
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
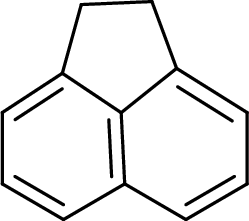
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
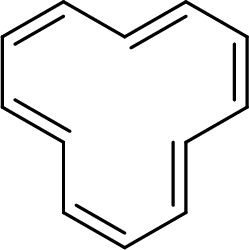
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
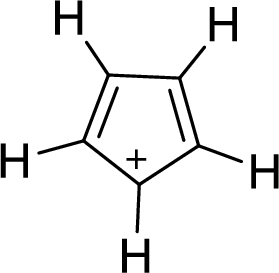
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
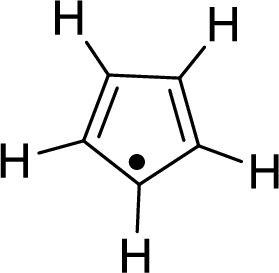
No. of double bonds:
So, the number of
There is an unpaired free-radical electron which is represented by a single dot. This unpaired free-radical electron will be in resonance with the
Therefore, the total number of
(e)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
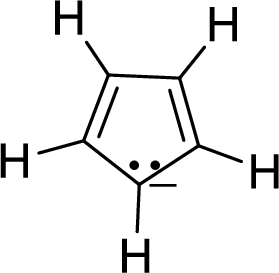
No. of double bonds:
So, the number of
There is a pair of electrons which is represented by two dots with a negative sign. This pair of electrons will be in resonance with the
Therefore, the total number of
(f)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
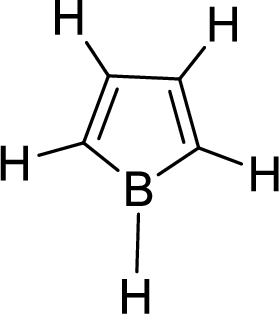
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(g)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
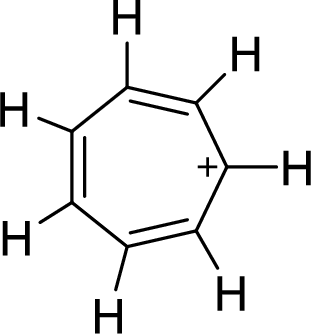
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(h)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
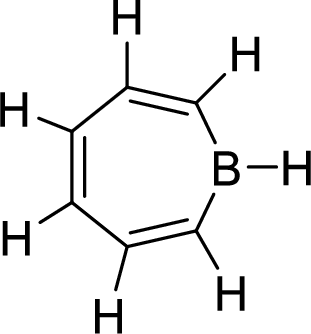
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(i)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
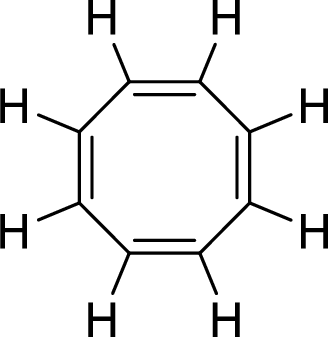
No. of double bonds:
So, the total number of
(j)
Interpretation:
The number of
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown here:
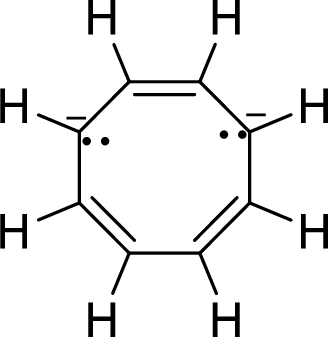
No. of double bonds:
So, the number of
There are two pairs of electrons and each pair is represented by two dots with a negative sign. These two pair of electrons will be in resonance with the
Therefore, the total number of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Identify hybridization in each Carbon atom of given molecules.arrow_forwardDraw the complete p molecular orbital diagram (energy diagram) for allyl anion and fill up the orbitals with the appropriate number of p electrons. As well as the cation please ( "draw the resonance structure before starting the energy diagram")arrow_forwardHow many p orbitals are present on the following molecule?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





