
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of chlorination product obtained from radical chlorination of methylcyclohexane has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
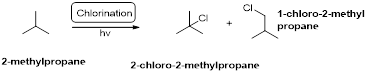
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in greater yield should be given and explained.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
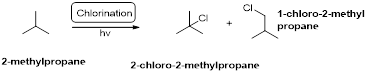
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of monochlorination products obtained by considering all stereoisomers should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
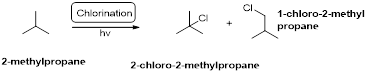
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- a. When HBr adds to a conjugated diene, what is the rate-determining step? b. When HBr adds to a conjugated diene, what is the product-determining step?arrow_forwardIndane can undergo free-radical chlorination at any of the alkyl positions onthe aliphatic ring.(a) Draw the possible monochlorinated products from this reactionarrow_forwardWhy do these two dienes react at different temperatures?arrow_forward
- Indane can undergo free-radical chlorination at any of the alkyl positions onthe aliphatic ring.Draw the possible dichlorinated products from this reaction.arrow_forwardFor Sn1 and Sn2 reactions, explain why one type of carbon should react faster than others.arrow_forwardWhen HBr adds to a conjugated diene, what is the rate-determining step?arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of the minor product formed in the reaction of 2-methylbut-1-ene with concentrated sulfuric acid Explain why thid is the major product? Structure of minor product? Explanation?arrow_forwardDraw all the different monochlorinated products one would obtain by the radical chlorination of methylcyclopentanearrow_forwardBased on the hydrogenation and the bromination reaction information, how many different alkene structures can you draw that could be Compound X? (If enantiomers are possible, count each pair of enantiomers as one structure.)arrow_forward
- Draw all the different monochlorinated products one would obtain by the radical chlorination of 2-methylbutane.arrow_forwardExplain the importance of Pericyclic Reactions? Why should we study ?arrow_forwardPlease explain Consider the reaction between methylcyclohexene and the hydroxyl radical.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
