
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of the conjugate acid of monosodium phosphate (base) needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:Bronsted and Lowry purposed the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory. It states that acid can give
(b)
Interpretation: The reason of ineffective use of an aqueous solution of monosodium phosphate for extracting benzoic acid from a diethyl ether solution needs to be explained, if the pKa of conjugate acid of monosodium phosphate is 2.1.
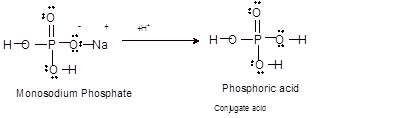
Concept Introduction:Bronsted and Lowry purposed the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory. It states that acid can give
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
- If the G for a reaction is 4.5 kcal/mol at 298 K, what is the Keq for this reaction? What is the change in entropy of this reaction if H = 3.2 kcal/mol?arrow_forwardWhen aniline, C6H5NH2(Kb=7.41010) , reacts with a strong acid, its conjugate acid, C6H5NH3+, is formed. Calculate the pH of a 0.100 M solution of C6H5NH3+ and compare it with the pH of acetic acid (Ka=1.86105) .arrow_forwardAcid-Base Equilibria Many factors contribute to the acidity of organic compounds. Electronegativity, resonance, induction, hybridization, aromaticity, and atomic size, all play a role. In the following comparisons, you are asked to identify the factor(s) that would be most important to analyze when predicting relative acidity, and then to predict the trend in acidity and pKa values. For each of the following pairs of compounds answer the following two multiple-choice questions. 1. What factor(s) are the most important to consider when predicting the relative acidity of the two compounds? a. Electronegativity of the atom possessing the hydrogen. b. Resonance stabilization of the anionic conjugate base. c. Inductive stabilization of the anionic conjugate base. d. Hybridization of the atom possessing the hydrogen. e. The atomic size of the atom possessing the hydrogen.arrow_forward
- Write an equation for the reaction of chloroacetic acid (Ka=1.5103) with trimethylamine (Kb=5.9105) . Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction. If 0.10 M solutions of these two species are mixed, what will be their concentrations at equilibrium?arrow_forwardWhat is the pKa of the conjugate acid of the reaction?arrow_forwardWrite the chemical equation for the acid dissociation of acetaminophen, C8H9O2N. Write the Ka expression for the acid dissociation of acetaminophen.arrow_forward
- The dissociation constant of ethanolamine is 2.77 x 10 – 5 at25 °C. Calculate its pKb value.arrow_forwardChemical Equilibrium Write the equilibrium-constant expressions and obtain numerical values for each constant in (a) the basic dissociation of aniline, C6H5NH2. (b) the acidic dissociation of hypochlorous acid, HClO. (c) the acidic dissociation of methyl ammonium hydrochloride, CH3NH3Cl. (d) the basic dissociation of NaNO2. (e) the dissociation of H3AsO3 to H3O+ and AsO33- Using step-by-step processarrow_forwardChoose from the options A-E and explain briefly by illustrations the chemistry behind each answer.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

