
Concept explainers
DNA footprint protection (described in Research Technique
a. Explain why this gel provides evidence that the cloned DNA may act as a promoter sequence.
b. Approximately what length is the DNA region protected by RNA pol II and TFIIs?
c. What additional genetic experiments would you suggest to verify that this region of cloned DNA contains a functional promoter?
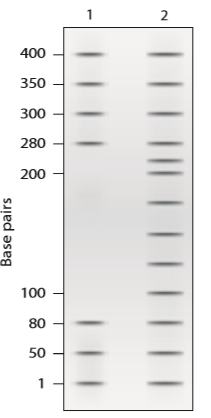
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- Suppose you have a 1-kb segment of cloned DNA that is suspected to contain a eukaryotic promoter including a TATA box, a CAT box, and an upstream GC-rich sequence. The clone also contains a gene whose transcript is readily detectable. Your laboratory supervisor asks you to outline an experiment. (1) determine if eukaryotic transcription factors (TF) bind to the fragment and, if so, (2) identify where on the fragment the transcription factors bind. All necessary reagents, equipment, and experimental know-how are available in the laboratory. Complete the outline of an experiment, which determines if eukaryotic transcription factors (TF) bind to the fragment. Assume all necessary reagents, equipment, and experimental how are available in the laboratory. Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences. Not all terms will be used. For the band shift assay, two samples of the DNA fragment are analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis: one sample is…arrow_forwardseveral options can be correct Consider the following segment of DNA, which is part of a linear chromosome: LEFT 5’.…TGACTGACAGTC….3’ 3’.…ACTGACTGTCAG….5’ RIGHT During RNA transcription, this double-strand molecule is separated into two single strands from the right to the left and the RNA polymerase is also moving from the right to the left of the segment. Please select all the peptide sequence(s) that could be produced from the mRNA transcribed from this segment of DNA. (Hint: you need to use the genetic codon table to translate the determined mRNA sequence into peptide. Please be reminded that there are more than one reading frames.) Question 6 options: ...-Asp-Cys-Gln-Ser-... ...-Leu-Thr-Val-... ...-Thr-Val-Ser-... ...-Leu-Ser-Val-... ...-Met-Asp-Cys-Gln-...arrow_forwardDescribe the banding pattern seen in the gel. What does that tell you about the role of annealing temperature in gene amplification?arrow_forward
- 5 5 S 6 5 5 5 6 U 6 U 6 5:14 PM | 0.2KB/s HHHHH R R U RUUR ARU AP AP R U U R R AP R R R AP MOLECULAR...GENETICS. Describe gene regulation at transcription level. Explain the role of antsense RNA in control mechanism. Describe translational control mechanisms. Describe common DNA damages. Distinguish excision and mismatch repair. Describe the role of recA protein in recombination repair Elaborate on SOS repair mechanism. Define thymine dimer. How are they formed and repaired? Describe the molecular basis of mutation. 11 Leu+ Met+ Arg+ Write a detailed note on spontaneous mutation. Explain about mutant detection methods. Define reverse mutation. Describe the mechanism underlying Intragenic and intergenic suppressor mutations Describe the transposition mechanisms. 13 Vo LTE UNIT IV Time (Min) Describe the process of generalised transformation occurring in bacterial chromosome and plasmid. Elaborate on molecular mechanism and significance of transformation 22 Describe the process of…arrow_forwardWhat is meant by the term chromatin remodeling? Describe the importance of this process to transcription.arrow_forwardImmortality of Stem cells is supported by the expression of telomerase that can extend the telomere sequence. However, one daughter cell created by division of stem cells will not be immortal due to lack of telomerase expression. What difference will you expect in regulation of the telomerase coding gene between the two daughter cells produced by cell division of stem cells? How might the cells be different in terms of chromatin structure at that loci?arrow_forward
- The diagram below depicts an active transcription bubble after a short period of RNA synthesis during the transcription process of a prokaryotic gene. Redraw the diagram and label parts (i) to (v) on the diagram. Motivate your answers. (i) the template and the non-template strands; (ii) the orientation (direction) of both DNA strands and that of the newly synthesised RNA strand; (iii) the location of a possible promotor sequence; (iv) the location of a possible Shine-Dalgarno sequence; (v) the specific area of activity of a RNA polymerase.arrow_forwardThe pre-mRNA transcript and protein made by several mutant genes were examined. The results are given below. Determine where in the gene a likely mutation lies: the promoter region, exon, intron, cap on mRNA, or ribosome binding site. a. normal-length transcript, normal-length nonfunctional protein b. normal-length transcript, no protein made c. normal-length transcript, normal-length mRNA, short nonfunctional protein d. normal-length transcript, longer mRNA, shorter nonfunctional protein e. transcript never madearrow_forwardWhat could be a probable fate of the segment of the DNA strand encircled in red? Polypeptides can now be translated from the encircled region as the two antiparrallel strands separate. The encircled DNA region can now be used as a template for transcription. it will relax right away on its own so that helicase can separate the two complementary strands with much ease If the encircled region will not be relaxed by another enzyme, it will experience supercoiling and will most likely break.arrow_forward
- DNA polymerases are capable of editing and error correction, meaning it is able to edit and correct single base error so that the gene is not affected. However, RNA polymerase has a limited capacity for error correction. Given that a single base error in either replication or transcription can lead to error in protein synthesis, suggest a brief explanation for this difference in the capability of error correction between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase.arrow_forwardYou made four mutants for a promoter sequence in DNA and studied them for transcription. The results of the amount of gene expression or transcription (based on beta-Gal activity shown on Y-axis) for these DNAs (X-axis) are shown. The sequence of the wild-type and mutant DNAs, and consensus sequence from many promoters are shown here for your convenience. From this experiment you can conclude that: Nucleotide substitution can identify important bases of the binding sites or promoter in DNA (e.g., -10 and -35 promoter sequences of lac operon). True or false: Spacer (a) -10 region -35 region TTGACA Consensus sequence TATAAT Wild-type Lac promoter GGCTTTACACTTTATGCTTCCGGCTCGTATGTTGTGTGGAATT Mutant 1 GGCTTTACACTTTATG-TTCCGGCTCGTATGTTGTGTGGAATT Mutant 2 GGCTTTACACTTTATGCTTCCGGCTCGTATAATGTGTGGAATT Mutant 3 GGCTTTACACTTTATG-TTCCGGCTCGTATAATGTGTGGAATT Mutant 4 GGCTTGACACTTTATG-TTCCGGCTCGTATAATGTGTGGAATT (b) 700 600- 500- 400- 300- 200- 100. 0 ● True O False B-Galactosidase activity Wild-type…arrow_forwardYou isolate a mouse Tau-gene-containing DNA fragment from the chicken and hybridize it to the freshly-made and isolated hnRNA (primary transcript) from the nucleus of the mouse cells transcribed from the Tau gene (immediately after it was produced), allowing no time for processing of the hnRNA. Describe what you see when you look at the DNA/RNA hybrid molecule under the electron microscope.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
