
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The strucutral formula for each of the given compound has to be proposed using the given NMR data.
Concept Introduction:
The
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
13C NMR Spectroscopy: This type of NMR splitting of signals tells us numbers of hydrogens atoms are attached to each carbon. The triangle rule (n+1) C. The chemical shift explains the different hybridization
(a)
Explanation of Solution
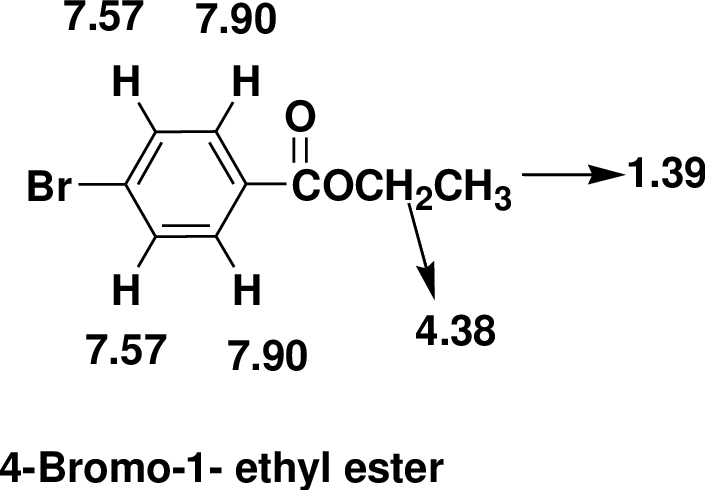
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula F is
We calculate the
From the molecular formula
The one signal in the
There are also one
Therefore, the based on above spectral details the structure that is consistent with the all of these facts is 4-Bromo-1- ethyl ester.
(b)
Interpretation:
The strucutral formula for each of the given compound has to be proposed using the given NMR data.
Concept Introduction:
The
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
13C NMR Spectroscopy: This type of NMR splitting of signals tells us numbers of hydrogens atoms are attached to each carbon. The triangle rule (n+1) C. The chemical shift explains the different hybridization
(b)
Explanation of Solution
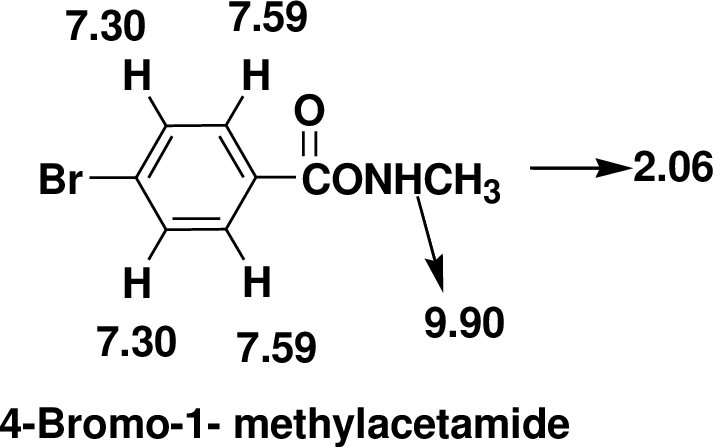
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula F is
We calculate the
From the molecular formula
The one signal in the
There are also one
Therefore, the based on above spectral details the structure that is consistent with the all of these facts is 4-Bromo-1- methylacetamide.
(c)
Interpretation:
The strucutral formula for each of the given compound has to be proposed using the given NMR data.
Concept Introduction:
The
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
13C NMR Spectroscopy: This type of NMR splitting of signals tells us numbers of hydrogens atoms are attached to each carbon. The triangle rule (n+1) C. The chemical shift explains the different hybridization
(c)
Explanation of Solution
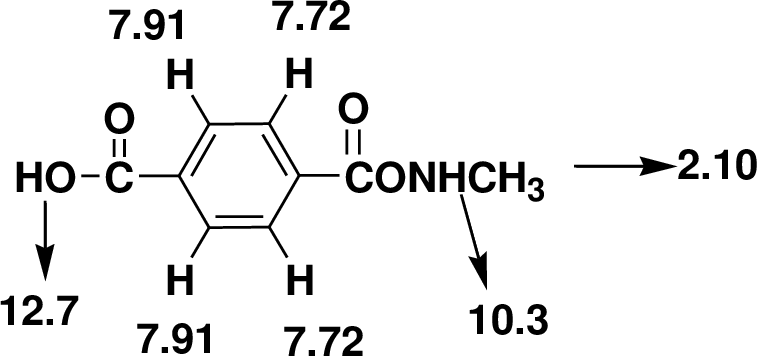
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula F is
We calculate the
From the molecular formula
The one signal in the
There are also one
Therefore, the based on above spectral details the structure that is consistent with the all of these facts is acid substituted phenylacetamide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Compound P has molecular formula C5H9ClO2. Deduce the structure of Pfrom its 1H and 13C NMR spectra.arrow_forwardCompound P has molecular formula C5H9ClO2. Deduce the structure of P from its 1H and 13C NMR spectra.arrow_forwardCompound C has molecular formula C5H8O. The IR, mass, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR spectra are shown below. Suggest a structure for C and explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Propose a structure of compound C (molecular formula C10H12O) consistent with the following data. C is partly responsible for the odor and flavor of raspberries. Compound C: IR absorption at 1717 cm-1arrow_forwardPropose a structure for D (molecular formula C9H9ClO2) consistent with the given spectroscopic data. 13C NMR signals at 30, 36, 128, 130, 133, 139, and 179 ppmarrow_forwardPropose a structure for a compound of molecular formula C3H8O with an IR absorption at 3600–3200 cm−1 and the following NMR spectrum:arrow_forward
- Compounds B and C are isomers with molecular formula C5H9BrO2. The 1H NMR spectrum of compounds B and C are shown below. The IR spectrum corresponding to compound B showed strong absorption bands at 1739, 1225, and 1158 cm-1, while the spectrum corresponding to compound C have strong bands at 1735, 1237, and 1182 cm-1. 1.Based on the information provided, determine the structure of compounds B and C. 2.Assign all peaks in 1H NMR spectrum of compounds B and C.arrow_forwardPropose a structure for a compound of molecular formula C7H14O2 with an IR absorption at 1740 cm−1 and the following 1H NMR data:arrow_forward2. DEDUCE THE STRUCTURE FOR EACH COMPOUND WITH THE INDICATED MOLECULAR FORMULA AND THE 1H-NMR AND IR SPECTRA PROVIDED. (a) Formula: C4H8O2arrow_forward
- Compound A undergoes an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. One of the products (B) that is isolated gives the following 1H NMR spectrum. Identify the compounds A and Carrow_forwardPropose a structure for D (molecular formula C9H9ClO2) consistent withthe given spectroscopic data. 13C NMR signals at 30, 36, 128, 130, 133,139, and 179 ppmarrow_forwardCompound A with molecular formula C6H10 has two peaks in its 1H NMR spectrum, both of which are singlets (with ratio 9 : 1). Compound A reacts with an acidic aqueous solution containing mercuric sulfate to form compound B, which gives a positive iodoform test and has an 1H NMR spectrum that shows two singlets (with ratio 3 : 1). Identify A and B.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





