
Interpretation:
The principal product of each of the given reactions is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The nitro group can be reduced to primary amine by the catalytic hydrogenation or by the action of iron or tin in hydrochloric acid.
The amides are reduced to
The arenes undergo acylation when reacted with acyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride.
When primary amines react with an
The amide can be prepared by the nucleophilic substitution of acyl chloride by amine.
The secondary amine can be converted to tertiary amine when reacted with a primary
In an acidic condition, the amide gets hydrolyzed to corresponding carboxylic acid and amine.
The aryl diazonium salt is a key intermediate in the synthesis of
Electron donating groups activate the arenes and give electrophilic substitution at ortho-para position.
The reaction of aryl diazonium salt with potassium iodide gives the iodobenzene derivatives.
The aryl cyanide is prepared by the reaction of an aryl diazonium salt with
Chlorobenzene or a bromobenzene can be synthesized from aryl diazonium salt by heating it with cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide in
The aryl amine diazonium salt on reaction with hypophosphorous acid or ethanol
The aromatic fluoride substitution occurs by heating aryl diazonium salt with
The diazonium salt, on hydrolysis, gets converted to phenol.
In the reaction of the phenol and a diazonium salt, the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with diazonium salt.
The
Answer to Problem 39P
Solution:
a)
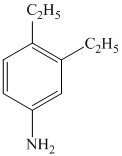
b)
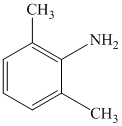
c)
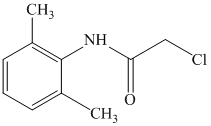
d)
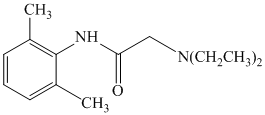
e)
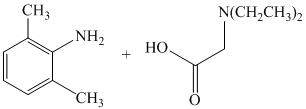
f)
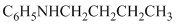
g)
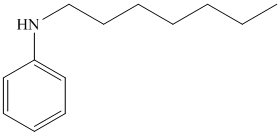
h)
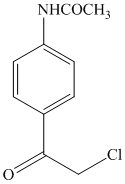
i)
j)
k)
l)
m)
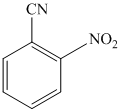
n)
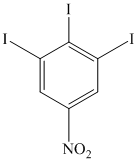
o)
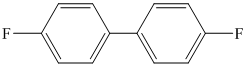
p)
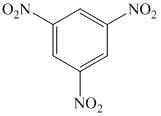
q)
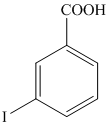
r)
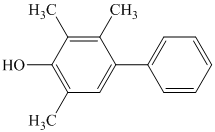
s)
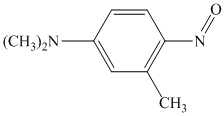
Explanation of Solution
a) The given reaction is shown below:
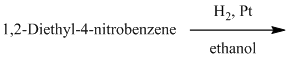
The given reactant has a nitro functional group that gets reduced on catalytic hydrogenation and converted to amine functional group, as shown in following equation.
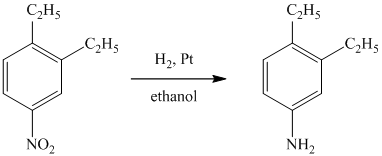
b) The given reaction is shown below:

The given reactant has a nitro functional group that gets reduced in the presence of tinchloride in hydrochloric acid followed by hydroxide and converted to amine functional group, as shown in following equation.
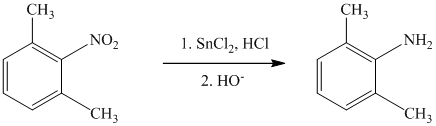
c) The given reaction is shown below:
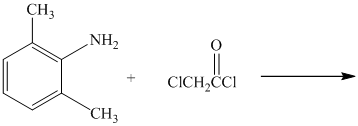
The primary amine, on reaction with acyl chloride, undergoes acylation and forms secondary amide by replacing the chlorine atom directly bonded to carbonyl carbon.
