
SYSTEM DYNAMICS CONNECT
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781264201730
Author: Palm
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.3P
For the mass shown in Figure 3.1.3b.
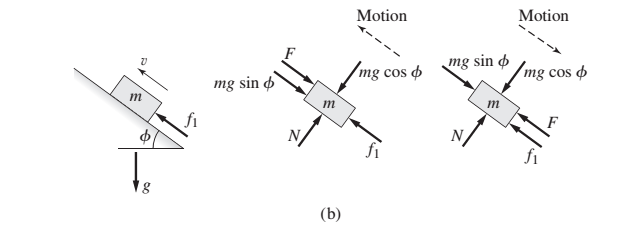
Figure 3.1.3 Motion with friction a) on a horizontal surface and b) on an inclined plane.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In figure 2 show below, the body reaches a velocity of 12 m/ sec during traveling 30 m starting from rest moving with constant acceleration. Find the coefficient of friction between the body and ground? P =300 N , W = 200 N
This most likely is made to be a probelm about mx''+bx'+kx=f(t)
m = mass
b = friction
k = spring constant
4. A mass weighing four pounds stretches a spring 24 in. Suppose the mass is atequilibrium and is set into motion with a velocity of 6 inches per second. The mass is in a mediumwhere friction is small, and we assume it is zero. Note that the acceleration due to gravity near theearth’s surface where the experiment takes place can be taken as 32 ft/s2.(a) Suppose that in addition to the conditions described above, a hammer strikes the mass everyπ/2 seconds starting at t = 0. A delta function with impulse of 1 pound-second models theforce of each blow to the mass. Find the function x(t) for the displacement from equilibrium infeet of the mass at time t in seconds. Express x(t) as a piecewise defined function without the use ofunit step or Heaviside functions and such that in each time window it is a different multiple of the samesinusoidal function.(b) Now assume the same spring-mass…
A disk rotating with constant acceleration of 0.005 revolutions / s2
And the movement starts from rest. What is the angle velocity after one minute? How many turns makes the same disc in point number one after one minute. If an external force does not affect the body, what does that mean? And if the body is in free fall, is its speed constant or variable, what is its acceleration equal, and how can the friction be reduced between the contact surfaces
Chapter 3 Solutions
SYSTEM DYNAMICS CONNECT
Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.1PCh. 3 - A baseball is thrown horizontally from the...Ch. 3 - For the mass shown in Figure 3.1.3b. m=10 kg, =25...Ch. 3 - A particle of mass m=19 kg slides down a...Ch. 3 - A particle of mass m slides down a frictionless...Ch. 3 - A radar tracks the flight of a projectile (see...Ch. 3 - Table 3.2.1 gives the inertia IO for a point mass...Ch. 3 - A motor supplies a moment M to the pulley of...Ch. 3 - Figure P3.9 shows an inverted pendulum. Obtain the...Ch. 3 - The two masses shown in Figure P3.10 are released...
Ch. 3 - The motor in Figure P3.11 lifts the mass mL by...Ch. 3 - Instead of using the system shown in Figure 3.2.6a...Ch. 3 - Consider the cart shown in Figure P3.13. Suppose...Ch. 3 - Consider the cart shown in Figure P3.13. Suppose...Ch. 3 - Consider the spur gears shown in Figure P3.15,...Ch. 3 - Consider the spur gears shown in Figure P3.15,...Ch. 3 - Derive the expression for the equivalent inertia...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.18PCh. 3 - The geared system shown in Figure P3.19 represents...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.20PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.21PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.22PCh. 3 - For the geared system shown in Figure P3.23,...Ch. 3 - For the geared system discussed in Problem 3.23,...Ch. 3 - The geared system shown in Figure P3.25 is similar...Ch. 3 - Consider the rack-and-pinion gear shown in Figure...Ch. 3 - The lead screw (also called a power screw or a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.29PCh. 3 - Derive the equation of motion of the block of mass...Ch. 3 - Assume the cylinder in Figure P3.31 rolls without...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.33PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.34PCh. 3 - A slender rod 1.4 m long and of mass 20 kg is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.36PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.37PCh. 3 - The pendulum shown in Figure P3.38 consists of a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.39PCh. 3 - A single link of a robot arm is shown in Figure...Ch. 3 - 3.41 It is required to determine the maximum...Ch. 3 - Figure P3.42 illustrates a pendulum with a base...Ch. 3 - Figure P3.43 illustrates a pendulum with a base...Ch. 3 - 3.44 The overhead trolley shown in Figure P3.44 is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.45PCh. 3 - The “sky crane” shown on the text cover was a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of