
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(a)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is phenyl formate.
The molecular formula of phenyl formate is
The structure of phenyl formate is given as,
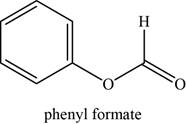
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(b)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is cyclohexyl benzoate.
The molecular formula of cyclohexyl benzoate is
The structure of cyclohexyl benzoate is given as,
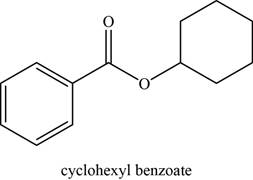
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(c)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is cyclopentyl phenylacetate.
The molecular formula of cyclopentyl phenylacetate is
The structure of cyclopentyl phenylacetate is given as,
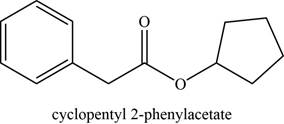
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(d)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is N-butylacetamide.
The molecular formula of N-butylacetamide is
The structure of N-butylacetamide is given as,
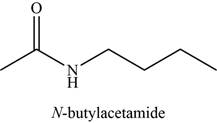
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(e)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is N,N-dimethylformamide.
The molecular formula of N,N-dimethylformamide is
The structure of N,N-dimethylformamide is given as,
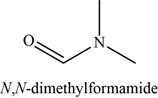
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(f)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is benzoic propionic anhydride.
The molecular formula of benzoic propionic anhydride is
The structure of benzoic propionic anhydride is given as,
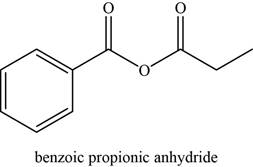
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(g)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is benzamide.
The molecular formula of benzamide is
The structure of benzamide is given as,
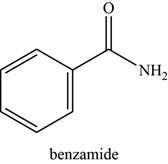
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(h)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The molecular formula of
The structure of
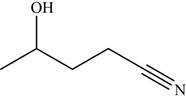
Figure 8
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(i)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The molecular formula of
The structure of
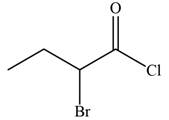
Figure 9
(j)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(j)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The molecular formula of
The structure of
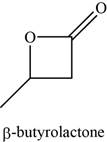
Figure 10
(k)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(k)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is phenyl isocyanate.
The molecular formula of phenyl isocyanate is
The structure of phenyl isocyanate is given as,
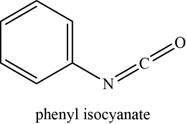
Figure 11
(l)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(l)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is cyclobutyl ethyl carbonate.
The molecular formula of cyclobutyl ethyl carbonate is
The structure of cyclobutyl ethyl carbonate is given as,
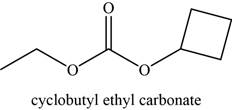
Figure 12
(m)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(m)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The molecular formula of
The structure of
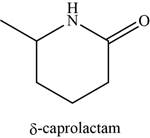
Figure 13
(n)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(n)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is trichloroacetic anhydride.
The molecular formula of trichloroacetic anhydride is
The structure of trichloroacetic anhydride is given as,
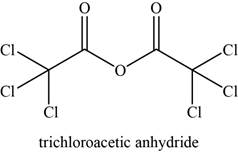
Figure 14
(o)
Interpretation:
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because common names do not follow any rule, whereas IUPAC names follow specific rules. The common name does not include any suffix, prefix, and numbers.
(o)
Answer to Problem 21.42SP
The structure to correspond with the given common and systematic names is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is Ethyl-N-methyl carbamate.
The molecular formula of Ethyl-N-methyl carbamate is
The structure of Ethyl-N-methyl carbamate is given as,
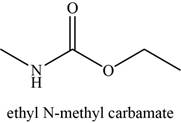
Figure 15
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
- We saw that it is necessary to use excess amine in the reaction of an acyl chloride with an amine. Explain why it is not necessary to use excess alcohol in the reaction of an acyl chloride with an alcohol.arrow_forwardI have questions about p-nitroaniline: Why we are not starting from aniline but from acetanilide What is a protecting group? What are the important characteristics of the protecting grouparrow_forwardWhich of the following will not oxidize benzaldehyde? -- acidified KMnO4 -- acidified K2CrO4 -- Tollen’s reagent followed by H3O+ -- Basic I2 in KIarrow_forward
- Two Compounds: 3-methylbutyric acid and 4,5-dimethyldecane Suppose you took your two compounds, dissolved them in tertbutyl methyl ether and then added them to a separatory funnel. Now suppose you add in aqueous sodium bicarbonate. _____________________ will be dissolved in the terbutyl methyl ether. ________________________ will be dissolved in the aqueous sodium bicarbonate layer. Draw the EXACT chemical structure that will exist in each of the layers after shaking with sodium bicarbonate. (Is it neutral or charged?)arrow_forwardWhat happens when (write reactions involved) iv and varrow_forwardFind two practical methods to prepare phenyl benzoatearrow_forward
- Case: In an attempt to synthesize compound 1a, the researchers mixed benzaldehyde, dimedone (IUPAC: 5,5-dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione), and 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole in ethanol as the solvent. A catalyst that acts both as a Bronsted-Lowry and as a Lewis acid was also added to aid the reaction. Benzaldehyde and dimedone reacts first with each other, then the resulting intermediate eventually reacts with the aminotriazole to form 1a. 1. Explain how benzaldehyde and dimedone reacts with each other, and then with the aminotriazole to form compound 1a in the presence of an acid catalyst. Provide a detailed reaction mechanism.arrow_forwardIllustrate the Separation of cyclohexanamine and cyclohexanol by an extraction procedure ?arrow_forwardKhanna et al (1993) found that the following essential oil had a sedative effect more powerful than the drug chlorpromazine (Largactil) and was also an analgesic: Choose one answer. a. black cumin b. neroli c. rose d. ravensaraarrow_forward
- Why is the water solubility of a carboxylate salt greater than that of its parent carboxylic acid? A) A carboxylate salt is an ionic compound which is soluble in water. B) A carboxylate salt is less polar than its parent carboxylic acid. C) A carboxylate salt has a lower boiling point than its parent carboxylic acid. D) A carboxylate salt is more readily reduced to an aldehyde than its parent carboxylic acid.arrow_forwardPrimary amines can also be prepared by the reaction of an alkyl halide with azide ion, followed by catalytic hydrogenation. What advantage do this method and the Gabriel synthesis have over the synthesis of a primaryamine using an alkyl halide and ammonia?arrow_forwardWhich of these statements is NOT true about the reaction of amines with a cyclic anhydride like phthalic anhydride? a. Dimethylamine will give a cyclic imide product. b. Aniline will give a cyclic imide product. c. Triethylamine will give a cyclic imide product. d. The reaction undergoes a nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanism.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





