
Interpretation:
The predominant species of glutamic acid in strongly acidic and basic solutions and at its isoelectric point is to be predicted, and the higher isoelectric point of glutamine than that of glutamic acid is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids contain both acidic (
In solid state, it exists as dipolar or zwitter ionic state, where
In aqueous state, equilibrium exists between cationic and anionic form. The predominant form depends on the pH and the nature of amino acid.
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
a)
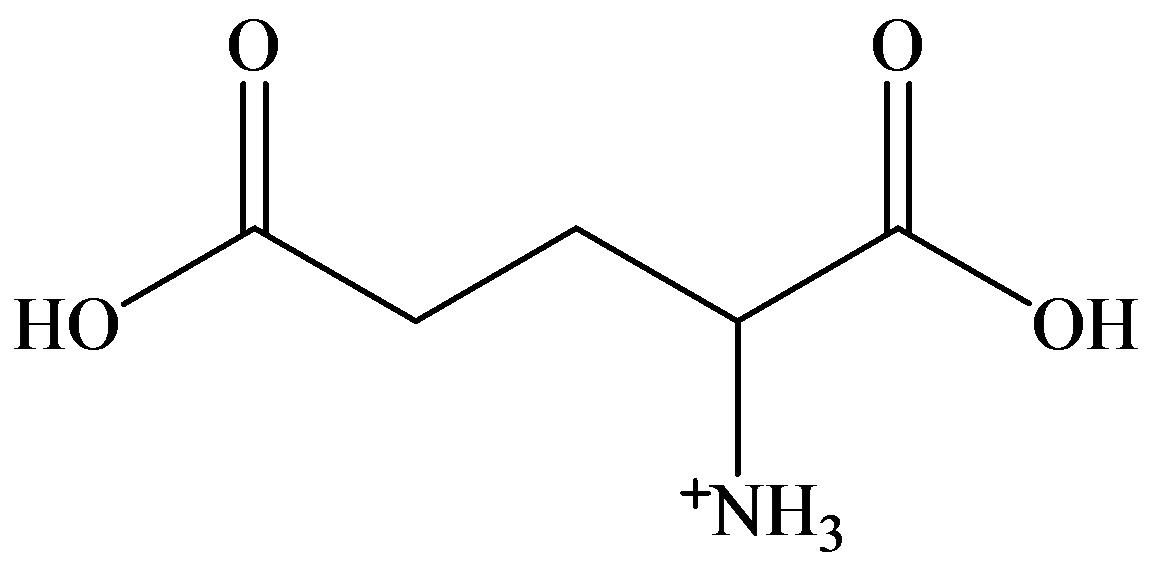
b)
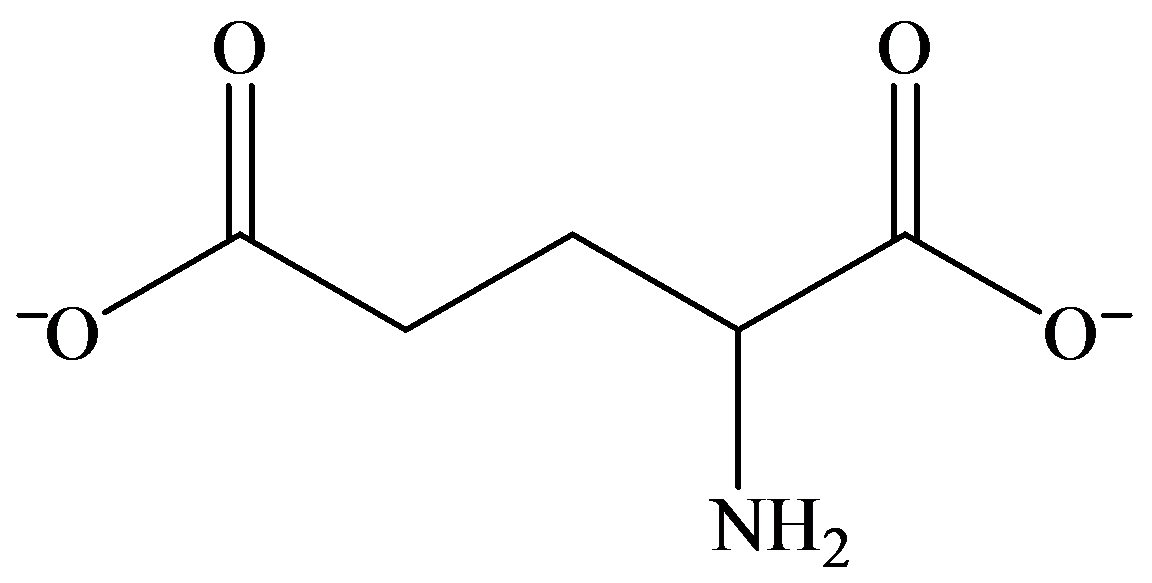
c)
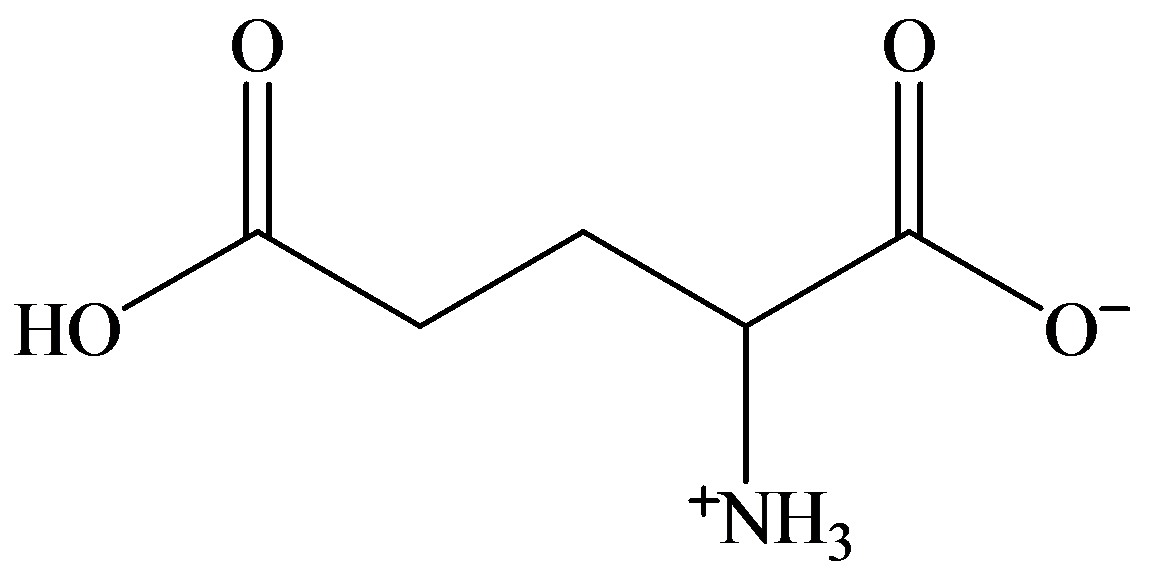
d)
Glutamic acid is a dicarboxylic acid, whereas glutamine with only one carboxyl group has a resemblance with glycine or phenylalanine. Moreover, its isoelectric point exists at a higher
