Find the net potential (DE°) and DG° (in kJ/mol) and Keg for the reaction below and determine if the reaction is spontaneous. Also identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent: Malate + NAD+ → Oxaloacetate + NADH + H* Please use the table of standard reduction potential (E°) below for completing your calculations. Handwrite the answer to this question on a sheet of paper, scan it and upload your answers. Show detailed steps! Just showing the final numerical value for the answer for each question will receive no credit. TABLE 9.1 Standard Reduction Potentials* Standard Reduction Potentials (Eº) (V) Redox Half-Reaction 2H + 2e → H2 -0.42 a-Ketoglutarate + CO2 + 2H* + 2e¯ → isocitrate NADP+ + H* + 2e → NADPH -0.38 -0.324 NAD* + H* + 2e - NADH S+2H* + 2e – H;S FAD + 2H* + 2e™ → FADH, -0.32 -0.23 --0.22 Acetaldehyde + 2H* + 2e¯ → ethanol Pyruvate + 2H* + 2e¯ → lactate -0.20 -0.19 Oxaloacetate + 2H* + 2e¯ → malate --0.166 Cu2+ + e → Cu* +0.16 Fumarate + 2H + 2e → succinate Cytochrome b (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome b (Fe2*) Cytochrome c, (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome c, (Fe2+) Cytochrome c (Fe3+) + e → cytochrome c (Fe2+) Cytochrome a (Fe3+)+ e→ cytochrome a (Fe2+) NO,-+ 2H* + 2e → NO,- + H20 1. +0.031 +0.075 +0.22 +0.235 +0.29 +0.42 OCT 3. étv
Find the net potential (DE°) and DG° (in kJ/mol) and Keg for the reaction below and determine if the reaction is spontaneous. Also identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent: Malate + NAD+ → Oxaloacetate + NADH + H* Please use the table of standard reduction potential (E°) below for completing your calculations. Handwrite the answer to this question on a sheet of paper, scan it and upload your answers. Show detailed steps! Just showing the final numerical value for the answer for each question will receive no credit. TABLE 9.1 Standard Reduction Potentials* Standard Reduction Potentials (Eº) (V) Redox Half-Reaction 2H + 2e → H2 -0.42 a-Ketoglutarate + CO2 + 2H* + 2e¯ → isocitrate NADP+ + H* + 2e → NADPH -0.38 -0.324 NAD* + H* + 2e - NADH S+2H* + 2e – H;S FAD + 2H* + 2e™ → FADH, -0.32 -0.23 --0.22 Acetaldehyde + 2H* + 2e¯ → ethanol Pyruvate + 2H* + 2e¯ → lactate -0.20 -0.19 Oxaloacetate + 2H* + 2e¯ → malate --0.166 Cu2+ + e → Cu* +0.16 Fumarate + 2H + 2e → succinate Cytochrome b (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome b (Fe2*) Cytochrome c, (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome c, (Fe2+) Cytochrome c (Fe3+) + e → cytochrome c (Fe2+) Cytochrome a (Fe3+)+ e→ cytochrome a (Fe2+) NO,-+ 2H* + 2e → NO,- + H20 1. +0.031 +0.075 +0.22 +0.235 +0.29 +0.42 OCT 3. étv
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
100%
Find the net potential
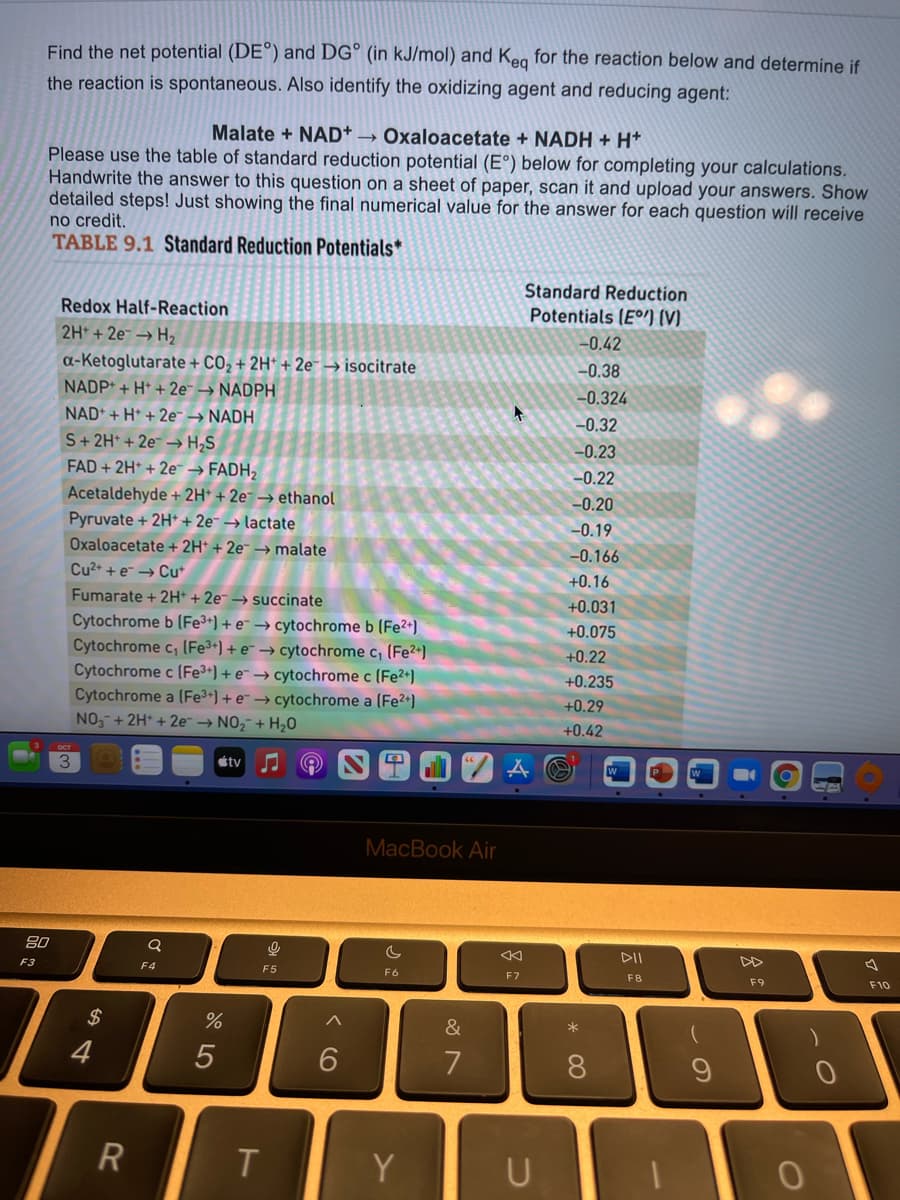
Transcribed Image Text:Find the net potential (DE°) and DG° (in kJ/mol) and Keg for the reaction below and determine if
the reaction is spontaneous. Also identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent:
Malate + NAD* → Oxaloacetate + NADH + H*
Please use the table of standard reduction potential (E°) below for completing your calculations.
Handwrite the answer to this question on a sheet of paper, scan it and upload your answers. Show
detailed steps! Just showing the final numerical value for the answer for each question will receive
no credit.
TABLE 9.1 Standard Reduction Potentials*
Standard Reduction
Redox Half-Reaction
Potentials (EºI (V)
2H + 2e¯ → H2
a-Ketoglutarate + CO2 + 2H* + 2e¯→ isocitrate
-0.42
-0.38
NADP* + H* + 2e¯ → NADPH
-0.324
NAD* + H* + 2e¯ → NADH
-0.32
S+2H* + 2e – H;S
-0.23
FAD + 2H* + 2e → FADH,
-0.22
Acetaldehyde + 2H* + 2e¯ → ethanol
-0.20
Pyruvate + 2H* + 2e¯ → lactate
-0.19
Oxaloacetate + 2H* + 2e¯ → malate
-0.166
Cu2+ + e → Cu+
+0.16
Fumarate + 2H* + 2e¯ → succinate
+0.031
Cytochrome b (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome b (Fe2*)
Cytochrome c, (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome c, (Fe²+)
Cytochrome c (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome c (Fe2+)
Cytochrome a (Fe3+) + e → cytochrome a (Fe2+)
NO,-+ 2H* + 2e → NO,¯ + H,0
+0.075
+0.22
+0.235
+0.29
+0.42
3
éty
MacBook Air
80
DD
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
$
&
4
5
7
8.
R
T.
