
Biology
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781260487947
Author: BROOKER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.1, Problem 1CS
Core Skill: Connections Look back at Figure 3.11. What is the physical/chemical reason why phospholipids tend to form a bilayer?
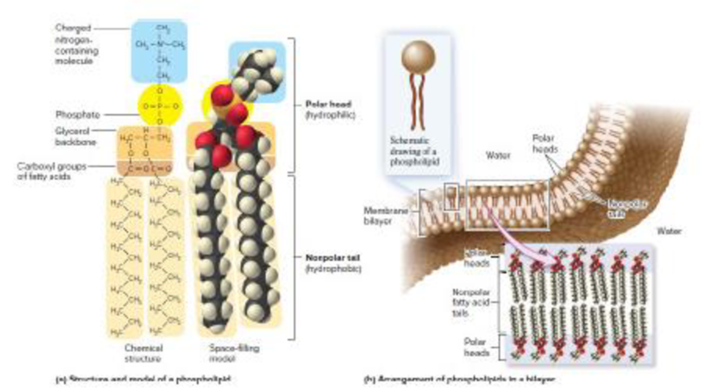
Figure 3.11 Structure of phospholipids, (a) Chemical structure and space-filling model of phosphatidylcholine, a common phospholipid found in living organisms. Phospholipids contain both polar and nonpolar regions, making them amphipathic. The fatty-acid tails are nonpolar. The rest of the molecule is polar, (b) Arrangement of phospholipids in a biological membrane, such as the plasma membrane that encloses cells. The polar regions of the phospholipids face the watery environment, whereas the nonpolar regions associate with each other in the interior of the membrane, forming a bilayer.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
VISUAL SKILLS Carbohydrates are attached to plasmamembrane proteins in the ER (see Figure 7.9). On whichside of the vesicle membrane are the carbohydrates during transport to the cell surface?
xplain how the following affect membrane fluidity:– Level of phospholipid tail saturation– Level of cholesterol– Phospholipid tail length
Thanks in advance!!!1) What are the basic components of a cell’s membrane and how is it organized? What are the functions? Why is it called a “fluid mosaic” membrane?2) Distinguish Ionic, Covalent, Hydrogen Bonding, and Van der Waals (Hydrophobic).4) Distinguish DNA from RNA, what is the same, what is different? Importance in function?. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside. 5) Why can cell membranes be polar? What does polar mean?6) What are the basic cytoskeletal components of a cell? What does an animal cell have that no other cell has in the cytoskeleton? 7) How does an enzyme help a reaction proceed? How does heat, chemicals, and pH affect enzyme activity? 8) From a cellular standpoint, what is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? What is the major molecule that cells use for energy? What are high energy molecules found in the cell and how are used to make ATP?9) What are NAD+, NADH, FAD+, FADH2. How’s it regulated? 10) What are the four…
Chapter 4 Solutions
Biology
Ch. 4.1 - What properties of deep-sea vents made them...Ch. 4.1 - Which protobiont seems most similar to todays...Ch. 4.1 - Core Skill: Connections Look back at Figure 3.11....Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 4.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 4.2 - Prob. 2CCCh. 4.3 - Prob. 1CSCh. 4.3 - Prob. 1CCCh. 4.3 - Prob. 2CSCh. 4.4 - Prob. 1CS
Ch. 4.4 - Describe the type of movements that occur between...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 2CSCh. 4.5 - Prob. 1CCCh. 4.5 - Prob. 1CSCh. 4.5 - If we consider the Golgi apparatus as three...Ch. 4.5 - The Nucleus and Endomembrane System Experimental...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 2EQCh. 4.5 - Prob. 3EQCh. 4.5 - Prob. 3CCCh. 4.6 - Prob. 1CCCh. 4.6 - Core Skill: Connections Look ahead to Figure...Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 1CCCh. 4.7 - Prob. 2CCCh. 4 - The cell theory states that a. all living things...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2TYCh. 4 - Prob. 3TYCh. 4 - Prob. 4TYCh. 4 - Each of the following is part of the endomembrane...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6TYCh. 4 - Functions of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8TYCh. 4 - Prob. 9TYCh. 4 - Which of the following observations would not be...Ch. 4 - What are the four stages that led to the origin of...Ch. 4 - Explain how motor proteins and cytoskeletal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 3CQCh. 4 - Discuss the roles of the genome and proteome in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2COQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give typing answer with explanation and conclusion 6. Which chemical properties of phospholipids make them suited to the task of forming cell membranes? Could carbohydrates be used to replace phospholipids as the main component of cell membranes? Explain. Incorporate the following terms into your answer: hydrophobic; hydrophilic; semipermeable.arrow_forwardQ8: The primary structural components of the cell membrane areO proteins and cellulose.O glycoproteins and cholesterol.O cholesterol and proteins.O phospholipids and cellulose.O phospholipids and proteins.arrow_forwardMAKE CONNECTIONS What is electronegativity, andhow does it affect interactions between water molecules?arrow_forward
