
Concept explainers
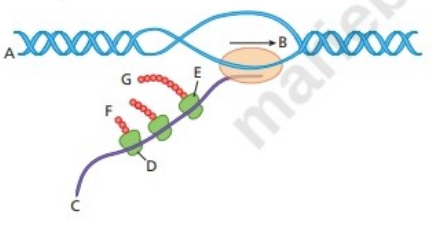
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Is the
Which end of the
What structure is closest to
What is the name of the molecule closest to
Which end of the molecule is closest to
What structure is closest to
What structure is closest to
What name is given to the object looking like a string of beads that is closest to
Indicate where
Which end of the polypeptide is closest to
What process(es) are illustrated in the diagram?
Does the diagram depict molecular activity in a bacterium of a eukaryote? Explain the reasoning for your answer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- All ingredients required for the synthesis of DNA were placed in a test tube. The primer has the sequence 5’-TCGATCA-3’. First determine where the primer will bind to the DNA template given below (Do this by writing the sequence of the primer on top of the template – make sure you find a location that is complementary in sequence and that the primer is antiparallel with respect to the template) and then indicate the nucleotides that DNA polymerase would attach onto the primer as it synthesizes DNA (hint: in which direction does DNA polymerase attach nucleotides onto a primer?) See figure 13.16 in book. 5’-GACGTAGTCTGATGCTAGCATGCTGATCGAAAGAG-3’arrow_forwardUsing the figure below, what is molecule "A" (type a 1, 2 or 3 in the blank) nuclease ligase DNA polymerase What is the function of molecule "A"? to separate the double helix into two to piece together the Okazaki segments to copy the new DNA strand to the old strand by complementary base pairing Using the figure below, what is molecule "G" (type a 1, 2 or 3 in the blank) nuclease ligase DNA polymerase What is the function of molecule "G"? to separate the double helix into two to piecearrow_forwardUsing the figure below, what is molecule "A" (type a 1, 2 or 3 in the blank) nuclease ligase DNA polymerase What is the function of molecule "A"? to separate the double helix into two to piece together the Okazaki segments to copy the new DNA strand to the old strand by complementary base pairing Using the figure below, what is molecule "G" (type a 1, 2 or 3 in the blank) nuclease ligase DNA polymerase What is the function of molecule "G"? to separate the double helix into two to piece together the Okazaki segments to copy the new DNA strand to the old strand by complementary base pairing Which of the following statements best describes why one of the daughter strands is synthesized in pieces? the enzymes that synthesize DNA are slower that the enzymes that unwind the double helix and this produces 'lagging time' the enzymes that synthesize DNA can only do so in a 5' --->3' direction this figure illustrates a eukaryotic cell since prokaryotic cells do not synthesize DNA…arrow_forward
- Shown below is a portion of a wild-type DNA sequence that encodes the last amino acids of a protein that is 270 amino acids long. The first three bolded base pairs indicate the frame and include the coding region. 5^ ...GCTAAGTATTGCTCAAGATTAGGATGATAAATAACTGG 3^ 3^.. CGATTCATAACGAGTTCTAATCCTACTATTTATTGACC 5^ Which strand is the template strand for transcription of this gene? Briefly explain how you know. An insertion of one base pair causes the protein to decrease in length by seven amino acids. With respect to the sequence given above, where does this insertion occur? A change of one base pair leads to the protein increasing in the length by one amino acid. With respect to the sequence given above, which base pair would you change, and what would you change this base pair for the protein to increase in the length by one amino acid?arrow_forwardThe sequence of the DNA template strand is 3’–ATGGCAATAC–5’: What is the sequence of the DNA informational strand? What are the amino acids present in this sequence?arrow_forwardThe following is diagram of a generalized tetranucleotide. Carbons exist at corners on the shapes and phosphate groups are filled circles. A. Is this a DNA or an RNA Molecule? B. Where is the 3’ end of this tetranucleotide? C. Given that the DNA strand which served as a template for the synthesis of this tetranucleotide was composed of the bases 5’-ACAG-3’, where are the expected bases?arrow_forward
- A lagging strand is sketched below. The Okazaki fragment DNA is red, and the RNA primers aredashed orange lines. Which Okazaki fragment was made first? When ligase joins fragments Aand B, will it act at arrow 1, arrow 2, or both?arrow_forwardLook at the double-stranded segment of DNA shown below. Imagine that the two strands have already been denatured, and the temperature has been decreased to an appropriate annealing temperature. Show where the two primers would anneal to the strands, then indicate the direction of extension on each new strand with an arrow. 5’--T C A G G A C G T A A G C T T G C A T A T C T C G A T G C T A A A T C A T—3’ 3’--A G T C C T G C A T T C G A A C G T A T A G A G C T A C G A T T T A G T A—5’ Primer #1: 3’ A C G A T T T 5’ Primer #2: 5’ G G A C G T A 3’arrow_forwardBelow is a sample of a segment of DNA…(copy from left to right) 3’ TACAATGGGCGACGCGCTTCGTTTCAGATT 5’ 5’ ATGTTACCCGCTGCGCGAAGCAAAGTCTAA 3’ 1.Assume the 6th amino acid is changed from T to G on the DNA template strand. What type of mutation is this? What effect would this have on the protein? Look up an example for this type of mutation. 2, Assume the 5th and 6th amino acids are removed from the DNA template strand. What type of mutation is this? How would this affect the protein? Look up an example of this type of mutation. 3.Which mutation changes the protein more...a point mutation or a frameshift mutation. Explain your reasoning. 4.What would be the problem if ATT was inserted into the DNA template strand after the second codon? (Be sure to consult the coding chart for amino acids). 5. What if the second amino acid was repeated over 5Ox. What amino acid is repeated? What type of mutation is this? If this is on chromosome 4, what genetic disorder is this?…arrow_forward
- Examine the following DNA sequence (only one strand is shown). The shown strand will be referred to as Strand 1. The complementary strand will be referred to as Strand 2: 5’ TTTAAGCCGTACCGATATAATGTAAGGCGAGCTTGACCGTCTTGGGCATCATA 3’ There is an eleven (11) base pair sequence that serves as a replication origin. Write below the most likely 11 nucleotides on this strand that serve as the replication origin. Think carefully about base pairing.arrow_forwardDescribe the d=features of the following DNA-binding domains and how they interact with DNA. Helix-turn-Helix Zinc Finger Leucine Zipper Helix-loop-Helixarrow_forwardWrite out the DNA sequence using the following instructions: This is a double stranded DNA hydrogen bonding with each other following the principle of complementary base-pairing Each strand contains ten nucleotides Each strand contains all four different types of nucleotides You should indicate clearly the directionality of each strand in your answer You do not need to draw the full nucleotide structure. Use the one-letter code (A, T, G, C, or U) to represent each nucleotidearrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