Y
U
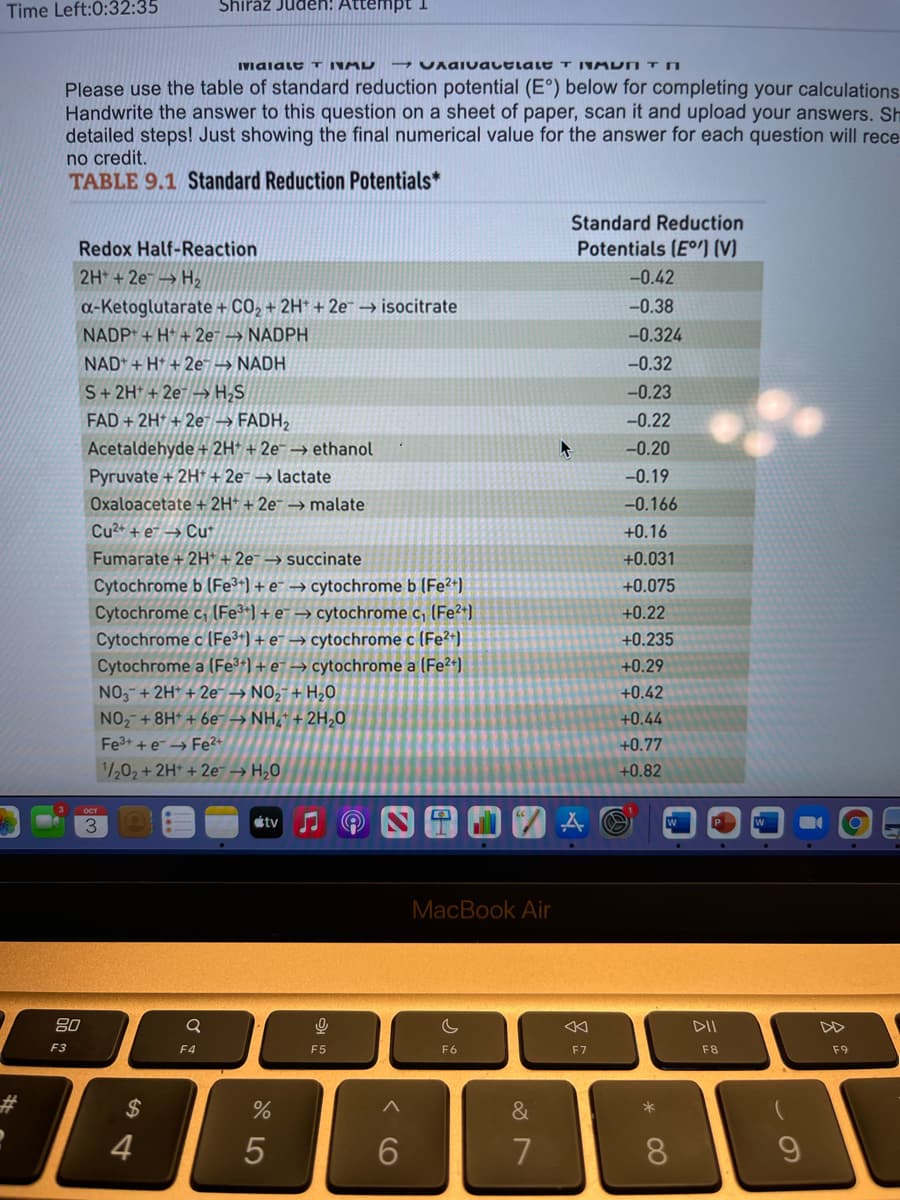
Transcribed Image Text:Time Left:0:32:35
Shiraz Juden: Attempt 1
IVaiale T INAD
UAGIvauelaLE T INM DN T N
Please use the table of standard reduction potential (E°) below for completing your calculations
Handwrite the answer to this question on a sheet of paper, scan it and upload your answers. Sh
detailed steps! Just showing the final numerical value for the answer for each question will rece
no credit.
TABLE 9.1 Standard Reduction Potentials*
Standard Reduction
Redox Half-Reaction
Potentials (E) (V)
2H +2e → H,
-0.42
a-Ketoglutarate + CO, + 2H* + 2e → isocitrate
NADP* + H* + 2e → NADPH
-0.38
-0.324
NAD* + H* + 2e- → NADH
-0.32
S+ 2H* + 2e – H;S
FAD + 2H + 2e → FADH2
-0.23
-0.22
Acetaldehyde + 2H* + 2e¯ → ethanol
-0.20
Pyruvate + 2H + 2e → lactate
-0.19
Oxaloacetate + 2H* + 2e¯ → malate
-0.166
Cu2+ + e¯ → Cu
+0.16
Fumarate + 2H* + 2e¯ → succinate
+0.031
Cytochrome b (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome b (Fe²+)
Cytochrome c, (Fe3*) + e¯ → cytochrome c, (Fe?+)
Cytochrome c (Fe³*) + e¯ → cytochrome c (Fe²*)
Cytochrome a (Fe3+) + e¯ → cytochrome a (Fe²+)
NO,-+ 2H* + 2e¯ → NO,- + H,0
NO, +8H* + 6e → NH,* + 2H,0
+0.075
+0.22
+0.235
+0.29
+0.42
+0.44
Fe3+ + e → Fe?+
+0.77
1/202 + 2H* + 2e → H,0
+0.82
3
étv
W
MacBook Air
80
DII
DD
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
%23
%24
&
4
5
6.
7
8.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON