
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The carbocation carbon that is farthest to have an octet should be identified with proper reasons.
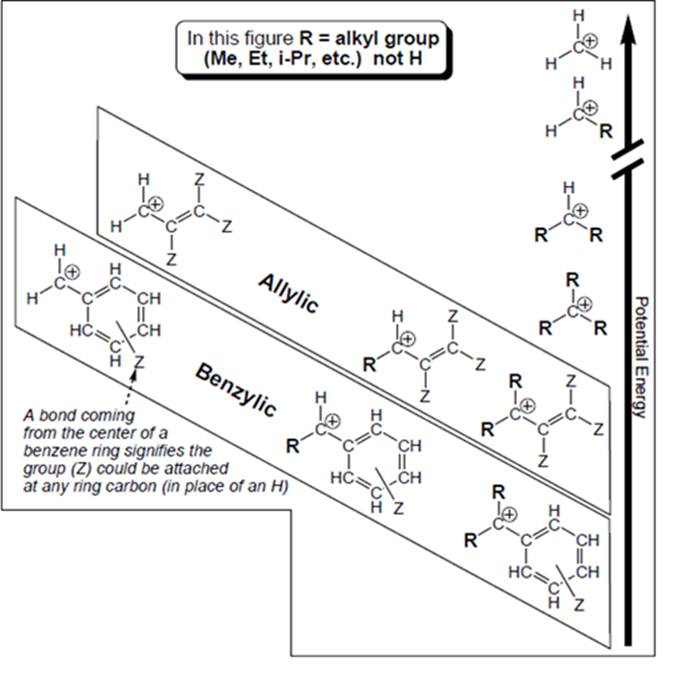
Concept introduction: Organic compounds are covalent in nature that undergoes a reaction by heterolytic cleavage or homolytic cleavage.
In heterolytic cleavage, shared pair of electrons is taken away by one of the atoms which result in charged species. In homolytic cleavage, shared pair of electrons are equally distributed between two atom that results in free radicals.
Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
A carbocation is classified as
Explanation of Solution
Allylic and benzyl carbocations are primary carbocation but are stable due to resonance effect. In both cases the vacant
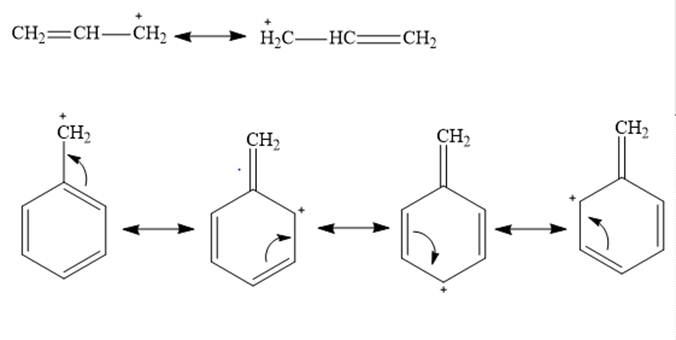
In both benzyl cation and allylic cation, delocalization occurs through resonance effect but allylic cation has 2 contributing structures whereas benzyl cation has 4 contributing structures. Greater the contributing structures greater will be stability. Therefore benzyl cation is more stable than allylic cation.
Outside box methyl carbocation, ordinary primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations are stabilized by electron releasing nature of alkyl groups. This electron releasing nature is due to inductive effect of alkyl groups. They do not exhibit any resonance.
In general, resonance effect dominates over inductive effect. The carbocations that involve delocalization through resonance effect are more stable than those where inductive effect causes stabilization.
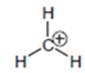
Hence, methyl carbocation is farthest to have an octet as electron releasing nature of hydrogen is less than methyl group so is the inductive effect and it involves no resonance stabilization.
The carbocation that is farthest to have an octet is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