Explanation of Solution
a) Strongly acidic solution
In strongly acidic solution, all amino acids are present as cations. Here,
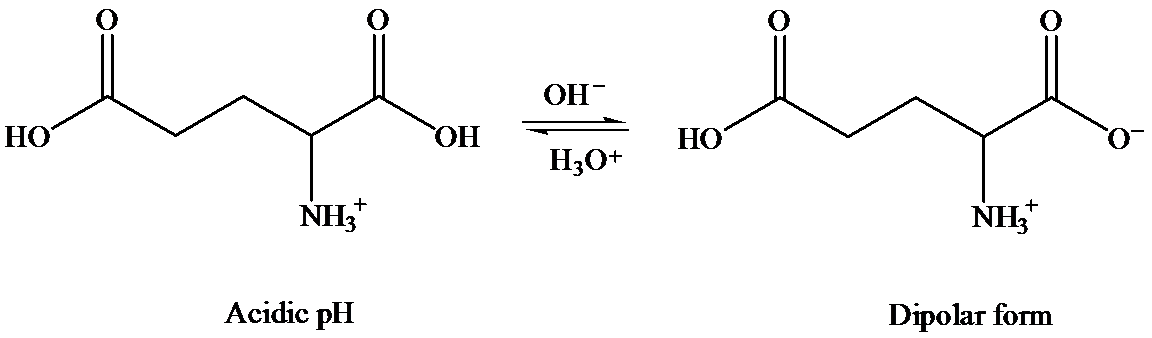
b) Strongly basic solution
In strongly basic solution, all amino acids are present as anions. The addition of base causes removal of proton from both carboxylic acid groups, resulting in a dianion. The amine group is electrically neutral.
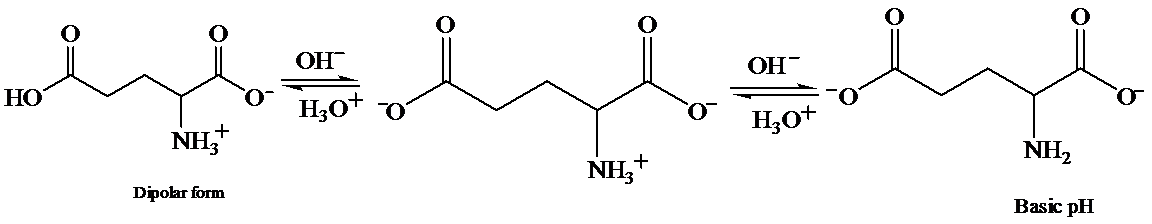
c) At the isoelectric point (pl=3.2)
Each amino acid has a particular intermediate pH at which the concentration of dipolar ion will be maximum, and the concentration of cations and anions will be equal. This point is called isoelectric point and will be different for each amino acid.
