
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 8, Problem 2E
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The reason the below product are not formed in addition reactions should be explained.
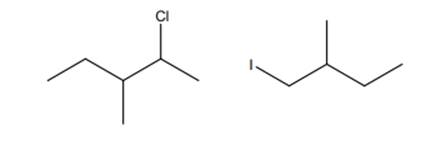
Concept introduction:
The product formed is governed by Markovnikov’s Rule. Rule suggests that negative part of halo acid HX must go to the carbon that has more alkyl substituents or less
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
This is the reaction I was referring to, I have no idea of what reagents can lead me to the products.
What is the main product from the reaction sequence below?
what is the product of the reaction sequence below? explain for your choice.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 2CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 4CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 5CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 6CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 7CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 9CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 8 - Draw the products that result from the electron...Ch. 8 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 8 - Draw the products that would result if the arrow...Ch. 8 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 8 - What information (if any) from the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 16CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 17CTQCh. 8 - The reactants, intermediates, final products, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 19CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 20CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 21CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 22CTQCh. 8 - Explain how you can tell from the energy diagram...Ch. 8 - Explain why the following mechanism for hydration...Ch. 8 - Prob. 25CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 26CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 27CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 28CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 29CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 30CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 31CTQCh. 8 - The hydration above is one of a family of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33CTQCh. 8 - Which statement is false? a. A mechanistic step...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 36CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 37CTQCh. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism including the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2ECh. 8 - Explain why ethene does not react with HX ( X=Cl ,...Ch. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism of each pair of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5ECh. 8 - Prob. 6ECh. 8 - Prob. 7ECh. 8 - Prob. 8ECh. 8 - Prob. 9ECh. 8 - Prob. 10ECh. 8 - Prob. 11ECh. 8 - Prob. 12ECh. 8 - Prob. 15ECh. 8 - A student proposes the following reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17ECh. 8 - Prob. 18ECh. 8 - Prob. 19E
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Draw the structure of the major organic product for each of the reactions below.arrow_forwardProduct Y is the major product of the reaction sequence below. Which product Y: *arrow_forwardwhat are the 8 steps needed to make this benzene ring into the substituted benzene derivative shown belowarrow_forward
- The following reactions do not afford the major product that is given. Explain why this is so, and draw the structure of the major product actually formed.arrow_forwardWhich would be the best reagent for carrying out the reaction shown below?arrow_forwardthe major product in the reaction sequence below is:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning