
Biological Science (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134678320
Author: Scott Freeman, Kim Quillin, Lizabeth Allison, Michael Black, Greg Podgorski, Emily Taylor, Jeff Carmichael
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 40, Problem 14PIAT
Summary Introduction
To review:
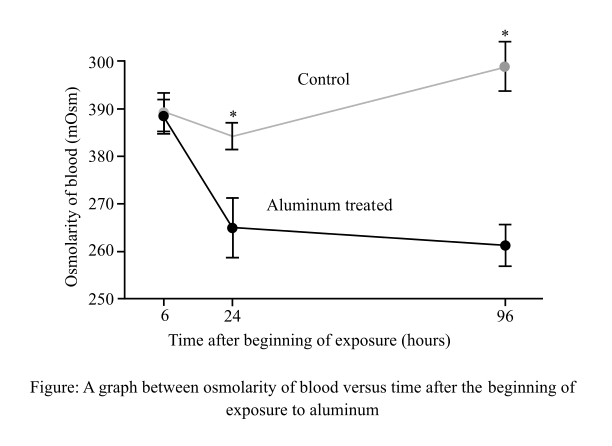
The results related to the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase (sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase) in the gills of the fish exposed to aluminum and its comparison with the control fish.
Introduction:
The Na+/K+- ATPase is the enzyme, which works as a pump, and is found in the plasma membrane of the cell. Its function is to allow the movement of sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. Scientists exposed freshwater bony fish (Prochilodus lineatus) exposed to water with high aluminum level and another set of fish that was exposed to water with normal aluminum levels (control). The results of the data are shown in graph below:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What strategy would best measure the influence of temperature and PTU on oxygen
consumption?
OI will compare how the weights of the control mouse (not treated with PTU) and
the experimental mouse (treated with PTU) change with temperature.
I will compare the oxygen production of a control mouse (not treated with PTU)
and an experimental mouse (treated with PTU)
I will compare the normalized oxygen consumption at different temperatures for
a control mouse (not treated with PTU) and an experimental mouse (treated with
PTU)
-Inhibitor
+Inhibitor
[S] (mM)
Vη&νβσπ: (μmol/sec).
ν0&νβσπ;&νβσπ:(μmol/sec)
0.0001
33
17
0.0005
71
50
0.001
83
67
0.005
96
91
0.01
98
95
What is the TYPE of iinhibitor?
Intestinal epithelial cells pump glucose into the cell against its concentration gradient using the Nat-glucose symporter. Recall
that the Na+ concentration is significantly higher outside the cell than inside the cell. The symporter couples the "downhill"
transport of two Na+ ions into the cell to the "uphill" transport of glucose into the cell.
If the Na+ concentration outside the cell ([Na+]out) is 155 mM and that inside the cell ([Na+ lin) is 21.0 mM, and the cell
potential is -52.0 mV (inside negative), calculate the maximum energy available for pumping a mole of glucose into the cell.
Assume the temperature is 37 °C.
AGgluc
=
kJ
mol
What is the maximum ratio of [glucose] in to [glucose]out
that could theoretically be produced if the energy
coupling were 100% efficient?
O 2700
7.89
O 1.14
3.7 x 10-4
Chapter 40 Solutions
Biological Science (7th Edition)
Ch. 40 - Prob. 2TYKCh. 40 - 3. What effect does antidiuretic hormone (ADH)...Ch. 40 - Fill in the blank: In Gila monsters, the organ in...Ch. 40 - Prob. 5TYUCh. 40 - Prob. 6TYUCh. 40 - Prob. 7TYUCh. 40 - 8. Scientists have noted that marine invertebrates...Ch. 40 - Prob. 9TYPSSCh. 40 - Prob. 10TYPSSCh. 40 - Prob. 11PIAT
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A laboratory in Japan performed a similar experiment on earthworms from different localities of the Japanese archipelago, but instead of linking trypsin activity within worms to anatomical features, they were interested in geographical differences in the ability of the worms to breakdown environmental pollutants using the enzyme polyphenol oxidase. The protocol was similar to the one you used, except that enzyme activity was measured from 100 µl of worm extract. Data obtained are displayed below: Locality Replicate Amount of product Concentration of total protein in worm extract (µg/ml) liberated over 10 minutes (pmol) Hokkaido 1 101 4 87 3 3 107 4 4 88 3 5 89 Hon-shu 1 126 2 2 120 3 3 156 4 4 153 5 5 119 4 Куu-shu 1 103 4 2 99 5 3 94 4 108 3 5 110 5 Okinawa 1 88 3 2 90 4 3 96 4 100 112 5 5 3 From the data in the table, calculate the specific activity of polyphenol oxidase (in units of umol/min/mg protein) from each locality, presenting the data as mean + standard error (n=5).arrow_forwardAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors cause blood vessels to relax, thereby reducing blood pressure. Although Captopril is part of the group of antihypertensive drugs widely used as ACE inhibitors, new research is constantly being carried out with the aim of selecting compounds that are more kinetically advantageous than Captopril. Therefore, a BioPharma employee selected some prototypes and performed kinetic tests, finding the result shown in the figure below. Based on the statement and the graphic above, mark the incorrect alternative. A) It is a graph for determining kinetic parameters according to Lineweaver-Burk. In that case, the coefficient a B) Comparing the prototypes with the reference drug, Prototype 1 has a higher Vmax value. C) Comparing the prototypes with the reference drug, Prototype 2 has a lower Vmax value. D) Captopril has a Vmax of approximately 0.730 and Km of approximately 0.669. E) The two prototypes have Km values lower than those of Captopril and,…arrow_forwardCalculate, or make a best estimate of, the unknown factors in the situations listed in Table 1. Table 1. Data for problem 1. To find Data (i) Ek [K+]out = 4 mM; [K+]in = 130 mM (ii) [Cl-]in [Cl-]out = 570 mM; ECl = -65 mV (iii) ECl [Cl-]out = 150 mM; [Cl-]in = 8 mM; in a mammal (iv) [Na+]in Overshoot of action potential = +35 mV; saline [Na+] = 112 mM (v) [K+]in Blood [K+] = 3.2 mM; undershoot of action potential = -87 mV (vi) ECa [Ca2+]out = 5.6 mM; free [Ca2+]in = 0.8 mM (vii) [K+]out [K+]in = 350 mM; Ek = -82 mVarrow_forward
