
Concept explainers
(a)
INTREPRETATION:
The product formed for the reaction between fumarate and
CONCEPT INTRODUCTION:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
The curved arrows are generally used to indicate the flow of electrons present in the reaction.
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Oxidizing Reagents: The chemical agents used to add oxygen or remove hydrogen which finally reduced on oxidizing the other compound.
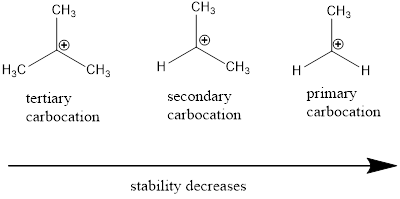
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(b)
INTREPRETATION:
The product formed for the reaction between maleate and
CONCEPT INTRODUCTION:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Chemical reaction involves bond making and breaking of two or more reactants in order to attain products from the reactants.
The curved arrows are generally used to indicate the flow of electrons present in the reaction.
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Oxidizing Reagents: The chemical agents used to add oxygen or remove hydrogen which finally reduced on oxidizing the other compound.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- Name an aldohexose other than d-glucose that is oxidized to d-glucaric acid by nitric acid. a. What is another name for d-glucaric acid? b. Name another pair of aldohexoses that are oxidized to identical aldaric acids.arrow_forwardAssume that for your Biochemistry practical, you were asked to synthesise D-Galactose. You went to chemical storage room to take some D-lyxose to use as the starting material. But there you found that labels had fallen off from the bottles containing D-lyxose and D-xylose. How could you determine which bottle contains D- lyxose?arrow_forwardWhat is a reducing sugar? What other types of sugars besides glucose might you measure using the dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) reagent?arrow_forward
- (a) Which of the d-aldopentoses will give optically active aldaric acids on oxidation with HNO3 ?(b) Which of the d-aldotetroses will give optically active aldaric acids on oxidation with HNO3 ?(c) Sugar X is known to be a d-aldohexose. On oxidation with HNO3, X gives an optically inactive aldaric acid. WhenX is degraded to an aldopentose, oxidation of the aldopentose gives an optically active aldaric acid. Determine thestructure of X.(d) Even though sugar X gives an optically inactive aldaric acid, the pentose formed by degradation gives an opticallyactive aldaric acid. Does this finding contradict the principle that optically inactive reagents cannot form opticallyactive products?(e) Show what product results if the aldopentose formed from degradation of X is further degraded to an aldotetrose.Does HNO3 oxidize this aldotetrose to an optically active aldaric acid?arrow_forwardWhen some sugars dissolve in water they spontaneously undergo changes in optical rotation called mutarrotation. The Mutarrotation of D-glucopyranose is catalyzed by acid and bases. 2-Hydroxypyridine is a more effective catalyst than phenol and pyridine for this reaction because: a.Both oxygen and N in 2-hydroxypyridine act as bases increasing the rapid interconversion of sugar b. The OH of 2-hydroxypyridine serves as the base while the current N as the acid. c. 2-hydroxypyridine acts both as a base to remove the proton from the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal and as an acid to provide a proton to the oxygen in the hemiacetal. d.Phenol and pyridine are very expensive.arrow_forward1. Carbohydrates classification. 2. Write down the reactions: a) α,D-Glucopyranose + C2H5OH → b) D-Glucose + [Ag(NH3)2]+ → c) D-Glucopyranose + (CH3CO)2 O → d) D-Glucopyranose + CH3I → e) D-Glucose + HNO3 → f) D-Glucose + H2 → g) Lactose formation h) Sucrose hydrolysis 3. Write down the formula of β,D-galactopyranosearrow_forward
- Explain about Stemoamide ?arrow_forwardThe carbonyl group on D-glucose can be reduced to d-glucitol. Identify the reagents that can chrry out this reduction. A.water in acidic solution B. hydrogen with a Platinum catalyst (Hy/Pt) C. Sodium dichromate (NaCr2O) in acidic solution D. Benedict’s reagent E. Enzymesarrow_forward1.Explain what is anomeric effect and why it happens? 2.Explain how a glycosyl acetimidate can loss its glycosyl donor activity?arrow_forward
- What is the difference in results for sucrose and hydrolyzed sucrose when reacted with Benedict's reagent?arrow_forwardA. Compare and contrast Benedict’s Tests for identifying or determining the reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars. B. What is meant by word “reagent” C.what is its importance in Reagent Test Striparrow_forwardPropose a reagent or reagents to bring about the conversion of F to fluoxetine. Note that the bracketed intermediate formed in this step is an N-substituted carbamic acid. Such compounds are unstable and break down to carbon dioxide and an amine.arrow_forward
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
