
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule that corresponds to the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:
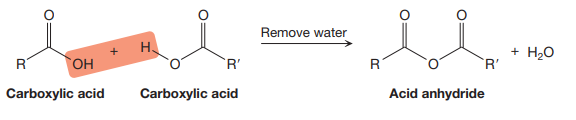
If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are the same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic anhydride in which the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule that corresponds to the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are the same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydrides are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule is to be drawn that corresponds to the given IUPAC name.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydride are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
Substituents attached to the carbon chain of any carboxylic acid portion are written as prefix in the IUPAC name.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule is to be drawn that corresponds to the given IUPAC name.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydride are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
Substituents attached to the carbon chain of any carboxylic acid portion are written as prefix in the IUPAC name.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter F Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- A B ) Which of the above molecules (A or B) have a higher rate of reaction towards aromatic electrophilic reaction? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation needed..use more than 1 set of the reagents to get the productarrow_forwardWrite a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..Draw the alcohol product and the conjugate bade of ketonearrow_forwardDraw a stepwise mechanism for the attached substitution. Explain why 2-chloropyridine reacts faster than chlorobenzene in this type of reaction.arrow_forwardExplain why metal hydride reduction gives an endo alcohol as the major product in one reaction and an exo alcohol as the major product in theother reaction.arrow_forward
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..identify reagents that complete the reactionarrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of attached compound from the indicated startingmaterial. You may also use any organic compounds with one or two carbons and any needed inorganic reagents.arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution...Draw the following organic compoundarrow_forward
- Explain the reaction for the formation of acetal and hemiacetal. Explain why N,N-disubstituted amide is less acidic than ester. Why only methyl ketone do undergoes haloform reaction. LDA is the base of choice for carbonyl compound to completely convert into enolate. Why?arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of attached alkene using a Wittig reaction to form the double bond. You may use benzene and organic alcohols having four or fewer carbons as starting materials and any required reagents.arrow_forwardWhich is the most acidic among the ff. compounds: a) benzoic acid, b) benzamide c) methylbenzoate or d) benzoylchloride?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

