
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
It should be determined that the product obtained from the reaction of Ethyl butanoate with
Concept introduction:
Reduction of carbonyl, carboxylic acid and ester using
Reduction of an ester (Methyl-2-pentenoate) by using
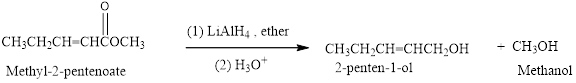
(b)
Interpretation:
It should be determined that the product obtained from the reaction of Methyl benzoate with
Concept introduction:
Reduction of carbonyl, carboxylic acid and ester using
Reduction of an ester (Methyl-2-pentenoate) by using
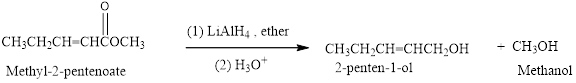
(c)
Interpretation:
It should be determined that the product obtained from the reaction of Pentatonic acid
with
Concept introduction:
Reduction of carbonyl, carboxylic acid and ester using
Reduction of a carboxylic acid (oleic acid) by using
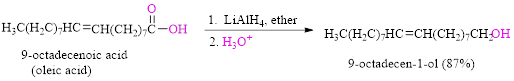
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- The compound obtained by treating propan-1-ol with PCC followed by excess of ethanol in presence of dry HCl(g) is: propanoic acid 1,1-Diethoxypropane 1-methoxypropan-1-ol Propylethanoatearrow_forwardThe oxidation of 3-methylbutanal with potassium permanganate in an acid medium produces compound A and the reduction of cyclohexanone with NaBH4 produces compound B. Indicate the CORRECT alternative: a) A reacts rapidly with water to produce a carboxylic acid. b) Reaction of B with methylamine produces an amide. c) Reaction of A with an acyl chloride produces an ester. d) B reacts with HCN to produce a cyanohydrin. e) The reaction of A and B in an acid medium produces cyclohexyl 3-methylbutanoate.arrow_forwardPropose a method to separate a mixture containing phenol, benzoic acid, naphthalene, and p-nitroaniline. Phenol is soluble in sodium hydroxide solution but insoluble in neutral water or sodium bicarbonate solution. Benzoic acid is soluble in either sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate solutions. Write out the structures of the molecules in your scheme.arrow_forward
- Why do you wash the dichloromethane solution of your reductive amination product with sodium bicarbonate, rather than dilute aqueous HCl? a) Sodium bicarbonate is a good method of removing aldehydes from organic solvent.b) The amine product will be protonated by acid and remain in the aqueous layer as a salt.c) Sodium bicarbonate transfers the amine starting material into the aqueous layer.d) Sodium bicarbonate reacts with leftover NaBH(OAc)3 and removes it from the mixture.arrow_forwardA compound of molecular formula C5H10O forms a yellow precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent and a yellow precipitate with reagents for the iodoform test. a) Draw the structural formulae b) Name the two (2) compounds that fit these tests.arrow_forwardWhat is the role of an acid catalyst in nucleophilic addition of aldehydes and ketone?arrow_forward
- Why is only one amide obtained from the reaction of acetyl chloride with an equivalent of ethylamineand an equivalent of triethylamine?arrow_forwardOn synthesis of esters via nucleophilic acyl substitution: How is excess alcohol eliminated from the crude product? Write the chemical equation involved in the reaction between the excess acid and NaHCO3. Given this, briefly explain why NaHCO3 is preferred over NaOH for the neutralization of excess acid.arrow_forwardGive the products expected when acetic formic anhydride reacts with (i) aniline and(ii) benzyl alcoholarrow_forward
- (a) How will you carry out the following conversions?(i) Acetylene to Acetic acid (ii) Toluene to m-nitrobenzoic acid(iii) Ethanol to Acetone(b) Give reasons :(i) Chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid.(ii) pH of reaction should be carefully controlled while preparing ammonia derivatives of carbonyl compounds.arrow_forward1. If 2 g of aniline is allowed to react with 2.5 ml acetic anhydride( density is 1.08g/ml), a)Which one is limiting reagent and which one is excess reagent? b) what will be the theoretical yield of the reaction? c) If 2 g of acetanilide is produced, what will be the percentage yield of the reaction?arrow_forwardWhat products are obtained from the reaction of the following compounds with LiAlH4 followed by treatment with dilute acid? a. ethyl butanoate c. methyl benzoate b. benzoic acid d. pentanoic acidarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
