
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.3P
The complete mechanism of the reaction can be drawn as
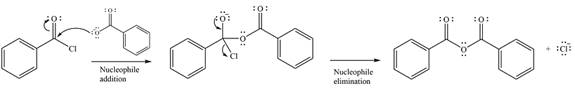
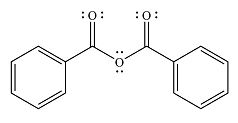
The major product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
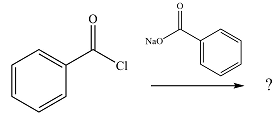
The substrate is an acid chloride, the least stable of the carboxylic acid derivatives. It will, therefore, undergo an acyl substitution via nucleophilic addition-elimination to form an acid anhydride.
The reagent is ionic, and essentially behaves as a negatively charged nucleophile, a carboxylate anion. It will attack and add to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon from the acid chloride. This will result in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, with the negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen of the substrate.
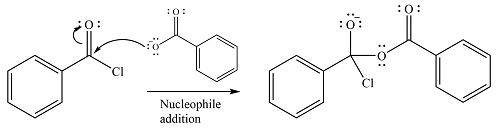
In the next step, the leaving group, chloride ion is eliminated to form the product.
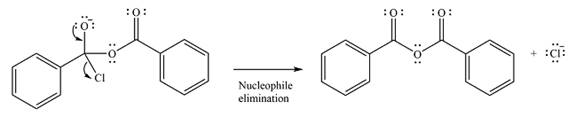
The product is more stable than the substrate, therefore, the reaction will occur.
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
And the major product of the reaction ss

The mechanism and the major product of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination provided the possible product is of comparable or higher stability.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.3P
The complete mechanism of the reaction can be drawn as
The major product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
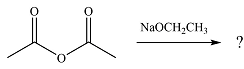
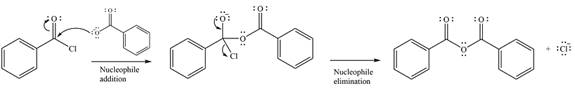
The substrate is an acid anhydride and the reagen is essentially the anionic nucleophile
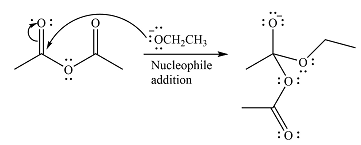
The second step is nucleophilic elimination. The acyl group from the original anhydride is eliminated to form the product, an ester.
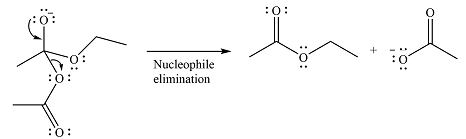
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
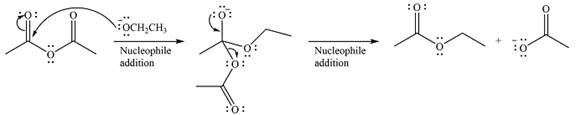
Since an ester is more stable than an acid anhydride, the reaction will occur, and the major product will be

The mechanism and the major product of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination provided the possible product is of comparable or higher stability.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.3P
The complete mechanism of the reaction can be drawn as
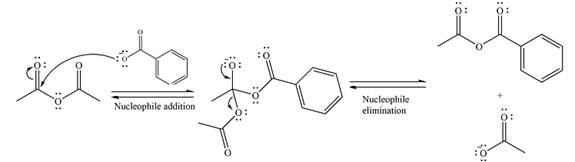
The major product of the reaction is
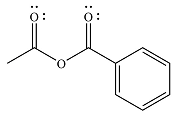
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
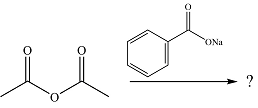
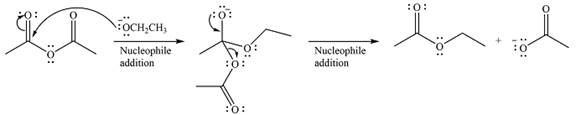
The substrate is an anhydride, with electrophilic carbons. The reagent is an ionic compound, which will essentially act as an anionic nucleophile, a carboxylate ion.
In the first step, the carboxylate ion will add to one of the carbonyl carbons of the anhydride. This will result in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate with the negaive charge shifting to the ccorresponding carbonyl oxygen.
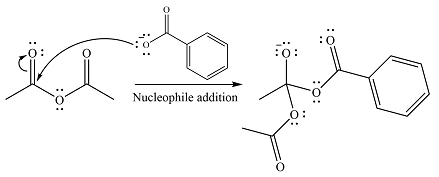
In the next step, the leaving group will be liminated as a carboxylate anion.
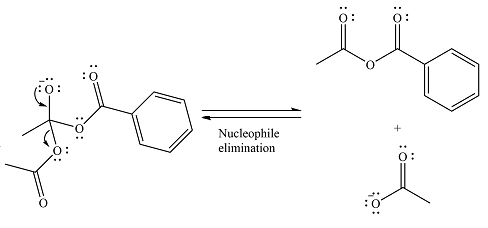
The major product is another acid anhydride of comparable stability. This means the reaction will occur, with reversible addition and elimination steps.
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
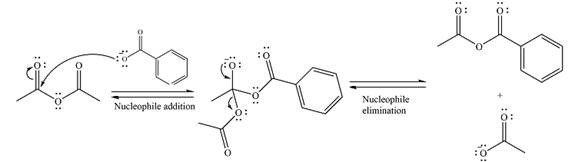
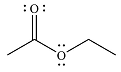
Thus, the major product will be

The mechanism and the major product of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination provided the possible product is of comparable or higher stability.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.3P
There is no reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
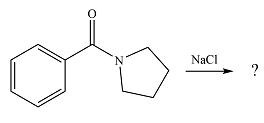
The substrate is a highly stable amide. If the
Since the possible product is of lower stability than the substrate, the reaction will not occur.
The reaction will not occur if the possible product is of lower stability than the susbtrate.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.3P
There is no reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
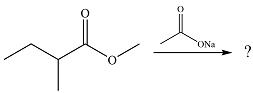
The substrate is an ester while the possible product of the reaction would be an acid anhydride. Since an ester is more stable than an acid anhydride, the reaction will not occur.
The reaction will not occur if the possible product is of lower stability than the susbtrate.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.3P
The complete mechanism of the reaction can be drawn as
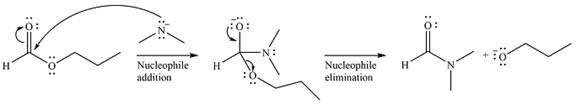
The major product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
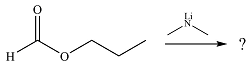
The substrate is an ester, with an electrophilic carbonyl carbon. The reagent is essentially an anionic nucleophile
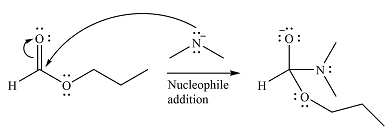
In the second step, the alkoxide group from the original ester will be eliminated to form the product, an amide.
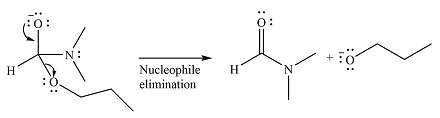
Since the product is more stable than the substrate, the reaction will occur.
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

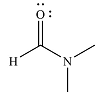
And the product of the reaction will b

The mechanism and the major product of the given reaction were determined based on nucleophilic addition-elimination provided the possible product is of comparable or higher stability.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Draw a complete, detailed mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forwardDraw the complete mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions.arrow_forwardDetermine the major product of each reaction in Problem and draw the complete, detailed mechanism. Pay attention to stereochemistry where appropriate.arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following reactions. Draw the complete, detailed mechanism that leads to the formation of each of those products.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions.arrow_forwardPredict the major product of each of the reactions shown here and provide the complete, detailed mechanism.arrow_forward
- Draw a complete, detailed mechanism AND predict the major organic product for the following transformations a, b & c.arrow_forwardDraw a detailed mechanism of the following reactions and determine the major product:arrow_forwardHelp, explain in detail please. Thank you! Did the overal reaction shown here occur by and SN2, Sn1, E2, or E1 mechanism? How do you know? Draw the complete, detailed mechanism to account for the formation of both products.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





