
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept introduction:
The IUPAC name of a compound is made up of three parts: prefix, root, and suffix. If the compound contains different
If any chiral carbons are present, their absolute configurations are determined on the basis of Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules and listed at the start along with the carbon number.
Answer to Problem F.1P
The IUPAC name of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
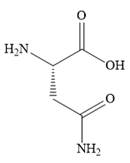
The highest priority function group in
There are two other functional groups,
The root carbons are numbered from the carboxylic acid carbon as shown below.
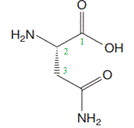
This puts the amino group on C2 and the carbamoyl on C3. The carbon to which the amine group is attached is a chiral carbon. Based on the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules, the absolute configuration at this carbon is S.
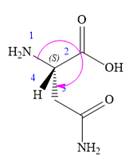
Apparently, the three highest priority groups are arranged clockwise, but with the lowest priority hydrogen pointing toward the observer. Therefore, the actual configuration is S.
Therefore, the complete IUPAC name of
The highest priority functional group is considered as suffix, and the other remaining groups are considered as substituents for writing IUPAC name of the molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed....identify the structural formula that corresponding to the compound names. If you give correct answer all compounds I will give you upvotearrow_forwardGive a clear handwritten answer with explanation..give the IUPAC name of given bleow structure with textual explanationarrow_forwardGive detailed Solution...Draw the following organic compoundarrow_forward
- Name the following by numbering the benzene ring. IUPAC-acceptable common names may be used where appropriate: a. b.arrow_forwardDecide which N atom in each molecule is most basic, and draw theproduct formed when each compound is treated with CH3CO2H.Zolpidem (trade name Ambien) is used to treat insomnia, whereasaripiprazole (trade name Abilify) is used to treat depression,schizophrenia, and bipolar disorders.arrow_forwardstructures for compounds A–F.arrow_forward
- a.Draw all reasonable resonance structures for pyrrole, and explain why pyrrole is less resonance stabilized than benzene. b.Draw all reasonable resonance structures for furan, and explain why furan is less resonance stabilized than pyrrole.arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for each compound. Can you answer/explain d, e, and f for me please?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
