
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An ester consists of a
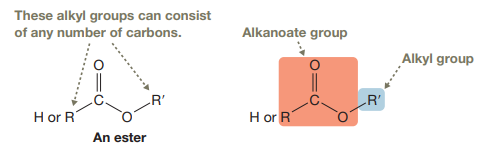
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An ester consists of a

(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An ester consists of a

(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An ester consists of a

(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An ester consists of a

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter F Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Both OH groups of the β,β-diol react with excess ethyl chloroformate, but only one OH group of the b,a-diol reacts under the same conditions.Explain the difference in reactivity.arrow_forwardr Plase don't provide handwritten solution Write carbonyl compound & phosphonium ylide that yield below alkene upon reactionarrow_forwardThe following SN2 reaction gave J as a major product. Determine the structure of J. Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- Outline a synthesis of each Wittig reagent from Ph3P and an alkyl halide.arrow_forwardA key step in the synthesis of β-vetivone, a major constituent of vetiver, a perennial grass found in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, involved the reaction of compound A and dihalide B with two equivalents of LDA to form C. Draw a stepwise mechanism for this reaction. β-Vetivone contains a spiro ring system—that is, two rings that share a single carbon atom.arrow_forward(−)-Hyoscyamine, an optically active drug used to treat gastrointestinal disorders, is isolated from Atropa belladonna, the deadly nightshade plant, by a basic aqueous extraction procedure. If too much base is used during isolation, optically inactive material is isolated. (a) Explain this result by drawing a stepwise mechanism. (b) Explain why littorine, an isomer isolated from the tailflower plant in Australia, can be obtained optically pure regardless of the amount of base used during isolation.arrow_forward
- The following compound readily eliminates CO; to form a conjugated six membered ring. (a) Complete the reaction with drawing the possible structure and (b) explain why this reaction goes steadily.arrow_forwardUsing any necessary organic and inorganic reagents, show how you can carry out the chemical conversions shwon below. Please answer parts a, b, and c.arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation needed..Draw the alcohol product and the conjugate bade of ketonearrow_forward
- One step in the synthesis of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug rofecoxib (trade name Vioxx) involves Suzuki coupling of A and B. What product is formed in this reaction?arrow_forward1. Explain how you could synthesize butane. Be sure to list all reactants and reagents required. 2. Explain how Hammond's postulate accounts for the higher selectivity of bromination reactions as compared to chlorination reactions.arrow_forwardA B ) Which of the above molecules (A or B) have a higher rate of reaction towards aromatic electrophilic reaction? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
