reaction in which the tetrahedral intermediate is formed. In the second step, nucleophilic elimination takes place to produce an alkoxide ion and the corresponding carboxylic acid. The alkoxide ion rapidly irreversibly deprotonates the carboxylic acid, leading to form the carboxylate ion and alcohol. Finally, on acid workup step, carboxylic acid is regenerated.
Answer to Problem 20.28P
The product for the reaction between
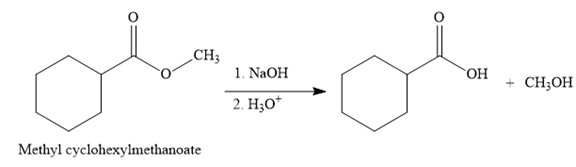
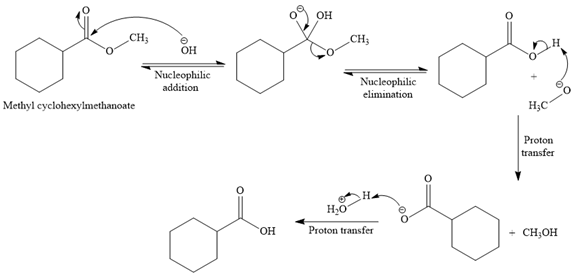
The complete detailed, mechanism for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
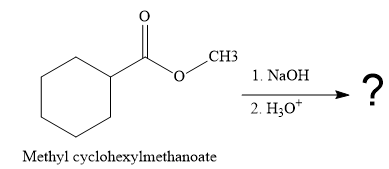
So this is a saponification reaction of
In the second step, nucleophilic elimination takes place to produce an alkoxide ion and corresponding carboxylic acid. These steps are reversible.
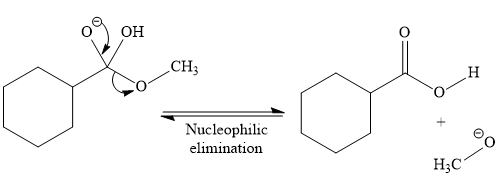
In the third step, irreversible deprotonation of the carboxylic acid takes place and the carboxylate ion is formed. Finally, on acid workup step, protonation of the carboxylate ion takes place to form the carboxylic acid.
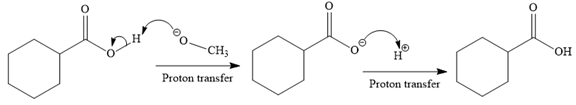
Thus, the products of the given reaction are
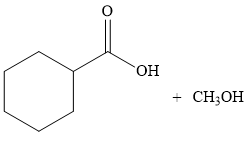
The product is predicted by using transesterification concept and the detailed mechanism is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction between
Concept introduction:
The reaction in which one form of an ester is converted to another form by changing the carbon skeleton of the alkoxide part (OR) of the ester is called transesterification. The transesterification reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction. In the first step, the nucleophile adds the electro-poor carbonyl carbon of the ester, which forces the bonding pair of carbonyl p bond onto the O atom. A negative charge is produced on that O, and a tetrahedral intermediate is formed. In the second step, tetrahedral intermediate undergoes nucleophilic elimination to form the transesterification product. The transesterification is a reversible reaction. The base hydrolysis of an ester to produce corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol is called a saponification reaction.
Answer to Problem 20.28P
The product for the reaction between
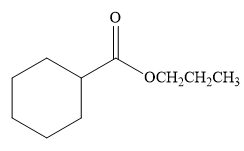
The complete detailed, mechanism for the given reaction is
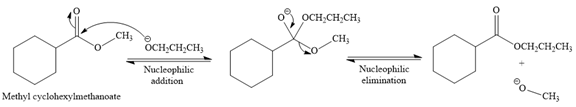
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
This is a transesterification reaction of
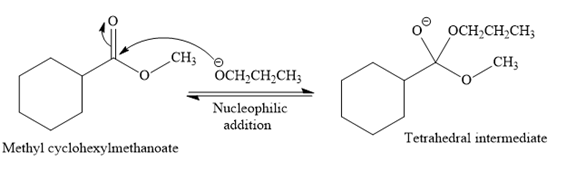
In the second step, the tetrahedral intermediate undergoes nucleophilic elimination to form the transesterification product.
