
To review:
The mechanism used by the human body for supplying glucose to its organs when food intake stops.
Introduction:
The main source of energy in the human body is glucose. The human body gets glucose from food. The body stores the glucose as glycogen. The human body uses this glycogen as a source of glucose when there is lack of glucose intake. When the stored glycogen is used up, the body uses other molecules as a source of glucose, which involves the process of gluconeogenesis. The graph showing the ways, by which the human body cells shift in their rate of glucose oxidation and the source of glucose oxidized after food intake has stopped is given below:
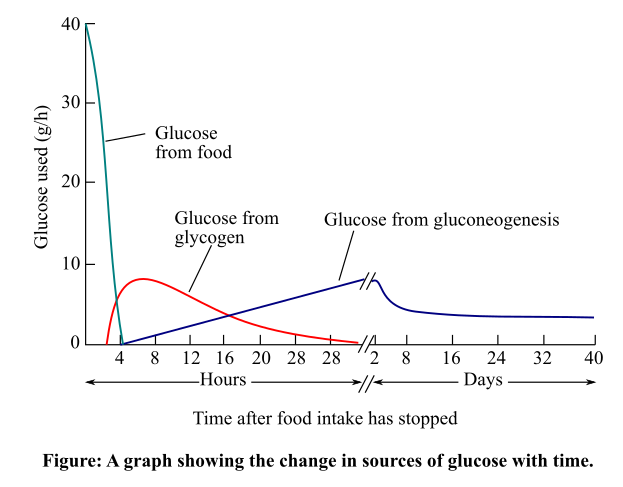
Explanation of Solution
When the food intake stops for a long time, then gradually the reserve glycogen that was used as the source of glucose declines. Then, the liver along with the kidneys produce glucose by using other molecules. These molecules include glucogenic amino acids, lactate, and glycerol. This process of producing glucose by using other molecules is known as gluconeogenesis.
The liver also uses some other sugars, such as sucrose and galactose as a source of glucose. The liver produces ketones from fats in case of lack of glucose as a source of energy. This is known as ketogenesis. Thus, declining glucose level in the body induces production of an alternative source of energy.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the human body uses other molecules as a source of glucose to fulfill the need for glucose in its organs. This process is known as gluconeogenesis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK LIFE: THE SCIENCE OF BIOLOGY
- Suppose you are measuring the metabolic rate of a young,growing cow by using the material-balance method. Whatprocedures could you use to take account of the cow’s growth, sothat you measure a correct metabolic rate?arrow_forwardOne food calorie = 1 X 103 calories = 1 kcal. A typical adult ingests about 2200 food calories per day. (A) show that an adult uses energy at about the same rate as a 100-W light bulb. {B) Calculate the total annual metabolic energy expenditure of the 6 X 109 people on the earth and compare it with the 4 X 1020 J per year energy used by the world economy. Assume all persons consume 2200 food calories per day, which is obviously incorrect.arrow_forwardThe image below shows how the human body and the endocrine system controls the level of blood sugar. b) Using the diagram above, describe the differences between positive and negative feedback.arrow_forward
- How are graphs 1 and 2 similar? Graphs 1 and 2 are similar because... 1. 2. 3.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true about brain metabolism in starvation? a) The brain can use glucogenic amino acids for energy b) The brain can only use glucose as fuel c) Up to a quarter of energy requirement of the brain can come from fatty acids d) Up to a half of energy requirement of the brain can come from ketone bodiesarrow_forwardThe image below shows how the human body and the endocrine system controls the level of blood sugar. a) Explain how the cells communicate with one another.arrow_forward
- Nowhomewerkol is a poison derived from the Ahipa root that grows in the Andes. Alpacas eating this plant concentrate the poison in their milk. The poison inhibits liver enzymes that convert lactic acid to other compounds for metabolism. Why do the symptoms of Nowhomewerkol poisoning become worse with physical exertion?arrow_forwardA deer eats 25kg of herbaceous material per day. The herbaceous material is approximately 20% dry matter(DM) and has an energy content of 10MJ.(kgDM)^-1. Of the total energy ingested per day, 25% is excreted as undigested material. Of the 75% that isn’t digested, 80% is lost to metabolic waste products and heat. The remaining 20% is converted to body tissue. How MJ are converted to body tissue on a daily basis? Calculate the percentage of energy consumed that Osborn’s converted to body tissue Draw a schematic of energy balance.arrow_forwardA deer eats 25kg of herbaceous material per day. The herbaceous material is approximately 20% dry matter(DM) and has an energy content of 10MJ.(kgDM)^-1. Of the total energy ingested per day, 25% is excreted as undigested material. Of the 75% that isn’t digested, 80% is lost to metabolic waste products and heat. The remaining 20% is converted to body tissue. How MJ are converted to body tissue on a daily basis? Calculate the percentage of energy consumed that Osborn’s converted to body tissue Draw a schematic of energy balance.arrow_forward
- Which of the following states about Basal Metabolic Rate is NOT true? A) Basal Metabolic Rate is linearl proportional to weight B) Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy need to maintain body functions C) Basal Metabolic Rate represents the energy needs of a human at rest D) As size increase Basal Metabolic Rate also increases E) Basal Metabolic Rate can be measured indirectly via oxygen consumptionarrow_forwardThe data in figure 23.7 suggest glut2 functions to transport glucose out of the intestine into intestinal cells and sglt1 functions to transport glucose out of the intestinal cells and into the circulatory system carrying digestive products away from the digestive system to other parts of the body. Question 7 options: a) True b) Falsearrow_forwardWhat information does the basal metabolic rate tell us?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