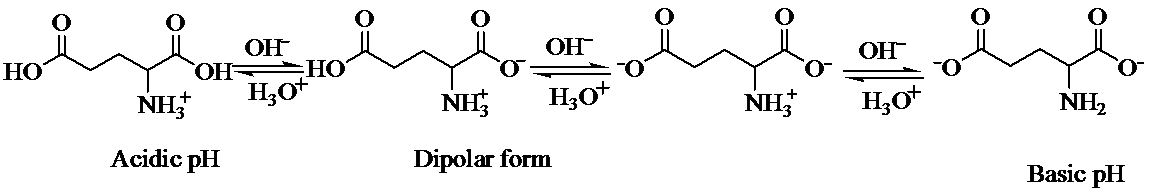
d) The isoelectric point of glutamic is consider higher than that of glutamic acid
The structure of glutamine and glutamic acid is as follows:
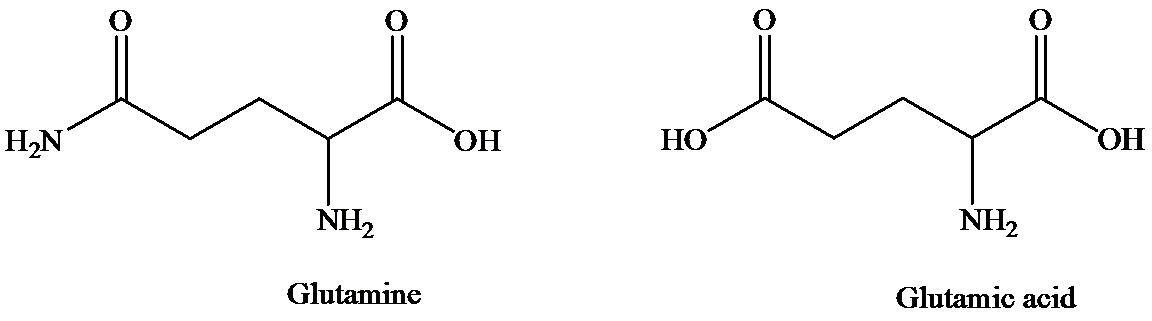
Glutamine contains only one carboxylic acid group, whereas glutamic acid has two. At isoelectric point, dipolar state exists that is there will be a carboxylate anion and an ammonium group. In order to maintain the dipolar form in glutamic acid, only one carboxylate ion is required. To suppress the ionization of second carboxylic acid, more acid is required than that for glutamine. That is pH of glutamic acid is maintained lower than that of glutamine to achieve isoelectric point. (Isoelectric point is the average of
Hence, isoelectronic point of glutamine is higher than that of glutamic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What will you do to detect the presence of protein in powdered casein? Briefly explain each process.arrow_forwardPredict the reactions ofcarbohydrates in acidic and basicsolutions, and with oxidizingand reducing agentsarrow_forward(a) Isoleucine has been prepared by the following sequence of reactions. Give the structure of compounds A through D isolated as intermediates in this synthesis.(b) An analogous procedure has been used to prepare phenylalanine. What alkyl halide would you choose as the starting material for this synthesis?arrow_forward
- The peptide Proline-Serine-Alanine-Phenylalanine-Glutamine is present at pH 7. Draw the peptide and include stereochemistry.arrow_forwardWrite a structural formula for the product formed by treatment of the N-terminal amino group with Sanger’s reagent and propose a mechanism for its formation.arrow_forwardThalidomide is a chiral molecule and it was identified that the R-isomerproduced the sedative properties whereas the S-isomer produced the teratogenic effects.Identify the chiral centre in the thalidomide molecule and, using your knowledge of enolisation, illustrate mechanistically, and explain, why there would be no benefit to a patient taking the chirally pure R-isomer of the drug to avoid the sideeffects of the other enantiomer.arrow_forward
- Sucrose, a non-reducing sugar, would not be expected to produce an osazone when treated with phenylhydrazine. Table I shows that an osazone does indeed form (in 30 minutes) and that the osazone derived from sucrose has a Melting Point identical to that of glucosazone and fructosazone. Why?arrow_forwardWrite out the steps needed to synthesize the following peptide using the Merrifield method.arrow_forwardSuggest a method for the synthesis of the unnatural d enantiomer of alanine from the readily available l enantiomer oflactic acid.CH3¬CHOH¬COOHlactic acidarrow_forward
- Suggest a b-aminoalcohol that would give cyclohexanecarbaldehyde as a product.arrow_forwardAn unknown decapeptide was isolated and characterized. Complete hydrolysis of this peptide gave : F(2), A,G,C,K,N,T, W and V. Treatment with carboxypeptidase releases A. Reaction with Edman’s reagent gave PTH-T and a nonapeptide. The nonapeptide was treated with trypsin and gave 2 peptides: (V-C-G-A) and (N-FF-W-K). Give the sequence of amino acid in the decapeptide.arrow_forwardLeuprolide is a synthetic nonapeptide used to treat both endometriosis in women and prostate cancer in men. (a) Both C-terminal and N-terminal amino acids in leuprolide have been structurally modified. Identify the modifications. (b) One of the nine amino acids in leuprolide has d stereochemistry rather than the usual L. Which one? (c) Write the structure of leuprolide using both one- and three-letter abbreviations. (d) What charge would you expect leuprolide to have at neutral pH?arrow_forward