The complete reaction is shown below:
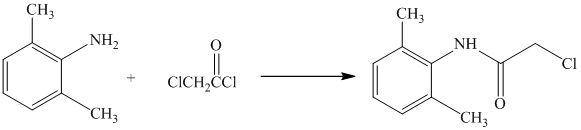
d) The given reaction is shown below:
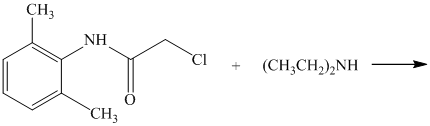
In the above reaction, the reactants are primary alkyl chloride and secondary amine. The nitrogen atom in a secondary amine acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon bonded to the chlorine atom. This nucleophilic substitution converts the secondary amine to a tertiary amine. The complete reaction is shown below:
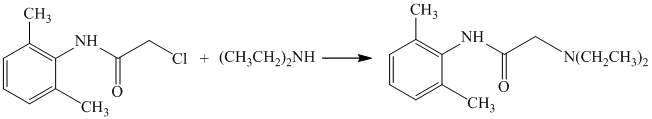
e) The given reaction is shown below:
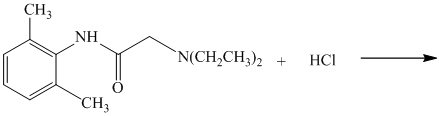
The given reactant has amide functional group in an acidic condition that gets hydrolyzed and produces derivatives of carboxylic acid and amine.
Their structures are shown in the following equation:
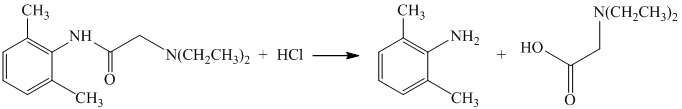
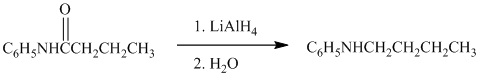
f) The given reaction is shown below:
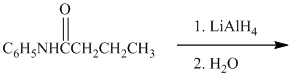
The reactant given in this reaction is a secondary amide, which is subjected to reduction by using the reagent lithium aluminum hydride and produces secondary amine, i.e.,
The complete reaction is shown below:
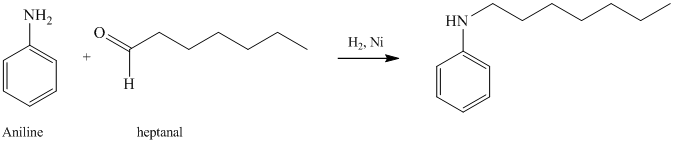
g) The given reaction is shown below:

The aniline, on reaction with heptanal, forms an imine which, on catalytic hydrogenation, forms
h) The given reaction is shown below:
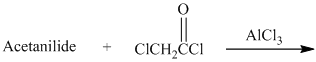
Acetanilide is an aromatic compound; the nitrogen atom bonded to benzene activates the ring and gives acylation at para position when reacted with acyl chloride in presence of aluminum chloride. The structure of the product formed is shown in following equation:
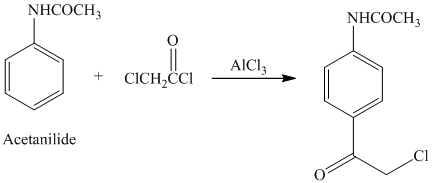
i) The given reaction is shown below:
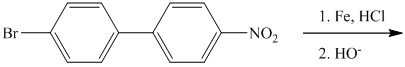
The given reactant has a nitro functional group that gets reduced to iron in hydrochloric acid followed by hydroxide and converted to amine functional group, as shown in following equation.

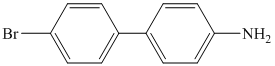
j) The given reaction is shown below:
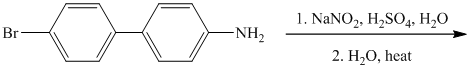
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt, on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. This diazonium salt, on hydrolysis, forms a phenol derivative.
