
(a)
Interpretation:
A complete orbital diagram of Helium with
Concept introduction:
Electronic configuration can be assigned to any elements in the ground when they follow certain rules like the Hund rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Aufbau rule. If the
No two electrons in an atom can have the same group of four quantum numbers and this is Pauli Exclusion Principle.
While filling of orbital’s, the electron first enters to each energy level with degenerate energy before the paring of electron begins and this is Hund’s rules.
(a)
Answer to Problem 39A
Complete orbital diagram of Helium with
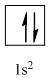
Explanation of Solution
As per the Aufbau rule, electrons are filled in lower energy orbitals that are closer to the nucleus before they are filled in higher energy ones. The order of orbital arranged in their increasing energies is as follows:
So, the complete electronic configuration of Helium with
Therefore, the complete orbital diagram of Helium with
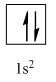
(b)
Interpretation:
A complete orbital diagram of Neon with
Concept introduction:
Electronic configuration can be assigned to any elements in the ground when they follow certain rules like the Hund rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Aufbau rule. If the atomic number of an element is
No two electrons in an atom can have the same group of four quantum numbers and this is Pauli Exclusion Principle.
While filling of orbital’s, the electron first enters to each energy level with degenerate energy before the paring of electron begins and this is Hund’s rules.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39A
Complete orbital diagram of Neon with
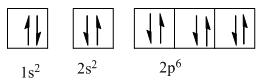
Explanation of Solution
As per Aufbau rule electrons are filled in lower energy orbitals that are closer to the nucleus before they are filled in higher energy ones. The order of orbital arranged in their increasing energies is as follows:
So complete electronic configuration of Neon with
Therefore, the complete orbital diagram of Neon with
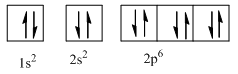
(c)
Interpretation:
A complete orbital diagram of krypton with
Concept introduction:
Electronic configuration can be assigned to any elements in the ground when they follow certain rules like the Hund rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Aufbau rule. If the atomic number of an element is
No two electrons in an atom can have the same group of four quantum numbers and this is Pauli Exclusion Principle.
While filling of orbital’s, the electron first enters to each energy level with degenerate energy before the paring of electron begins and this is Hund’s rules.
(c)
Answer to Problem 39A
Complete orbital diagram of krypton with

Explanation of Solution
As per the Aufbau rule, electrons are filled in lower energy orbitals that are closer to the nucleus before they are filled in higher energy ones. The order of orbital arranged in their increasing energies is as follows:
So, the complete electronic configuration of krypton with
Therefore, the complete orbital diagram of krypton with

(a)
Interpretation:
A complete orbital diagram of Xenon with
Concept introduction:
Electronic configuration can be assigned to any elements in the ground when they follow certain rules like the Hund rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Aufbau rule. If the atomic number of an element is
No two electrons in an atom can have the same group of four quantum numbers and this is Pauli Exclusion Principle.
While filling of orbital’s, the electron first enters to each energy level with degenerate energy before the paring of electron begins and this is Hund’s rules.
(a)
Answer to Problem 39A
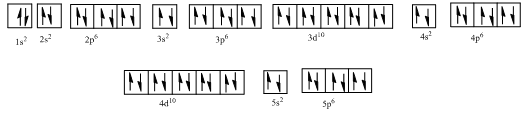
Complete orbital diagram of Xenon with
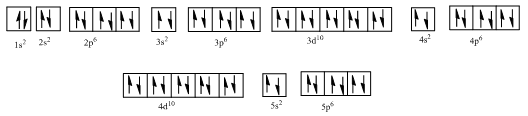
Explanation of Solution
As per the Aufbau rule, electrons are filled in lower energy orbitals that are closer to the nucleus before they are filled in higher energy ones. The order of orbital arranged in their increasing energies is as follows:
So, the complete electronic configuration of Xenon with
Therefore, the complete orbital diagram of Xenon with
Chapter 11 Solutions
World of Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





