
Observers at M and N arc looking at an image of the pin in the mirror.
1. Suppose that all but a small portion of the mirror were covered as shown at right.
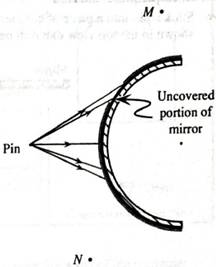
How, if at all, would this change affect what the observers at M and N see? Explain.
Determine the region in which an observer must be located in order to see an image of the pin. Discuss your reasoning with your partners.
Would two observers at different locations in this region agree on the approximate location of the image? Explain.
2. Suppose that all but a small portion of the mirror near the center were covered, as shown at right.
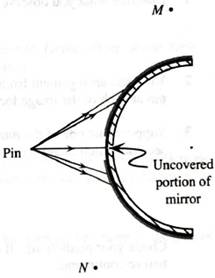
Determine the region in which an observer must be located in order to see an image of the pin.
Would two observers at different locations in this region agree on the approximate location of the image? If so, find the approximate image location. If not, explain how you can tell.
Check your answers experimentally.
While the image location is independent of observer location in certain cases (e.g., Plane mirrors), in general it is not. In many cases, however, it is possible to identify a limited range of locations for which the image location is essentially independent of the observer location. An example is when both the object and the observer lie very nearly along the axis of a cylindrical or spherical mirror. In this situation, all rays are said to be paraxial, that is, they make small angles with the axis of the mirror. Ray diagrams often specify the location of an image but not the observer’s location. For such a diagram, it should be assumed that the image location is independent of the observer’s location.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Modern Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
University Physics Volume 1
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
- A beam of light travels vertically downward and strikes a horizontal mirror, reflecting directly back vertically upward, as indicated by the black dashed line in the diagram at left. The mirror is now rotated, so that it is 10° away from horizontal, as is the red mirror in the diagram . The incident solid black ray is the same in both cases. a) At what angle from the vertical will the reflected beam (the red dashed arrow) now be seen? b) If the mirror is further rotated until it is 20° from the horizontal, what will be the new angle between the reflected beam and the vertical?arrow_forwardA ray of light travels through air until it strikes the interface between the air and another medium. The incident ray makes an angle of ?1 = 33.0° with the normal, as shown in the figure below. Upon passage into the second medium, the ray is refracted, emerging from the interface at an angle ?2 with respect to the normal. (a)Suppose that the second medium is ice. What is the angle of refraction, ?2 (in degrees)? (Enter your answer to at least one decimal place.) (b)Suppose that the second medium is crown glass. What is the angle of refraction, ?2,in this case (in degrees)? (Enter your answer to at least one decimal place.) (c)Finally, suppose that the second medium is ethyl alcohol. What is the angle of refraction, ?2, in this case (in degrees)? (Enter your answer to at least one decimal place.)arrow_forwardA narrow beam of light is incident on the left side of the prism shown in the figure below. The prism is a right triangle, with two of its angles measuring 45°. A) The transmitted beam that exits the hypotenuse of the prism makes an angle of ? = 17.5° with the direction of the incident beam. What is the index of refraction of the prism? B) In part (a), we assumed the beam was monochromatic. Consider instead the case where the beam was composed of white light. Because the index of refraction differs for different wavelengths, the white light would be dispersed into constituent colors. Assume the index of refraction for blue wavelengths is 1.01n and for red wavelengths it is 0.99n, where n is the index of refraction found in part (a). What is the angular spread (in degrees) between red and blue light exiting the prism?arrow_forward
- Construct ray diagrams for each marked dot to show the location and appearance of the image. Draw your rayslightly (but visibly) and mark your image points boldly1.Where does the image of the letter “A” appear?2. Is the image of the letter A larger, smaller, or the same size as the object?arrow_forwardhello i need help with both screenshots, for the second image, part B you need to fine the answer of N of revs. Thank youarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the following image making sure to answer part a and b.arrow_forward
- Need Short Answers 1. We have a green object explain what we see when: (a) white light fall on it , blue light falls on it, green light falls on it , yellow light falls on it 2. why does a fisherman aim at the tail of fish, during spear fishing? explain 3. Speed of light again becomes 3x10^8 m/s when it emerges out in air from denser material without the loss of energy. why? 4. why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium to another mediumarrow_forwardAnalyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance with object distance in case of a convex lens and answer the question that follow without doing any calculations1) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer2) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion.3) Take an appropriate scale to draw ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of the magnification.Class - 10thChapter - Light, reflection and refraction.arrow_forwardA beam of light that consists of a mixture of red, green and violet light strikes a prism(surrounded by air) as shown. Indices of refraction for this prism for the various colorsare indicated in the table. An observer is located to the right of the prism as shown. Determine which color(s) could, in principle, be seen by the observer? Carefully show your work/describe your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Could you help with question C and D? The 1st image is just for additional infoarrow_forward1. Find the focal length of a biconcave lens (n = 1.65) if the magnitudes of the radii of curvature are 0.40 m and 0.60 m. In your solution, did it matter which was surface A and which was surface B? Briefly explain (or show your solution). 2. When a glass lens is submerged in water, is its focal length less than, equal to, or greater than when it is surrounded by air? Explain using Snell’s law. 3. A small insect viewed through a convex lens is 1.8 cm from the lens and appears 2.5 times larger than its actual size. What is the focal length of the lens?arrow_forwardHello I help with (c) only in the second image, did part (a), (b), and (c) already.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