The complete equation is shown below:
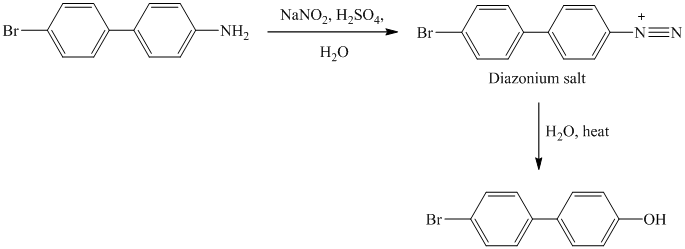
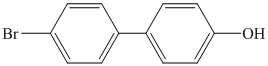
k) The given reaction is shown below:
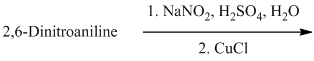
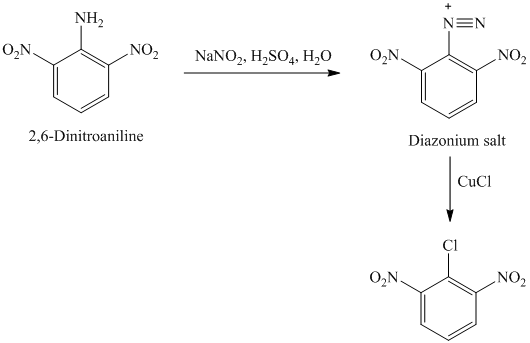
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The chloride substitution is done by treating this diazonium salt with cuprous chloride. The complete equation is shown below:
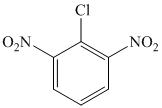
l) The given reaction is shown below:
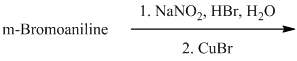
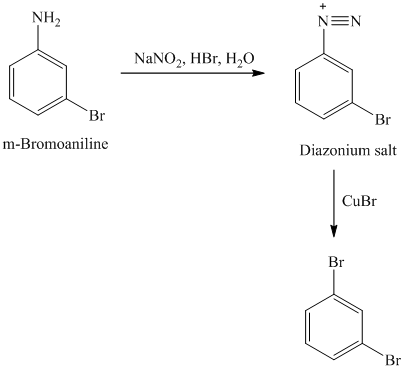
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The bromide substitution is done by treating this diazonium salt with cuprous bromide. The complete equation is shown below:
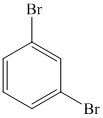
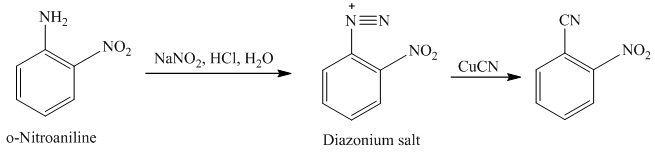
m) The given reaction is shown below:
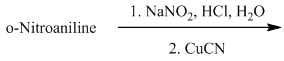
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. This diazonium salt, on reaction with
The complete equation is shown below:
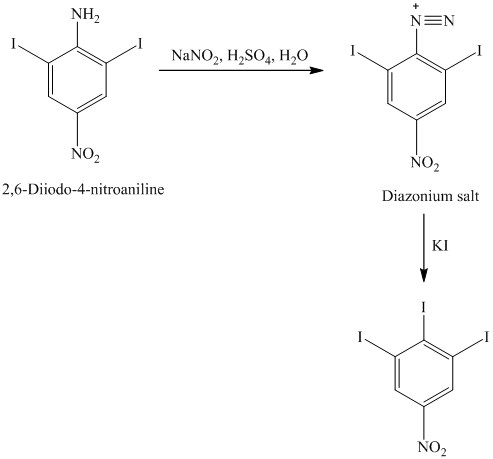
n) The given reaction is shown below:
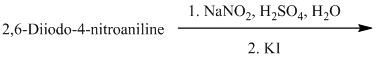
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. This aryl diazonium salt, on reaction with potassium iodide, introduces iodine to aryl by substitution reaction. The complete equation is shown below:
o) The given reaction is shown below:
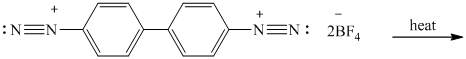
The given reactant has two diazonium saltsand on heating with two molar equivalent of
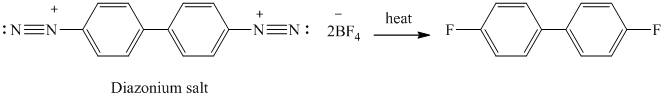
p) The given reaction is shown below:
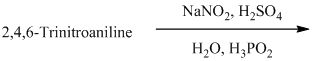
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The diazonium salt on treatment with hypophosphorous acid
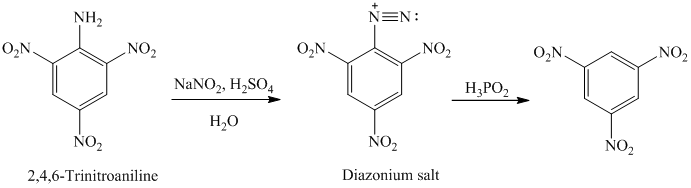
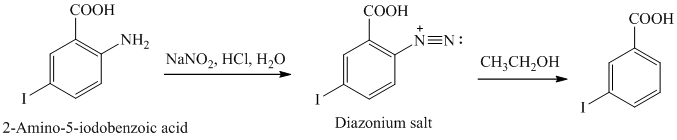
q) The given reaction is shown below:
The aryl amino group in the above reactant forms aryl diazonium salt on reaction with sodium nitrite in acidic condition. The
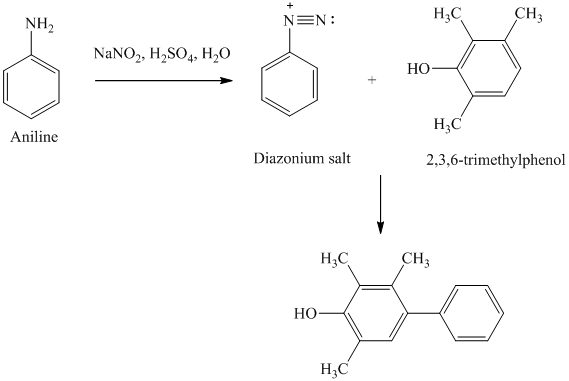
r) The given reaction is shown below:
The aniline, when reacted with sodium nitrite in acidic condition, produces aryl diazonium salt and gets coupled at para position to the of hydroxide group of
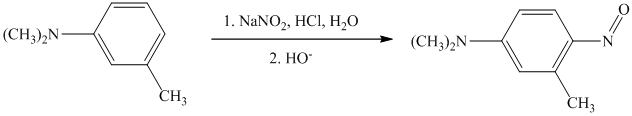
s) The given reaction is shown below:
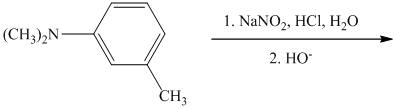
In the given aryl amine, the nitrogen is substituted with methyl groups; therefore, like primary aryl amines, the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..give the major products of the following reactionarrow_forwardprovide the organic product of the following reaction. Please provide reasoning.arrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions. Topic is reactions of alkynes.arrow_forward
- Following are the steps in the industrial synthesis of glycerin. Provide structures for all intermediate compounds (AD) and describe the type of mechanism by which each is formed.arrow_forwardGive a clear handwritten answer with explanation...complete the following reactions in detailedarrow_forwardprovide the major organic productarrow_forward
- Predict the organic product of the following process. Please label clearly and answer correctly.arrow_forwardCompound F may be synthesised by the method attached: Draw the structural formulas of compounds A, C, D, E and F in the boxes providedarrow_forwardGive a clear handwritten answer with explanation...give the complete reaction to given bleow reactions ..please give answer of all sub parts..arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
