
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for all the possible monochlorinated products obtained from halogenation of ethane has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Alkanes are not completely inert. Two important reactions that alkanes undergo are combustion and halogenation.
Combustion reaction is the one where reaction occurs between substance and oxygen which proceeds with evolution of light and heat. Due to the heat produced when alkanes are made to undergo combustion with oxygen, it is used as fuel.
Halogenation is a
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
Cycloalkanes are also similar to those of alkanes. Cycloalkanes also undergo combustion and halogenation reaction.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1.133EP
The monochlorinated product of ethane is,
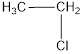
Explanation of Solution
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
General reaction for halogenation of alkane can be given as shown below,
The halogenation reaction takes place giving a mixture of products where the hydrogen atoms present in the alkane are substituted randomly.
Given alkane is ethane. This has a total of two carbon atoms which are of same nature. Only one kind of hydrogen is present in ethane. Therefore, chlorinaton of ethane will lead to the same monochlorinated product as shown below,

The structural formula for monochlorinated product of ethane was drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for all the possible monochlorinated products obtained from halogenation of butane has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Alkanes are linear chain saturated hydrocarbons. The reactivity of alkanes are very less. They can be heated for a very long time in strong acids and bases without any reaction. Even strong reducing and strong oxidizing agents have less effect on alkanes.
Alkanes are not completely inert. Two important reactions that alkanes undergo are combustion and halogenation.
Combustion reaction is the one where reaction occurs between substance and oxygen which proceeds with evolution of light and heat. Due to the heat produced when alkanes are made to undergo combustion with oxygen, it is used as fuel.
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
Cycloalkanes are also similar to those of alkanes. Cycloalkanes also undergo combustion and halogenation reaction.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1.133EP
The monochlorinated products of butane are,

Explanation of Solution
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
General reaction for halogenation of alkane can be given as shown below,
The halogenation reaction takes place giving a mixture of products where the hydrogen atoms present in the alkane are substituted randomly.
Given alkane is butane. Two kinds of hydrogen are present in butane. Therefore, chlorination of butane will lead to two monochlorinated products as shown below,
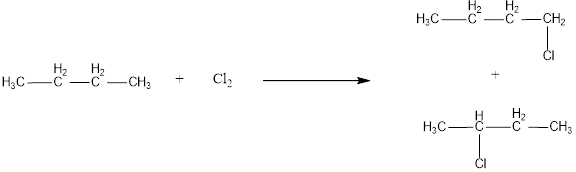
The structural formula for monochlorinated products of butane was drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for all the possible monochlorinated products obtained from halogenation of 2-methylpropane has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Alkanes are linear chain saturated hydrocarbons. The reactivity of alkanes are very less. They can be heated for a very long time in strong acids and bases without any reaction. Even strong reducing and strong oxidizing agents have less effect on alkanes.
Alkanes are not completely inert. Two important reactions that alkanes undergo are combustion and halogenation.
Combustion reaction is the one where reaction occurs between substance and oxygen which proceeds with evolution of light and heat. Due to the heat produced when alkanes are made to undergo combustion with oxygen, it is used as fuel.
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
Cycloalkanes are also similar to those of alkanes. Cycloalkanes also undergo combustion and halogenation reaction.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1.133EP
The monochlorinated products of 2-methylpropane are,
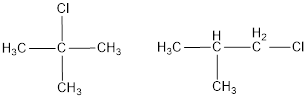
Explanation of Solution
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
General reaction for halogenation of alkane can be given as shown below,
The halogenation reaction takes place giving a mixture of products where the hydrogen atoms present in the alkane are substituted randomly.
Given alkane is 2-methylpropane. Two kinds of hydrogen are present in 2-methylpropane. Therefore, chlorination of 2-methylpropane will lead to two monochlorinated products as shown below,

The structural formula for monochlorinated products of 2-methylpropane was drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for all the possible monochlorinated products obtained from halogenation of cyclopentane has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Alkanes are linear chain saturated hydrocarbons. The reactivity of alkanes are very less. They can be heated for a very long time in strong acids and bases without any reaction. Even strong reducing and strong oxidizing agents have less effect on alkanes.
Alkanes are not completely inert. Two important reactions that alkanes undergo are combustion and halogenation.
Combustion reaction is the one where reaction occurs between substance and oxygen which proceeds with evolution of light and heat. Due to the heat produced when alkanes are made to undergo combustion with oxygen, it is used as fuel.
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
Cycloalkanes are also similar to those of alkanes. Cycloalkanes also undergo combustion and halogenation reaction.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1.133EP
The monochlorinated product of cyclopentane is,
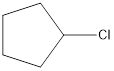
Explanation of Solution
Halogenation is a chemical reaction between a substance and halogen. The product of halogenation reaction is that one or more halogens are incorporated into molecules of the substance. Halogenation of hydrocarbon gives hydrocarbon derivatives as product where halogen atoms are substituted instead of hydrogen atoms.
Halogenation reaction of alkane is an example of substitution reaction. This is a reaction where a part of reacting molecule replaces an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
General reaction for halogenation of alkane can be given as shown below,
The halogenation reaction takes place giving a mixture of products where the hydrogen atoms present in the alkane are substituted randomly.
Given cycloalkane is cyclopentane. Only one kind of hydrogen is present in cyclopentane. Therefore, chlorinaton of cyclopentane will lead to the same monochlorinated product as shown below,

The structural formula for monochlorinated product of cyclopentane was drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Write structural formulas for all the possible halogenated hydrocarbon products from the monobromination of the following alkanes or cycloalkanes. a. Propane b. Pentane c. 2-Methylbutane d. Cyclohexanearrow_forwardWhat are the products of complete combustion of hydrocarbon? Write a balanced aquation for the complete combustion of cyclohexene.arrow_forward(a) What structural feature is associated with each type of hydrocarbon: alkane, cycloalkane, alkene, and alkyne?(b) Give the general formula for each type.(c) Which hydrocarbons are considered saturated?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