mass m1 = 20Kg is attached by an ideal pulley to a block of mass m2 = 2.5 kg on the surface of a table, between the surface of the table and the block m1 there is a friction coefficient of 0.4. The system starts from rest when both masses have moved 0.75m. Calculate: A) The total work of the system. B) The speed of the system when it has traveled the 0.75m. C) The total work of the M1 mass. D) The speed of the m1 mass when it has traveled the distance of 0.75m. E) The speed of the mass m2 when it has traveled the distance of 0.75 marrow_forwardAs seen in the figure, three masses are connected to each other with the system set up on a table. Table friction and kinetic coefficient of friction is 0.35. (g = 10m / s2). b) Find the acceleration of each mass. c) Find the tensile forces on the ropes. d) How many meters will the object of 6kg go down after t = 3s after the system is released?arrow_forwardA block weighing 200N rests on a horizontal floor. A horizontal force P=100N directed to the right is applied to the bloxk and it reaches a velocity of 12m/sec in 40 m distance starting from rest. What is the coefficient of friction between the block and the floor?arrow_forward
- A drop hammer weighing 40 KN is dropped freely and drives a concrete pile 150 mm into the ground. The velocity of the drop hammer at impact is6m/sec. what is the average resistance of the soil in KN?arrow_forwardKhufra works at a spring factory and he was assigned to test a certain spring, whose constant is 50 N/m attached to a 50-kg block in an incline (©=30°). With the spring initially at equilibrium position, the block was pushed 0.3 meters up the incline by a 50-N external force applied parallel to the path. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30. d) How much work is done by the block (in Joules) on the spring? e) How much work is done by the applied push on the block? f) How much work is done by friction?arrow_forwardAn accelerometer has a seismic mass of 44 g and a spring constant of 3 kN/m. Maximum mass displacement is ± 7 mm (before the mass hits the stops). Calculate the maximum measurable accelerationarrow_forward
- A string is wound around a pulley of diameter of 0.2 m. One of its ends is tied to the pulley and the other end to a weight hanging freely. The weight falls a distance of 4 m from the rest in 3 s. Determine the total distance through which the weight should fall so that the velocity of the pulley will be 400 rpm. OPTIONS: 1.Around 10 m 2.Around 15 m 3.Around 12 m 4.Around 6 m 5.Around 8 m 6.Nonearrow_forwardAn object, m1 with a mass of 10.0 kg placed on a frictionless, horizontal table. It is connected to a string that passes over a pulley and then is fastened to a hanging object, m2 with a mass of 14.0 kg. a. The tension in the string is? b. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the objectsarrow_forwardThe figure shown below is released from rest with the spring unstretched. Use the datum shown for zero gravitational potential energy. For the values given below answer the following questions:Position 1 is Ha1 μk=0.14 k=32.5 Nm hA1=0.6 m mA=4.6 kg mB=1.3 kg What is the Gravitational Potential Energy for mass mA at position 1 (remember your signs)? What is the Gravitational Potential at position 1 for mB? What is the Potential Energy of the spring at position 1? What is the Kinetic Energy at position 1 for mA? What is the Kinetic Energy at position 1 for mB? Again we have the figure shown below that was released from rest with the spring unstretched. Use the datum shown for zero gravitational potential energy. At position 2 the spring is at its max stretch. Remember we have the values below; answer the following questions: μk=0.14 k=32.5 Nm hA1=0.6 m mA=4.6 kg mB=1.3 kg What is the max stretch in the spring?arrow_forward
- Two blocks connected by a string are pulled across a horizontal surface by a force applied to one of the blocks, as shown below. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the surface is 0.25. If each block has an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 to the right, what is the magnitude F of the applied force?arrow_forwardClassical mechanics- obtain the equation of motion for a particle falling freely under the influence of gravity when frictional force obtainable from a dissipative function 1 by 2 k v square are present so that the maximum possible velocity for fall from the rest is v equals to MG by karrow_forwardAn elevator weighing 2,000 lb attain an upward velocity of 16 ft/sec in 4 seconds with uniform acceleration. What is the tension in the supporting cables?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY