
Experiments have been conducted to determine local heat transfer coefficients for flow perpendicular to a long, isothermal bar of rectangular cross section. The bar is of width c parallel to the flow, and height d normal to the flow. For Reynolds numbers in the range
The values of C and m for the front face, side faces, and back face of the rectangular rod are found to be the following: 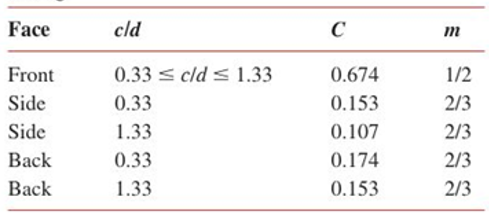
Determine the value of the average heat transfer coefficient for the entire exposed surface (that is, averaged over all four faces) of a
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
