
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The curved arrow to show electron movement in the first carbocation rearrangement should be drawn.
Concept introduction: Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
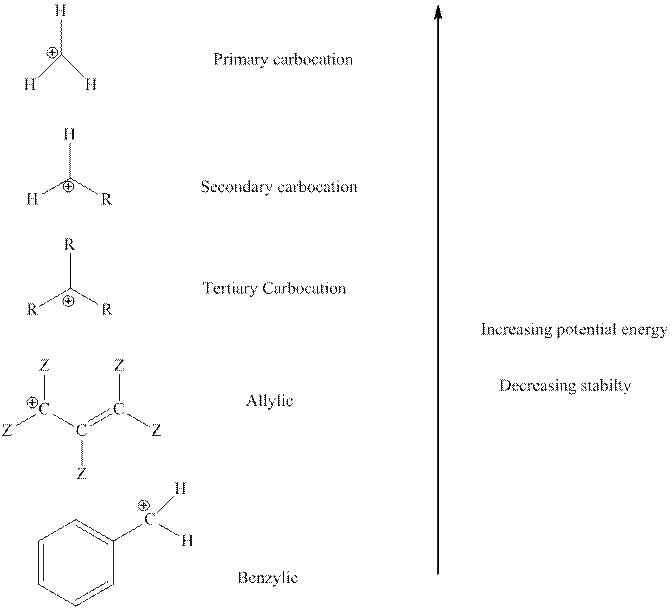
Some special carbocation may attain stability via ring explosion. This also occurs since five-membered rings are more stable than strained three or four-membered ring.
(b)
Interpretation: The curved arrow to show electron movement in the second carbocation rearrangement should be drawn.
Concept introduction: Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
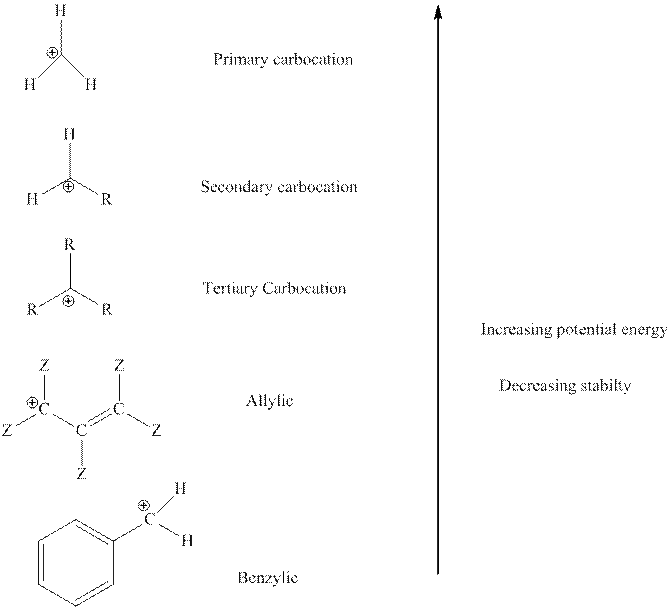
(c)
Interpretation: The force that drives this rearrangement should be illustrated.
Concept introduction: Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
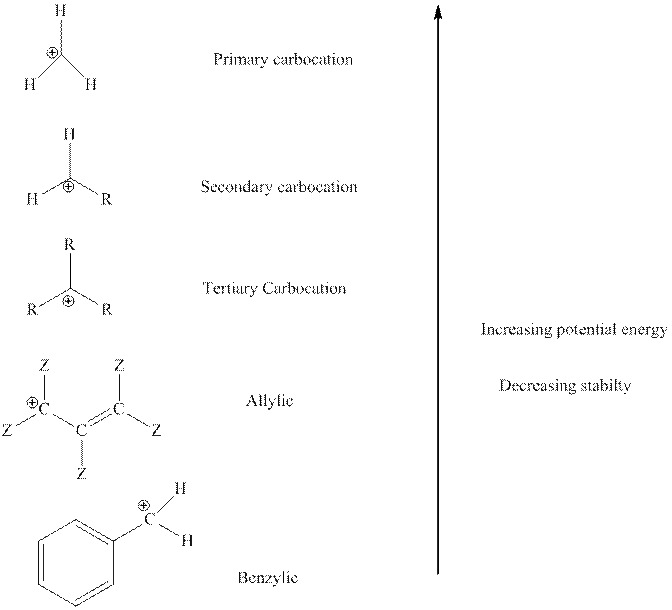
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
