
Concept explainers
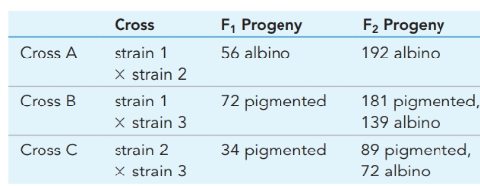
In rabbits, albinism is an autosomal recessive conditioncaused by the absence of the pigment melanin from skin and fur. Pigmentation is a dominant wild-type trait. Three purebreedingstrains of albino rabbits, identified as strains
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Individuals of genotype AaBb were mated to individuals of genotype aabb. One thousand offspring were counted, with the following results: 474 Aabb, 480 aaBb, 20 AaBb, and 26 aabb. What type of cross is it? Are these loci linked? What are the two parental classes and the two recombinant classes of offspring? What is the percentage of recombination between these two loci? How many map units apart are they?arrow_forwardHemophilia and color blindness are both recessive conditions caused by genes on the X chromosome. To calculate the recombination frequency between the two genes, you draw a large number of pedigrees that include grandfathers with both hemophilia and color blindness, their daughters (who presumably have one chromosome with two normal alleles and one chromosome with two mutant alleles), and the daughters sons. Analyzing all the pedigrees together shows that 25 grandsons have both color blindness and hemophilia, 24 have neither of the traits, 1 has color blindness only, and 1 has hemophilia only. How many centimorgans (map units) separate the hemophilia locus from the locus for color blindness?arrow_forwardFamilial retinoblastoma, a rare autosomal dominant defect, arose in a large family that had no prior history of the disease. Consider the following pedigree (the darkly colored symbols represent affected individuals): a. Circle the individual(s) in which the mutation most likely occurred. b. Is the person who is the source of the mutation affected by retinoblastoma? Justify your answer. c. Assuming that the mutant allele is fully penetrant, what is the chance that an affected individual will have an affected child?arrow_forward
- In dogs, dark coat color is dominant over albino, andshort hair is dominant over long hair. Assume that theseeffects are caused by two independently assorting genes.Seven crosses were done as shown below, in which D andA stand for the dark and albino phenotypes, respectively,and S and L stand for the short-hair and long-hairphenotypes.Number of progenyParental phenotypes D, S D, L A, S A, La. D, S × D, S 88 31 29 12b. D, S × D, L 19 18 0 0c. D, S × A, S 21 0 20 0d. A, S × A, S 0 0 29 9e. D, L × D, L 0 31 0 11f. D, S × D, S 45 16 0 0g. D, S × D, L 31 30 10 10Write the genotypes of the parents in each cross. Use thesymbols C and c for the dark and albino coat-color allelesand the symbols H and h for the short-hair and long-hairalleles, respectively. Assume parents are homozygousunless there is evidence otherwise.arrow_forwardThe genotype of EB27 and EB67 are unknown. Based on pedigree, what are the most likely genotype of each individual?arrow_forwardFrom a series of two-point crosses, the following mapdistances were obtained for the syntenic genes A, B,C, and D in peas:B ↔ C 23 m.u.A ↔ C 15 m.u.C ↔ D 14 m.u.A ↔ B 12 m.u.B ↔ D 11 m.u.A ↔ D 1 m.u.Chi-square analysis cannot reject the null hypothesis of no linkage for gene E with any of theother four genes.a. Draw a cross scheme that would allow you todetermine the B ↔ C map distance.b. Diagram the best genetic map that can be assembled from this data set.c. Explain any inconsistencies or unknown features inyour map.d. What additional experiments would allow you toresolve these inconsistencies or ambiguities?arrow_forward
- A female animal with genotype A/a ⋅ B/b is crossed with a double-recessive male (a/a ⋅ b/b). Their progeny include 442 A/a ⋅ B/b, 458 a/a ⋅ b/b, 46 A/a ⋅ b/b, and 54 a/a ⋅ B/b. Explain these results.arrow_forwardIn barley, a self-fertilizing species that can be cross-fertilized, two true-breeding strains with virescent leaves occur. In strain A, the trait is caused by a cytoplasmic gene while in strain B it is by a recessive chromosomal gene. What phenotypes would you expect among the progeny, and in what proportions in each of the following? Illustrate your crosses below, indicate and the female and male parent for each cross, and write the phenotype of all the parents and offspring(s). a. reciprocal crosses between A and Bb. crossing of each F1 in (a) to each of the paternal strainsc. self-fertilization of the F1’s in (a)d. reciprocal crosses between F1’s in (a) Use the following gene assignments: Strain A (trait is in Cytoplasm) A – virescent a – not virescent Strain B (recessive chromosomal gene) B – not virescent b - virescentarrow_forwardAn organism of the genotype AaBbCc was testcrossed to a triplyrecessive organism (aabbcc). The genotypes of the progeny are inthe following table.AaBbCc 20 AaBbcc 20aabbCc 20 aabbcc 20AabbCc 5 Aabbcc 5aaBbCc 5 aaBbcc 5 a.) Assuming simple dominance and recessiveness in each genepair, if these three genes were all assorting independently,how many genotypic and phenotypic classes would result inthe offspring, and in what proportion? b.) Answer part (a) again, assuming the three genes are sotightly linked on a single chromosome that no crossovergametes were recovered in the sample of offspring. c.) What can you conclude from the actual data about thelocation of the three genes in relation to one another?arrow_forward
- In barley, a self-fertilizing species that can be crossed fertilized, two true-breeding strains with virescent leaves exist. In strain A, the trait is caused by a cytoplasmic gene. In strain B, it is caused by a recessive nuclear gene. What phenotypes would you expect among the progeny and in what proportions in each of the following: a. cross between homozygous strain A and strain B b. reciprocal cross c. Self-fertilization of the F1 from a d. Self-fertilization of the F1 from barrow_forward. A corn geneticist has three pure lines of genotypes a/a ; B/B ; C/C, A/A ; b/b ; C/C, and A/A ; B/B ; c/c. All the phenotypes determined by a, b, and c will increase the market value of the corn; so, naturally, he wants to combine them all in one pure line of genotype a/a ; b/b ; c/c. a. Outline an effective crossing program that can be used to obtain the a/a ; b/b ; c/c pure line. b. At each stage, state exactly which phenotypes will be selected and give their expected frequencies. c. Is there more than one way to obtain the desired genotype? Which is the best way?Assume independent assortment of the three gene pairs. (Note: Corn will self or cross-pollinate easily.arrow_forwardIf genes A and B are linked, how would you figure out what would be the expected percentages of nonrecombinant and recombinant progeny in a test cross of AaBb heterozygotes?arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