- Answer and EXPLAIN 3. Whichbestdescribesthestructureofacellmembrane? a. proteins between two bilayers of phospholipids b. proteinsembeddedinabilayerofphospholipids c. a bilayer of protein coating a layer of phospholipids d. cholesterolembeddedinabilayerofphospholipids 4. A plant cell placed in distilled water will ______________; an animal cell placed in distilled water will ______________. a. burst ... burst b. becomeflaccid...shrivel c. become turgid . . . be normal in shape d. becometurgid...burst 5. The sodium concentration in a cell is 10 times less than the concentration in the surrounding fluid. How can the cell move sodium out of the cell? (Explain your answer.) a. passive transport b. receptor-mediatedendocytosis c. active transport d. facilitateddiffusion 6. The synthesis of ATP from ADP and P a. stores energy in a form that can drive cellular work. b. involvesthehydrolysisofaphosphatebond. c. transfers a phosphate, priming a protein to do work. d. isanexergonicprocess. 7.…arrow_forwardOsmosis Pre-Lab Question Research the structures that protect plant and animal cells from damage resulting from osmotic pressure. Write a few sentences explaining what they are, how they work, and where they are located.arrow_forwardWHAT IF? Some membrane proteins diffuse faster in the plasma membrane when the cytoskeleton or the extracellular matrix is artificially removed than when cells are unperturbed. Explain why.arrow_forward
- fully describe the structure of a phospholipid bilayer as seen in a membranous structure, such as tonoplast. How are the phospholipid molecules oriented? What characteristics of phospholipids allow for the bilayer to form?arrow_forwardPlease help: Question: Protein structure is central to our understanding biological systems. The tubular proteins that make up the cytoskeleton of the Amoeba are an example of complex Protein structure. Consider the following for the Amoeba and how it reacts to the outside world. Name the four levels of protein structure: How are these structural characteristics developed in the Endomembrane system of an Amoeba cell. Reminder, the endomembrane system includes the nucleus. How do the levels of protein structure explain the movement of the amoeba toward a stimulus.arrow_forwardWHAT IF? Suppose a membrane surrounded an oildroplet, as it does in the cells of plant seeds and in someanimal cells. Describe and explain the form it might takearrow_forward
- TAGS: Biology, Chemistry, Biochemistry, Cell Biology, Molecular Biology A group of researchers were tasked to design various synthetic cell membranes that could be used to simulatecellular activities of different organisms. Help the researchers assemble the structure of the major lipid component for a cell membrane (draw the strucutres clearly) that is appropriate for the following and briefly explain your answer: a prokaryotic cell thriving in a geyser at the Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, USA a muscle cell of a salmon fry in the Arctic Ocean a frog neurocyte Chemical structures of the compounds that are available are shown on the image.arrow_forwardQ1: Why is it important that the phosphate head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic? Q2: What essential component of a cell do liposomes lack, and why is that omission important? Q3: Could the tendency of phospholipid bilayers to spontaneously form spheres have played a role in the origin of life?arrow_forwardQ4: Describe the structure of plasma membrane. Suggest the mechanism(s) by which each of the following substances is transported across cell membranes: a. CO2 b. Glucose c. C1– d. K+ e. Fat moleculesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Types of Human Body Tissue; Author: MooMooMath and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O0ZvbPak4ck;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY