
(a)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction have to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
(b)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction have to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents approaches same side of
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
(c)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction have to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
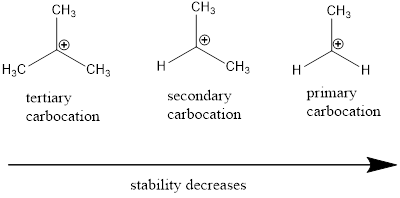
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
(d)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction have to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents approaches same side of
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
(e)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction have to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents approaches same side of
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
(f)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction have to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents approaches same side of
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- Assign the stereochemical configuration (E or Z) for the alkene below. Show your work, indicating clearly which groups are assigned high priority (e.g., through assigning the groups numbers, circling only the high priority groups, or labeling groups as high or low).arrow_forwardWhen Br2 is added to buta-1,3-diene at -15 °C, the product mixture contains 60% ofproduct A and 40% of product B. When the same reaction takes place at 60 °C, theproduct ratio is 10% A and 90% B.(a) Propose structures for products A and B. (Hint: In many cases, an allylic carbocationis more stable than a bromonium ion.)arrow_forwardOrder the following substituents from highest priority to lowest priority: CH3, OH, H,F. Use the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority system. a. F, CH3, OH, H b. H, CH3, F, OH c. F, OH, CH3, H d. H, CH3, OH, Farrow_forward
- A)Circle all of the stereo centers in MDMA. B) assign the absolute stereochemistry (R or S) for each stereo centerarrow_forwarda.What product(s) (excluding stereoisomers) are formed when Y is heated with Cl2? b.What product(s) (excluding stereoisomers) are formed when Y is heated with Br2? c.What steps are needed to convert Y to the alkene Z?arrow_forwardWhich isomer reacts more rapidly in an E2 reaction: cis-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane or trans-1bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- 2) Draw and name the organic compound found in every reaction. d) Reaction of cis-3,3-Dimethyl-4-propylocta-1,5-diene with two mole of HBr e) Reaction of trans-1-Bromo-3-chlorocyclopentane with potassium hydroxide f) Formation of Gilman reagent using isopropyl bromide g) Ozonolysis of 3,3-Dimethyloct-4-yne h) Complete halogenation (Cl2) of 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne i) Partial hydrogenation using Lindlar's Catalyst 2,2,5,5-Tetramethylhex-3-yne j) Reaction of 3,4-Dimethylcyclodecyne with sodium amidearrow_forwardPredict mechanistically what stereoisomers of 3-chloro-5-methylcyclohexene should form when (image below) is treated with Lucas reagent (ZnCl2/H30+Cl-).arrow_forwardWhen 2-bromo-3-phenylbutane is treated with sodium methoxide, two alkenes result (by E2 elimination). The Zaitsevproduct predominates.(a) Draw the reaction, showing the major and minor products.(b) When one pure stereoisomer of 2-bromo-3-phenylbutane reacts, one pure stereoisomer of the major product results.For example, when (2R,3R)-2-bromo-3-phenylbutane reacts, the product is the stereoisomer with the methyl groups cis.Use your models to draw a Newman projection of the transition state to show why this stereospecificity is observedarrow_forward
- When 2-bromo-3-phenylbutane is treated with sodium methoxide, two alkenes result (by E2 elimination). The Zaitsevproduct predominates.(a) Draw the reaction, showing the major and minor products.(b) When one pure stereoisomer of 2-bromo-3-phenylbutane reacts, one pure stereoisomer of the major product results.For example, when (2R,3R)-2-bromo-3-phenylbutane reacts, the product is the stereoisomer with the methyl groups cis.Use your models to draw a Newman projection of the transition state to show why this stereospecificity is observed.(c) Use a Newman projection of the transition state to predict the major product of elimination of (2S,3R)-2-bromo-3-phenylbutanearrow_forward1)Chemistry students are taking an experimental course in organic chemistry at a public university. During an experiment involving conjugated dienes, some doubts arose when discussing the results obtained so far: (a) A student obtained two products from the reaction of 1,3-cyclohexadiene with Br2. His lab partner was surprised to get only one product from the reaction of 1,3 - cyclohexadiene with HBr. Explain these distinct results. (b) One student, seeing the discussion of colleagues, commented that she obtained two distinct products when reacting 1,3,5-hexatriene with HBr, with different yields just by changing the reaction temperature. Explain the results she obtained using reaction mechanism and based on kinetic and thermodynamic control involving conjugated dienes.arrow_forwardExplain why the reaction of 2-bromopropane with NaOCOCH3 gives (CH3)2CHOCOCH3 exclusively as product, but the reaction of 2-bromopropane with NaOCH2CH3 gives a mixture of (CH3)2CH3 (20%) and CH3CH = CH2 (80%).arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


