
(a)
Interpretation:
The organic product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Multiple bonds in
Answer to Problem 24.57P
The structure of the product of the given reaction is
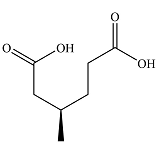
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
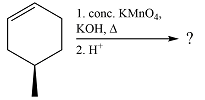
Hot, concentrated permanganate (
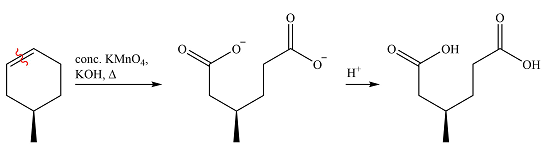
Therefore, the product of the reaction is

The products of the reaction were determined on the basis of the cleavage of the double bond by hot concentrated permanganate in basic medium and the oxidation of the two carbons to carbonyl groups.
(b)
Interpretation:
The organic product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Multiple bonds in alkenes and alkynes are cleaved when treated with hot, concentrated permanganate in a basic solution in an oxidative cleavage reaction. Both carbons of the alkyne are oxidized in the process to carboxyl groups. The end carbon of a terminal alkyne is oxidized completely to carbon dioxide. The final functional group that is formed depends on the reaction conditions. The permanganate ion is added across the multiple bonds in a way similar to the Diels-Alder reaction, a
Answer to Problem 24.57P
The structure of the organic product of the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is

Hot, concentrated permanganate (
![]()
Therefore, the organic product of the reaction is

The products of the reaction were determined on the basis of the cleavage of the triple bond by hot concentrated permanganate in basic medium and the oxidation of the internal carbon to carboxylic acid and the terminal carbon to carbon dioxide.
(c)
Interpretation:
The organic product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Multiple bonds in alkenes are cleaved when treated with ozone in a reaction called ozonolysis. Both carbons of the alkene are oxidized in the process to carbonyl groups. Ozone adds across the double bond in a
Answer to Problem 24.57P
The structures of the products of the given reaction are
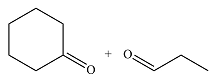
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
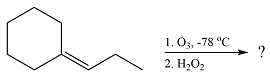
Ozone will add across the double bond to initially form a molozonide. The molozonide rearranges to an ozonide following a cycloelimination and a cycloaddition. The ozonide is then reduced by zinc-acetic acid to cyclohexanone and propanal.
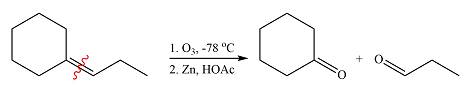
Therefore, the products of the reaction are

The products of the ozonolysis reaction were determined on the basis of cleavage of the double bond and oxidation of the two carbons to carbonyl groups.
(d)
Interpretation:
The organic product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Multiple bonds in alkenes are cleaved when treated with ozone in a reaction called ozonolysis. Both carbons of the alkene are oxidized in the process to carbonyl groups. Ozone adds across the double bond in a
Answer to Problem 24.57P
The structures of the organic products of the given reaction are
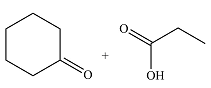
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
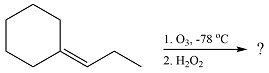
Ozone will add across the double bond to initially form a molozonide. The molozonide rearranges to an ozonide following a cycloelimination and a cycloaddition. One of the carbons of the double bond is oxidized initially to an aldehyde which is further oxidized to a carboxylic acid on treatment with
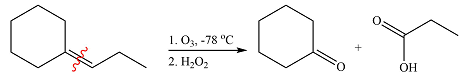
Therefore, the products of the reaction are

The products of the ozonolysis reaction were determined on the basis of cleavage of the double bond and oxidation of the two carbons to carbonyl groups.
(e)
Interpretation:
The organic product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Multiple bonds in alkenes and alkynes are cleaved when treated with osmium tetroxide and
Answer to Problem 24.57P
The structures of the organic products of the given reaction are
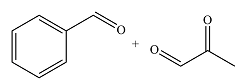
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
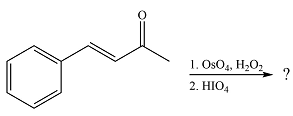
Osmium tetroxide adds across the double bond. Hydrolysis of the adduct yields a
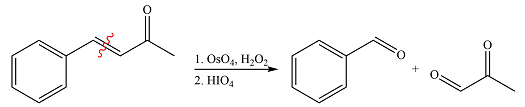
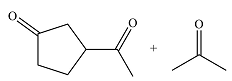
Therefore, the products of the reaction are

The products of the reaction were determined on the basis of addition of
(f)
Interpretation:
The organic product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Multiple bonds in alkenes and alkynes are cleaved when treated with hot, concentrated permanganate in a basic solution in an oxidative cleavage reaction. Both carbons of the alkene or alkyne are oxidized in the process to carbonyl groups or carbon dioxide. The final functional group that is formed depends on the reaction conditions. The permanganate ion is added across the multiple bonds in a way similar to the Diels-Alder reaction, a
Answer to Problem 24.57P
The structures of the organic products of the given reaction are
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
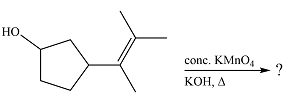
Hot, concentrated permanganate (
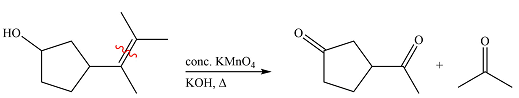
Therefore, the product of the reaction is

Hot concentrated permanganate in basic medium oxidized the double-bonded carbons of an alkene to carbonyl groups.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