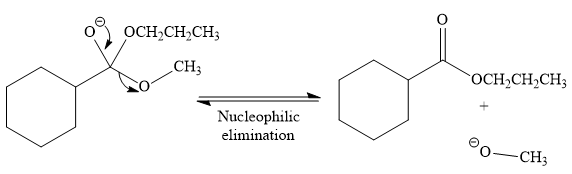
Thus, the product of the given reaction is

The product is predicted by using transesterification concept and the detailed mechanism is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction between
Concept introduction:
The reaction in which one form of an ester is converted to another form by changing the carbon skeleton of the alkoxide part (OR) of the ester is called transesterification. The transesterification reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction. In the first step, the nucleophile adds the electro-poor carbonyl carbon of the ester, which forces the bonding pair of carbonyl p bond onto the O atom. A negative charge is produced on that O, and a tetrahedral intermediate is formed. In the second step, tetrahedral intermediate undergoes nucleophilic elimination to form the transesterification product. The transesterification is a reversible reaction. The base hydrolysis of an ester to produce corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol is called a saponification reaction.
Answer to Problem 20.28P
The product for the reaction between
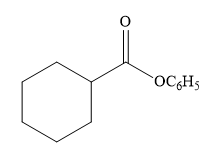
The complete detailed, mechanism for the given reaction is
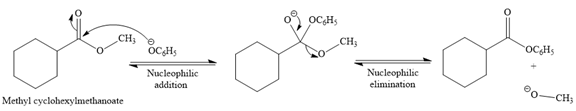
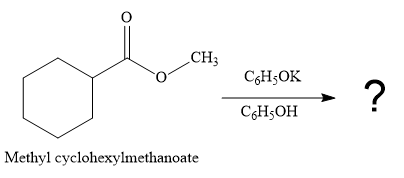
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
This is a transesterification reaction of the
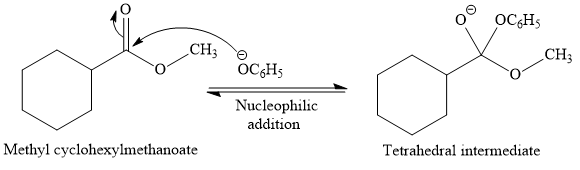
In the second step, tetrahedral intermediate undergoes nucleophilic elimination to form the transesterification product.
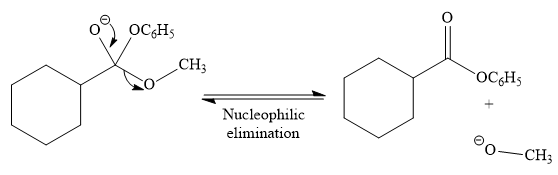
Since phenoxide ion (
Thus, the product of the given reaction is

The product is predicted by using transesterification concept and the detailed mechanism is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Please draw the reaction (attached)and explain the mechanism of an SN2 reaction then identify the nucleophile, substrate and the leaving group.arrow_forwardProvide the products, intermediates, and/or reagents forthe following reactions:arrow_forwardComplete the following reaction by providing missing reactant or product as appropriate.arrow_forward
- The reaction between 2-methyl-2-pentanol and sulfuric acid to yield 2-methyl-2-pentene goes via what mechanism?arrow_forwardFor the given SN2 reaction, draw the organic and inorganic products of the reaction, and identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group.arrow_forwardDraw the lewis structure for 2, 3, 3-trimethyl-1 - butene. Then, show the full curved arrow mechanisms when the alkene is Acid - catalyzed hydrated, reacted with water with a trace of acid catalyst like sulfuric acid H2SO4, WITHOUT a methyl shift.arrow_forward
- Reaction of but-1-ene with HBr gives two products in unequal amounts. In each case, identify the two products, state which is the major product, explain why it is the major product and give the mechanism for its formation.arrow_forwardGive the reactants and the mechanism to synthesize the following:arrow_forwardProvide the mechanism for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- Provide the mechanism for this reactionarrow_forwardThe question is: "Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction between pentan-2-one and (CH3)3O– in t-butanol to form an enolate. Draw all electrons and charges on both resonance structures. Then answer the question about the reaction." I got the initial arrows correct, but am not entirely sure what the carbanion intermediate would look like and then what the curved arrows would be to convert it to its final oxanion formarrow_forwardSupply the missing reagent for the following reactions.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

