
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The electron-poor H atom in methanol is to be identified, and the mechanism by which methanol acts as an acid in a proton transfer reaction with
Concept introduction:
An electron poor atom or a molecule is an atom or a site in a molecule that has fewer electrons than the number required for stability. In a proton transfer reaction, a proton is transferred from a Bronsted-Lowry acid (proton donor) to a Bronsted–Lowry base (proton acceptor). In an elementary step, electrons tend to flow from an electron-rich site to an electron-poor site. The curved arrow notation shows the movement of valence electrons.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
The electron-poor H atom in methanol is:
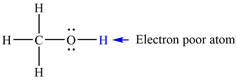
The mechanism by which methanol acts as an acid in a proton transfer reaction with
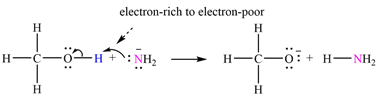
Explanation of Solution
Atoms in
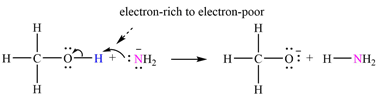
The curved arrows are drawn from the electron-rich site
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Please draw detailed mechanism for this reaction to produce corresponding boronic ester (picture as attached). if X group is electron withdrawing group, will the reaction have the higher chance of happening than in case -X group is electron donating group? Please also explain detailed your answer...arrow_forwardprovide the full reaction mechanism for each of the steps shown in the figurearrow_forwardIn the following enantioselective reaction find the product. A positive non-linear effect (NOE) was observed, Explain with reaction pathway.arrow_forward
- provide the mechanismarrow_forwardprovide the complete reaction mechanism for each of the following steps shown in the figurearrow_forwardFollow the format of solving the problem where you should write the GIVEN, ASKED, SOLUTION, and ANSWER. Add curved arrows to the following reactions to indicate the flow of electrons for all of the bond-forming and bond-breaking steps.arrow_forward
- please explain every step of the process, i am very confused. (answer is D)arrow_forwardI understand where the proton transfer occurs but not what the products will look like. Can you draw curved arrows to show proton transfer and what the reaction products would look like? And explain which side is favored and whyarrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry problem. Please help with finding the product of the reaction shown in the image (where the question mark is). Thank youarrow_forward
- I don't understand the mechanism , I want a more detailed explanationarrow_forwardFor each of the series of electron-pushing arrows, please draw the respective products. Also, indicate if each reaction is an example of initiation, propagation, or termination.arrow_forwardProvide reaction mechanismarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





