
Concept explainers
Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder in humans. It results from mutation of the gene on chromosome
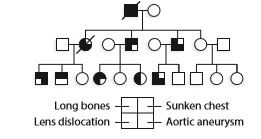
Since all cases of Marfan syndrome are caused by mutation of the fibrillin gene, and all family members with Marfan syndrome carry the same mutant allele, how do you e xplain the differences shown in the pedigree?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a disorder that primarily affects the function of skeletal muscles used for movement and cardiac muscles used for heart beating. Dystrophin is a protein encoded by a single gene, DMD, that is expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Some forms of muscular dystrophy may be caused by different mutations in the DNA sequence of the DMD gene. Because the DMD locus is on the X chromosome, males are affected at higher rates. Two brothers, one of whom has DMD and one of whom does not, worked with their genetic counselor (Links to an external site.) to have their DMD gene sequenced to identify genetic variation that may explain why one brother was affected and the other not. Because DMD is a very long gene, a fictionalized, simplified model of the results is presented here (Figure 1). The actual DMD mRNA is about 16,000 base-pairs!------Consider single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) #1 (Figure 1). Is this mutation likely to cause Duchenne muscular…arrow_forwardIn McCune-Albright syndrome, fibrous connective tissue replaces bone, tan patches (café-au-lait spots) dot the skin, and hormone abnormalities cause early puberty and malfunction of the thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal glands. The phenotype is highly variable, and all patients are somatic mosaics for the mutation, which is in the gene GNAS1. Why is the condition seen only in mosaics?arrow_forwardEach of the four types of structural chromosomal mutations is illustrated below. Label each picture with the type of chromosomal mutation that has occurred.arrow_forward
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is due to a mutation in a gene that encodesa protein called hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase(HPRT). HPRT is an enzyme that functions in purine metabolism.People afflicted with this syndrome have severe neurodegenerationand loss of motor control. The pedigree below contains severalindividuals with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, shown with blacksymbols. Based on this pedigree, does this syndrome appearto be inherited by an autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant,X-linked recessive, or X-linked dominant pattern? Explainyour reasoning.arrow_forwardSickle cell disease— what is the background of this disorder: include the name of the disorder, any alternate names used, provide a description of the disorder, and the typical age of onset. What is the Type of genetic disorder: explain if and how this disorder is inherited. Explain the genetic causes of the disorder. Is it inherited? Is the disorder a dominant or recessive trait? Which chromosome is affected in this disorder? Is a gene mutated? If so, name the gene that is affected? How is gene expression impacted (is it a particular type of mutation, a case of a misshapen protein, etc.?)arrow_forwardTwo related forms of muscular dystrophy—Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)—are both recessive, X-linked, single-gene conditions caused by point mutations, deletions, and insertion in the dystrophin gene. Each mutated form of dystrophin is one allele. Of the two diseases, DMD is much more severe. Given your knowledge of mutations, the genetic code, and translation, propose an explanation for why the two disorders differ greatly in severity.arrow_forward
- Ehler-Danlos syndrome is a rare disorder caused by a mutation ina gene that encodes a protein called collagen (type 3 A1). Collagenis found in the extracellular matrix that plays an important role inthe formation of skin, joints, and other connective tissues. Peoplewith Ehler-Danlos syndrome have extraordinarily flexible skin and very loose joints. The pedigree below contains several individualsaffected with this syndrome, shown with black symbols. Based onthis pedigree, does the syndrome appear to follow autosomalrecessive, autosomal dominant, X-linked recessive, or X-linkeddominant inheritance? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardA defective gene on chromosome 15 causes Tay-Sachs disease. It is a central nervous system neurodegenerative disease that most often affects infants, though older children and adults can have late-onset forms of the disease. The defective gene prevents the body from making a protein called hexosaminidase A. Without, hexosaminidase A, chemicals called gangliosides build up in the nerve cells of the brain, destroying brain cells. Pedigree information regarding the incidence of Tay-Sachs within a family is depicted above. The row below that indicates the genotypes of individuals II-1, II-2, and III-1 is Select one: a. II-1 II-2 III-1 Aa Aa aa b. II-1 II-2 III-1 XAY XAXa XAXa c. II-1 II-2 III-1 XAY XAXA XaXa d. II-1 II-2 III-1 AA aa Aaarrow_forwardThe dominant condition elliptocytosis causes red blood cells to become misshapen into oval-shaped cells. One of the genes responsible for the abnormal shape encodes the band 4.1 protein that together with ankyrin and other scaffold proteins creates and maintains the spherical concave shape of a normal red blood cell. The gene for band 4.1 protein, EPB41, is found on the p arm of chromosome 1. This is very close to the gene encoding the red blood cell Rhesus (Rh) blood type, either phenotype + (dominant) or - (recessive), with a recombination frequency of 2%. This means that 98% of the time alleles for these two genes are linked and are transmitted together. Diane and Jack are siblings, and both have elliptocytosis and Rh+ blood type. Due to the elliptocytosis, both had emergency splenectomies after having severe anemia. Their younger brother, Devonté, has not yet shown signs of elliptocytosis, but has Rh- blood. André, their dad, also has elliptocytosis and Rh+ blood; while their…arrow_forward
- Ehler-Danlos syndrome is a rare disorder caused by a mutation ina gene that encodes a protein called collagen (type 3 A1). Collagenis found in the extracellular matrix that plays an important role inthe formation of skin, joints, and other connective tissues. Peoplewith Ehler-Danlos syndrome have extraordinarily flexible skin andvery loose joints. The following pedigree contains several individualsaffected with this syndrome, shown with black symbols. Basedon this pedigree, does the syndrome follow autosomal recessive,autosomal dominant, X-linked recessive, or X-linked dominantinheritance? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardThe gene controlling ABO blood type and the gene underlying nail-patella syndrome are said to show linkage. What does that mean in terms of their relative locations in the genome? What does it mean in terms of how the two traits are inherited with respect to each other?arrow_forwardTheodor Boveri predicted that malignancies would often be associated with chromosomal mutation. What lines of evidence substantiate this prediction?arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
