
(a)
Interpretation:
The monomers required to produce the following
Whether the reaction is addition or condensation needs to be determined. Whether the given polymer is copolymer or not needs to be determined.
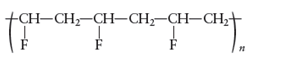
Concept Introduction :
The small unit of organic molecules that combines together to form larger molecules are said to be monomers, while polymer are complex molecules that have long interconnected chain of monomers.
(a)
Answer to Problem 72E
The monomer that is required to form the given polymer
is CH2=CHF
It is not a copolymer.
Explanation of Solution
From reviewing the given polymer, it can be noted that the molecules CH2- CHF are found to be repeating. Hence, for this polymer to be formed, the monomer reacting is CH2=CHF wherein the double bonds open up and link with the next molecule.
Therefore, the polymer is formed by monomer CH2=CHF. As it can be seen that this polymer is formed by addition
(b)
Interpretation:
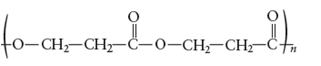
The monomers required to produce the following polymer needs to be determined.
Whether the reaction is addition or condensation needs to be determined. Whether the given polymer is copolymer or not needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction :
Monomers are small unit of organic molecules that combines together to form larger molecules. Polymers are complex molecules formed from combination of monomers and it has long interconnected chain. Copolymers are those molecules which have two or more than two different monomer species. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of two monomers that does not generate any other products. Condensation polymers are formed when two monomers add releasing some by product along with it. It is not a copolymer as the monomer species are the same.
(b)
Answer to Problem 72E
The monomer that is required to form the given polymer is as follows:
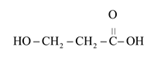
It is not a copolymer.
Explanation of Solution
From reviewing the given polymer, it can be noted that the monomer is as follows:
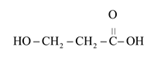
They react with each other to release water. The end molecule of carboxylic acid, namely H of one monomer and OH of the other monomer, reacts to give out water. As it releases water during formation of polymer, it is said to be condensation polymerization and the polymer formed is a condensation polymer. It is not a copolymer as the monomer species are the same.
(c)
Interpretation:
The monomers required to produce the following polymer needs to be determined.
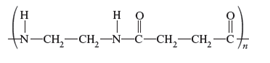
Whether the reaction is addition or condensation needs to be determined. Whether the given polymer is copolymer or not needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction :
The small unit of organic molecules that combines together to form larger molecules are said to be monomers, while polymer are complex molecules that have long interconnected chain of monomers. Copolymers are those molecules which have two or more than two different monomer species. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of two monomers that does not generate any other products. Condensation polymers are formed when two monomers when added release some by product along with it.
(c)
Answer to Problem 72E
The monomers required to form the given polymer are as follows:
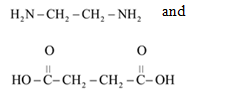
Explanation of Solution
From reviewing the given polymer, it is noted that there are two different molecules which are as follows:
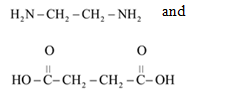
They react to give the polymer. The H molecule of monomer containing amino group and OH molecule of monomer containing carboxylic group combines to form water. As water is formed, the polymerization is said to be condensation polymerization. It is a copolymer as there are two different monomer species involved.
(d)
Interpretation:
The monomers required to produce the following polymer needs to be determined.
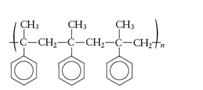
Whether the reaction is addition or condensation needs to be determined. Whether the given polymer is copolymer or not needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction :
The small unit of organic molecules that combines together to form larger molecules are said to be monomers, while polymer are complex molecules that have long interconnected chain of monomers. Copolymers are those molecules which have two or more than two different monomer species. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of two monomers that does not generate any other products. Condensation polymers are formed when two monomers when added release some by product along with it.
(d)
Answer to Problem 72E
The monomer that is required to form the given polymer is as follows:
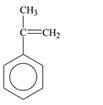
It is not a copolymer.
Explanation of Solution
From reviewing the given polymer, it is noted that the monomer is as follows:

It has double bond which opens up and link with the next monomer. In this way the same monomer s species repeats itself. Hence, the product is formed by addition polymerization. It is not a copolymer as the monomers are same species and not two different.
(e)
Interpretation:
The monomers required to produce the following polymer needs to be determined.
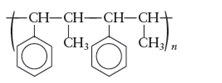
Whether the reaction is addition or condensation needs to be determined. Whether the given polymer is copolymer or not needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction :
The small unit of organic molecules that combines together to form larger molecules are said to be monomers, while polymer are complex molecules that have long interconnected chain of monomers. Copolymers are those molecules which have two or more than two different monomer species. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of two monomers that does not generate any other products. Condensation polymers are formed when two monomers when added release some by product along with it.
(e)
Answer to Problem 72E
The monomer that is required to form the given polymer is as follows:
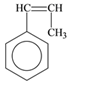
It is not a copolymer.
Explanation of Solution
From reviewing the given polymer, it is noted that the monomer is as follows:

It has double bond which opens up and link with the next monomer. In this way the same monomer species repeats itself. Hence, the product is formed by addition polymerization. It is not a copolymer as the monomers are same species and not two different.
(f)
Interpretation:
The monomers required to produce the following polymer needs to be determined.
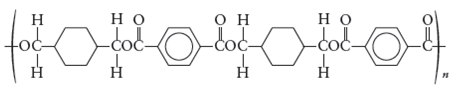
Whether the reaction is addition or condensation needs to be determined. Whether the given polymer is copolymer or not needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction :
Monomers are small unit of organic molecules that combines together to form larger molecules. Polymers are complex molecules formed by interconnecting of monomers. Copolymers are those molecules which have two or more than two different monomer species. Condensation polymers are formed when two monomers add releasing some by product along with it. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of two monomers that does not generate any other products.
(f)
Answer to Problem 72E
The monomers required to form the given polymer are as follows:
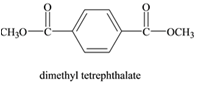 and
and 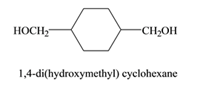
It is not a copolymer.
Explanation of Solution
From reviewing the given polymer, it is noted that the monomers are as follows:


These two monomers combine to give the polymer. The H and OH molecules of dimethyl terephthalate and 1,4 di(hydroxymethyl) cyclohexane combines to release water as by product. Hence, it is a condensation polymerization. The product is a copolymer as it has monomers of two different species.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
CHEM.PRINC.W/OWL2+REBATE+2 SUPPL.>IP<
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





