
Concept explainers
Synthetic Applications of Enamines
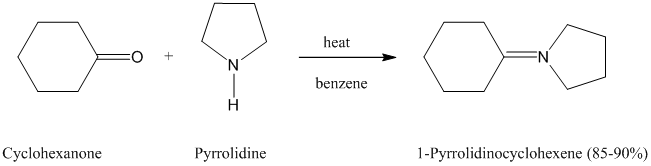
The formation of enamines by the reaction of
described in Section

When preparing enamines, the reaction is normally carried out by heating in benzene as the solvent. No catalyst is necessary, but
Enamines resemble enols in that electron-pair donation makes their double bond electron-rich
and nucleophilic.
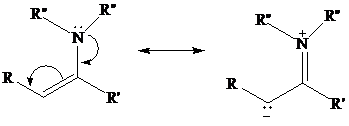
Because nitrogen is a better electron-pair donor than oxygen, an enamine is more nucleophilic thanan enol. Enamines, being neutral molecules, are, however, less nucleophilic than enolates, which areanions.
Reactions of enamines with electrophiles
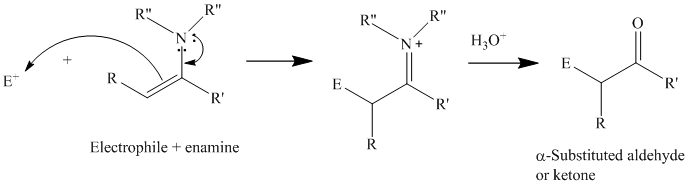
Pyrrolidine is the secondary amine used most often for making enamines from aldehydes and
ketones.
For synthetic purposes, the electrophilic reagents that give the best yields of
Acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides.
Michael acceptors:
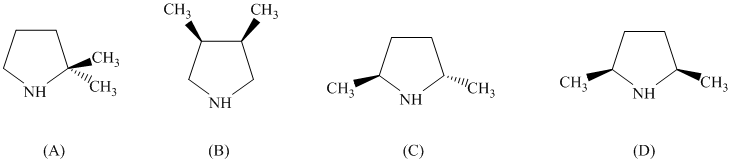
pyrrolidine derivative. Of the following, which one is the best pyrrolidine derivative to use
in this enantioselective synthesis?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry
- (a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C5H10O does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation, it gives ethanoic acid and propanoic acid. Identify the compound and write all chemical equations for the reactions.arrow_forwardEarly organic chemists used the Hofmann elimination reaction as the last step of a process known as a Hofmann degradation—a method used to identify amines. In a Hofmann degradation, an amine is methylated with excess methyl iodide in a basic solution, treated with silver oxide to convert the quaternary ammonium iodide to a quaternary ammonium hydroxide, and then heated to allow it to undergo a Hofmann elimination. Once the alkene product is identified, working backward gives the structure of the amine. Identify the amine in each of the following cases: a. 4-Methyl-2-pentene is obtained from the Hofmann degradation of a primary amine. b. 3-Methyl-1-butene is obtained from the Hofmann degradation of a primary amine. c. 2-Methyl-1-3-butadiene is obtained from two successive Hofmann degradations of a secondary amine.arrow_forwardA. The water solubility of amines found in medications can be increased by salt formation. Dextromethorphan hydrobromide, a cough suppresant, is the salt formed from dextromethorphan (XX) and hydrobromic acid (HBr). Write the equation for the formation of dextromethorphan hydrobromide. B. Suggest appropriate starting materials ( amine and alkyl halide) needed for the preparation of each of the following salts: 1. Cetylpyridinium chloride 2. Benzyldimethyltetradecylammonium chloridearrow_forward
- Grignard reagent is a versatile tool in synthetic organic chemistry. Using bromocyclopentane as a starting material, show how a Grignard reagent, X, is synthesized. Reaction of X with water produces compound Y while treatment in carbon dioxide followed by hydrolysis forms compound Z. 3-methyl-2butanone reacts with X and hydrolyses to yield compound AA. Draw the structural formulae of compounds Y, Z and AA and write the chemical equations respectively.arrow_forwardThe analgesic Tylenol is often taken by people who are allergic to aspirin. Tylenol contains acetaminophen (structure shown) as the active ingredient. Is the structure of acetaminophen similar to the structure of aspirin? In what way? Would acetaminophen give a positive phenol test? What products would be obtained if acetaminophen were hydrolyzed in acidic aqueous solution?arrow_forwardIn the following reactions, compounds A and B are the major products obtained in each of them. Indicate the TRUE alternative: a) The reaction of A with ethanol allows obtaining an ester. b) The hydrolysis of A in an acidic medium allows obtaining a carboxylate ion and an amine. c) Reaction (II) is faster than reaction (I). d) The reaction of compound B with ammonia in ethanol allows obtaining an amide. e) Reaction (I) necessarily requires a catalyst.arrow_forward
- In biochemical reactions, decarboxylation of carboxylic acids typically takes place for-keto carboxylic acids. Justify a rational why nature opted for-keto carboxylic acid decarboxylation. Among the following types of biochemical reactions, ester hydrolysis, rearrangement reactions, water elimination reactions, and anhydride hydrolyses, which one is the most favorable one. Rank the above reactions types in the order of being the most to least favorable reactionarrow_forwardExplain the experimental procedure of the laboratory preparation of the synthesis of alizarin from anthraquinone Explain the chemistry behind the synthesis of alizarin from anthraquinonearrow_forwardFollowing are structural formulas for two more widely used sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agents.Show how each might be synthesized by converting an appropriate amine to a carbamic ester and then treating the carbamate with the sodium salt of a substituted benzenesulfonamide.arrow_forward
- 1. ) 2-Pentanol when introduced with H2SO4 will become ____________ . H2SO4 is a Dehydrating agent (used the concept of Zaitsev to come up with the major product)1-Pentene 1-Pentanal2-Pentene2- Pentanone2.) Diabetic breath has a mild sweet odor because of AroamticAldehydeAlkeneKetone3.) The following compounds contain a Carbonyl group, exceptAcetaminophenCitric AcidPhenolDacroonarrow_forwardSulphuric acid catalyzes the reaction between compound D and compound E producing propl hexanoate. This reaction is an example of Fischer esterification. Compound D reacts with phosphorus tribromide to give alkyl bromide. Draw the structure and give the name of compound D and Earrow_forwardillustrate the chemical equation of N,N- Dimethyl aniline reacts with Diazotized Sulfanilic acid to form Methyl Orangearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

