
Concept explainers
Use the bond energies in Table 5.1 to calculate the energy changes associated with each of these reactions. Then, label each reaction as endothermic or exothermic.
- a. 2 H2(g) + CO(g) → CH3OH(g)
- b. H2(g) + O2(g) → H2O2(g)
- c. 2 BrCl(g) → Br2(g) + Cl2(g)
(a)
Interpretation:
The energy changes have to be calculated, the reaction is exothermic or endothermic has to be labelled.
Concept introduction:
Endothermic reaction: When the heat energy was absorbed by the system from the surrounding is called endothermic reaction.
Exothermic reaction: When heat energy or light energy was unconfined to the surrounding from the system is called exothermic reaction.
Net energy change is calculated from the difference between the total energy absorbed in breaking bonds and total energy released in forming bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The given is shown below,
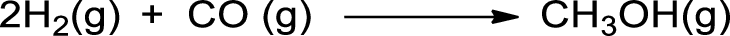
Bonds broken in the reactants are given below:
Bonds formed in the products are given below:
The overall energy change is negative, therefore, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The energy changes have to be calculated, the reaction is exothermic or endothermic has to be labelled.
Concept introduction:
Endothermic reaction: When the heat energy was absorbed by the system from the surrounding is called endothermic reaction.
Exothermic reaction: When heat energy or light energy was unconfined to the surrounding from the system is called exothermic reaction.
Net energy change is calculated from the difference between the total energy absorbed in breaking bonds and total energy released in forming bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The given is shown below,
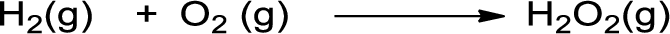
Bonds broken in the reactants are given below:
Therefore,
Bonds formed in the products are given below:
Therefore,
The overall energy change is negative, therefore, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The energy changes have to be calculated, the reaction is exothermic or endothermic has to be labelled.
Concept introduction:
Endothermic reaction: When the heat energy was absorbed by the system from the surrounding is called endothermic reaction.
Exothermic reaction: When heat energy or light energy was unconfined to the surrounding from the system is called exothermic reaction.
Net energy change is calculated from the difference between the total energy absorbed in breaking bonds and total energy released in forming bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The given is shown below,
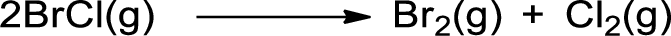
Bonds broken in the reactants are given below:
Therefore,
Bonds formed in the products are given below:
Therefore,
The overall energy change is negative, therefore, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry In Context
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Organic Chemistry
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
- Nitrogen monoxide, a gas recently found to be involved in a wide range of biological processes, reacts with oxygen to give brown NO2 gas. 2 NO(g) + O2(g) NO2(g)rH = 114.1 kJ/mol-rxn Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? What is the enthalpy change if 1.25 g of NO is converted completely to NO2?arrow_forwardThe equation for the fermentation of glucose to alcohol and carbon dioxide is: C6H12O6(aq) 2C2H5OH(aq) + 2CO2(g) The enthalpy change for the reaction is 67 kJ. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? Is energy, in the form of heat, absorbed or evolved as the reaction occurs?arrow_forwardAn important step in the production of sulfuric acid is the oxidation of SO2 to SO3. SO2(g) + O2(g) SO3(g) Formation of SO3 from the air pollutant SO2 is also a key step in the formation of acid rain. (a) Use standard enthalpies of formation to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? (b) Draw an energy level diagram that shows the relationship between the enthalpy change for the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 and the enthalpies of formation of SO3(g) and SO3(g).arrow_forward
- Consider the following potential energy diagrams for two different reactions. Which plot represents an exothermic reaction? In plot a, do the reactants on average have stronger or weaker bonds than the products? In plot b, reactants must gain potential energy to convert to products. How does this occur?arrow_forwardThe standard enthalpy of formation of solid barium oxide, BaO, is 553.5 kJ/mol, and the standard enthalpy of formation of barium peroxide, BaO2, is 634.3 kJ/mol. (a) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? 2 BaO2(s) 2 BaO(s) + O2(g) (b) Draw an energy level diagram that shows the relationship between the enthalpy change of the decomposition of BaO2, to BaO and O2, and the enthalpies of formation of BaO2(s) and BaO2(s).arrow_forwardEnthalpy a A 100.-g sample of water is placed in an insulated container and allowed to come to room temperature at 21C. To heat the water sample to 41C, how much heat must you add to it? b Consider the hypothetical reaction,2X(aq)+Y(l)X2Y(aq)being run in an insulated container that contains 100. g of solution. If the temperature of the solution changes from 21C to 31C, how much heat does the chemical reaction produce? How does this answer compare with that in part a? (You can assume that this solution is so dilute that it has the same heat capacity as pure water.) c If you wanted the temperature of 100. g of this solution to increase from 21C to 51C, how much heat would you have to add to it? (Try to answer this question without using a formula.) d If you had added 0.02 mol of X and 0.01 mol of Y to form the solution in part b, how many moles of X and Y would you need to bring about the temperature change described in part c. e Judging on the basis of your answers so far, what is the enthalpy of the reaction 2X(aq) + Y(l) X2Y(aq)?arrow_forward
- Chloromethane, CH3Cl, a compound found throughout the environment, is formed in the reaction of chlorine atoms with methane. CH4(g) + 2 Cl(g) CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) (a) Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction of CH4(g) and CI atoms to give CH3CI(g) and HCl(g). Is the reaction exo- or endothermic? (b) Draw an energy level diagram that shows how the various enthalpies in this problem are related.arrow_forwardA 0.470-g sample of magnesium reacts with 200 g dilute HCl in a coffee-cup calorimeter to form MgCl2(aq) and H2(g). The temperature increases by 10.9 C as the magnesium reacts. Assume that the mixture has the same specific heat as water and a mass of 200 g. (a) Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction. Is the process exothermic or endothermic? (b) Write the chemical equation and evaluate H.arrow_forwardThe enthalpy change for the reaction of hydrogen gas with fluorine gas (o produce hydrogen fluoride is 542 U for the equation as written: mg src=Images/HTML_99425-10-41QAP_image001.jpg alt="" align="top"/> l type='a'> What is the enthalpy change per mole of hydrogen fluoride produced? Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic as written? What would be the enthalpy change for the reverse of the given equation (that 1%, for the decomposition of HF into its constituent elements)?arrow_forward
- Use standard enthalpies of formation in Appendix L to calculate enthalpy changes for the following: (a) 1.0 g of white phosphorus burns, forming P4Ol0(s) (b) 0.20 mol of NO(g) decomposes to N2(g) and O2(g) (c) 2.40 g of NaCl(s) is formed from Na(s) and excess Cl2(g) (d) 250 g of iron is oxidized with oxygen to Fe2O3(s)arrow_forwardA commercial process for preparing ethanol (ethyl alcohol), C2H5OH, consists of passing ethylene gas. C2H4, and steam over an acid catalyst (to speed up the reaction). The gas-phase reaction is Use bond enthalpies (Table 9.5) to estimate the enthalpy change for this reaction when 37.0 g of ethyl alcohol is produced.arrow_forwardAssume 200. mL of 0.400 M HCl is mixed with 200. mL of 0.400 M NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter The temperature of the solutions before mixing was 25.10 C; after mixing and allowing the reaction to occur, the temperature is 27.78 C. What is the enthalpy change when one mole of acid is neutralized? (Assume that the densities of all solutions are 1.00 g/mL and their specific heat capacities are 4.20 J/g K.)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