- An experiment was carried out to measure the reaction rate of hydrolysis of acetylcholme (substrate) with serum enzymes (Eadie, 1949). In the experiment, two experiments were conducted, namely experiment 1 without using a prostigmine inhibitor and experiment 2 using a prostigmine inhibitor at 1.5 x 10^-7 mol/l. the data obtained are: a. Is prostigmine competitive or noncompetitive inhibitor? b. determine the value of km and rmax for the two experiments, comparearrow_forwardThe following kinetic data were collected for prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase, an enzyme involved in pain and inflammation. Using data in the first two columns, use a graphical analysis to determine the Vmax and the Km of the enzyme. Ibuprofen (Advil) is an inhibitor of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. By inhibiting this enzyme, ibuprofen helps to reduce pain and fever. Using the data in the first and third columns, determine the type of inhibition that ibuprofen exerts on prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. In the presence of the inhibitor, determine the Vmax and the Km of the enzyme. [S] mM Product formed Product formed (mmol/min) with 10 mg/mL ibuprofen mmol/min) 0.5 23.5 16.67 1.0 32.2 25.25 1.5 36.9 30.49 2.5 41.8 37.04 3.5 44.0 38.91arrow_forwardAnother member of your research group studied the kinetics of theGAPDH from the organism. They also determined if the GAPDH fromthe organism is also inhibited by the known inhibitor of GAPDH fromhumans. A. From the following data, determine the KM (Michaelis-Menten Constant) and the Vmax(maximum velocity) of the enzyme without and with the inhibitor. B. If GAPDH is inhibited, what specific type of inhibition is observed?arrow_forward
- A scientist is studying the enzyme X which is an important point of regulation in the metabolism of the inhabitants of Sumeru. He developed four Akademiyan-derived compounds which may possibly work against this enzyme, and tested using an eudiometer the metabolic rate of the sample cell lines. Data are below. Time for each compound (min) Eudiometer volume reading (mL) A B C D 0 83.1 62.6 89.0 66.4 5 83.2 100.6 90.2 71.4 10 83.2 83.6 95.0 77.2 15 83.2 83.6 100 84.6 20 83.3 110.8 104.6 88.2 Show the properly labeled volume versus time plot for each eudiometer, with the equation of the line and R2. What is the most effective inhibitor among the four compounds? It was found that the most effective inhibitor exhibits uncompetitive inhibition. Illustrate the Lineweaver-Burk plots of uninhibited and inhibited enzyme X with properly labeled axes.arrow_forwardA radiolabeled glucose solution is utilized as a nutrient source for a human myocyte in order to investigate the metabolic response under several conditions. This system was subjected to different conditions, and the CO₂(g) emitted is captured using carbon sequestration apparatus. The radioactivity of the sequestered gas is then measured. The following are the conditions (a to d). Arrange them in terms of expected radioactivity of the captured gas noting that higher radioactivity corresponds to increased concentration of CO2(g). Unless otherwise stated, all of these conditions are at room temperature. Explain the trend in 4 to 5 sentences. a. 1.0 M phosphate buffer, pH = 6.8 b. 0.1 M NaF c. 0.1 M citric acid d. 100 °Carrow_forwardWhat happens when the Na+-K+ pump is phosphorylated? When K+ binds to the pump protein?arrow_forward
- In an experiment where you use different concentrations of avocado catalase to determine how that affects rate of the reaction with its substrate, hydrogen peroxide, why was the amount(concentration) of peroxide kept the same for all tubes? Why was the total volume of every tube 10cm?arrow_forwardIntestinal epithelial cells pump glucose into the cell against its concentration gradient using the Na+– glucose symporter. Recall that the Na+ concentration is significantly higher outside the cell than inside the cell. The symporter couples the "downhill" transport of two Na+ ions into the cell to the "uphill" transport of glucose into the cell. If the Na+ concentration outside the cell ([Na+]out) is 163 mM and that inside the cell ([Na+]in) is 21.0 mM, and the cell potential is −54.0 mV (inside negative), calculate the maximum energy available for pumping a mole of glucose into the cell. Assume the temperature is 37 °C.arrow_forwardConsider the following experimental data from another experiment: [S] 1.5 2.00 2.50 5.00 10.00 V (No inhibitor) mmol ml¹ min¹ 0.167 0.204 0.232 0.313 0.385 V (inhibitor) mmol ml¹¹ min¹¹ 0.115 0.143 0.167 0.250 0.333 Calculate Km and V max and determine whether this inhibitor is competitive, non-competitive or uncompetitive.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Photosynthesis & Respiration | Reactions | Chemistry | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3XIyweZg6Sw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY