
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The correct structure is to be drawn from the given IUPAC name of the molecule.
Concept introduction:
The structure of a compound can be drawn on the basis of its IUPAC name. The IUPAC name is made of three parts, prefix, root, and suffix. The suffix indicates the highest priority group present. Its location is written as a prefix for the functional group name unless redundant. The root is the longest continuous carbon chain that also includes the highest priority functional group. Any other
If any chiral carbons are present, their absolute configurations are specified at the start along with the carbon number if necessary. Similarly, the stereochemistry (E/Z) of any double bond is also specified at the start. A prefix di, tri, etc., before a prefix or suffix indicates the number of instances of that functional group.
Answer to Problem F.6P
The correct structure of
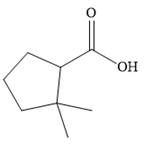
Explanation of Solution
The compound is a carboxylic acid, with the carboxyl functional group attached to a five-membered cyclopentane ring. Two other substituents are present on the ring, both methyl groups attached to the carbon next to the one carrying the carboxylic acid group. The suffix indicates that the carboxylic acid group is the higher priority group, so the numbering of the ring carbons starts at its point of attachment.
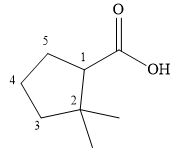
The methyl groups are then attached to the next ring carbon.
Therefore, the structure of

The structure of the compound can be drawn from its IUPAC name, which lists the functional groups attached to an alkyl/aryl root (parent).
(b)
Interpretation:
The correct structure is to be drawn from the given IUPAC name of molecule.
Concept introduction:
The structure of a compound can be drawn on the basis of its IUPAC name. The IUPAC name is made of three parts, prefix, root, and suffix. The suffix indicates the highest priority group present. Its location is written as a prefix for the functional group name unless redundant. The root is the longest continuous carbon chain that also includes the highest priority functional group. Any other functional groups present are listed alphabetically as prefixes along with their locants.
If any chiral carbons are present, their absolute configurations are specified at the start along with the carbon number if necessary. Similarly, the stereochemistry (E/Z) of any double bond is also specified at the start. A prefix di, tri, etc., before a prefix or suffix indicates the number of instances of that functional group.
Answer to Problem F.6P
The structure of
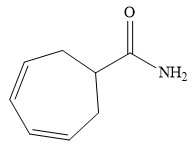
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the root is a seven carbon ring with two double bonds. The root name is, therefore, cycloheptadiene. The only functional group is an amide (
Thus, the structure of

The structure of the compound can be drawn from its IUPAC name, which lists the functional groups attached to an alkyl/aryl root (parent).
(c)
Interpretation:
The correct structure of
Concept introduction:
The structure of a compound can be drawn on the basis of its IUPAC name. The IUPAC name is made of three parts, prefix, root, and suffix. The suffix indicates the highest priority group present. Its location is written as a prefix for the functional group name unless redundant. The root is the longest continuous carbon chain that also includes the highest priority functional group. Any other functional groups present are listed alphabetically as prefixes along with their locants.
If any chiral carbons are present, their absolute configurations are specified at the start along with the carbon number if necessary. Similarly, the stereochemistry (E/Z) of any double bond is also specified at the start. A prefix di, tri, etc., before a prefix or suffix indicates the number of instances of that functional group.
Answer to Problem F.6P
The structure of
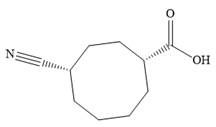
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the root is an eight carbon ring with two functional groups directly attached to ring carbons. The highest priority group is a carboxylic acid group, and the corresponding ring carbon is numbered 1. The second, nitrile group, is then on C4.
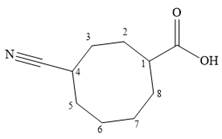
Both C1 and C4 are chiral carbons with R and S configurations respectively. According to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules, this means the priority groups 1 to 3 attached to C1 are arranged clockwise if the lowest priority group H is pointing away from the observer, or counterclockwise if H is pointing toward the observer. The priority groups 1 to 3 attached to C4 are arranged conterclockwise if the lowest priority H is pointing away, or clockwise if it is pointing toward the observer.
The structure of the compound can, therefore, be drawn as:
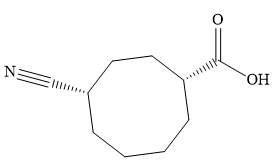
The structure of the compound can be drawn from its IUPAC name, which lists the functional groups attached to an alkyl/aryl root (parent).
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
The structure of a compound can be drawn on the basis of its IUPAC name. The IUPAC name is made of three parts, prefix, root, and suffix. The suffix indicates the highest priority group present. Its location is written as a prefix for the functional group name unless redundant. The root is the longest continuous carbon chain that also includes the highest priority functional group. Any other functional groups present are listed alphabetically as prefixes along with their locants.
If any chiral carbons are present, their absolute configurations are specified at the start along with the carbon number if necessary. Similarly, the stereochemistry (E/Z) of any double bond is also specified at the start. A prefix di, tri, etc., before a prefix or suffix indicates the number of instances of that functional group.
Answer to Problem F.6P
The correct structure of
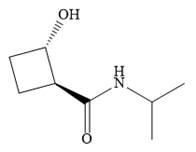
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the root is a cyclobutane ring. Two functional groups are attached to the ring, a secondary amide and a hydroxyl group. The amide is the higher priority group, so the ring atoms are numbered from the carbon to which it is attached. The hydroxyl group is then attached to the adjacent carbon C2.
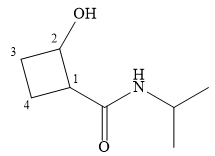
C1 and C2 are both chiral carbons with an absolute configuration of S. This means on each of these carbons, the priority 1 to 3 groups are arranged counterclockwise with the lowest priority H pointing away from the observer, or clockwise with the H pointing toward the observer.
The complete structure, using dash-wedge representation, for the two functional groups, can then be drawn as

The structure of the compound can be drawn from its IUPAC name, which lists the functional groups attached to an alkyl/aryl root (parent).
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
The structure of a compound can be drawn on the basis of its IUPAC name. The IUPAC name is made of three parts, prefix, root, and suffix. The suffix indicates the highest priority group present. Its location is written as a prefix for the functional group name unless redundant. The root is the longest continuous carbon chain that also includes the highest priority functional group. Any other functional groups present are listed alphabetically as prefixes along with their locants.
If any chiral carbons are present, their absolute configurations are specified at the start along with the carbon number if necessary. Similarly, the stereochemistry (E/Z) of any double bond is also specified at the start. A prefix di, tri, etc., before a prefix or suffix indicates the number of instances of that functional group.
Answer to Problem F.6P
The structure of
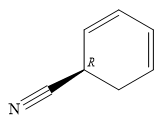
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the root is a six carbon ring, with two double bonds. The root name is, therefore, cyclohexadiene. One functional group, nitrile, is attached to the ring. The ring
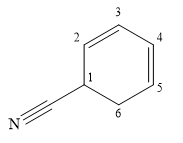
C1 is a chiral carbon with an absolute configuration of R. Therefore, the priority groups 1 to 3 attached to it must be arranged clockwise with the lowest priority hydrogen pointing away from the observer.
Thus, the structure of the compound can be drawn as
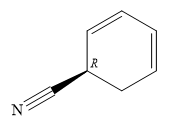
The structure of the compound can be drawn from its IUPAC name, which lists the functional groups attached to an alkyl/aryl root (parent).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Which reagent(s) sequence(s) is/are optimum for preparing butanoic acid from 1-propanol? i. K2Cr2O7 in acidii. (1) PBr3; (2) NaCN; (3) H2O; (4) [H+] iii. (1) NaCN; (2) H2O; (3) [H+]iv. LiAlH4arrow_forwardStructures A and B are best described asarrow_forwardplz provide DETAILED written explanation and AVOID USING MECHANISMS.arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic product of each reaction. Indicate the stereochemistry at the stereogenic center. Omit byproducts such as salts. If applicable, expand octets to minimize formal charges.arrow_forwardgive structure only letter b ,c ,darrow_forwardWrite down the reduction reaction of each molecule using appropriate reagents, listing the follo compounds according to their of reductionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





