
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is
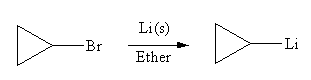
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
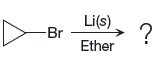
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Br bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. An alkyllithium reagent (RLi) can be synthesized from an alkyl bromide by treating it with solid lithium in ether. Therefore, the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:
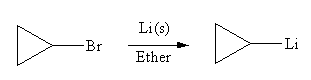
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
(b)
Interpretation:
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the alkyl halide reactant, the C atom bonded to the halogen atom bears a partial positive charge and is relatively electron poor. By contrast, that C atom has to become electron rich in the organometallic compound produced. An alkyl bromide can be converted to a Grignard reagent (RMgBr) simply by treating it with solid magnesium in an ether solvent such as tetrahydrofuran (THF).
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is shown below:
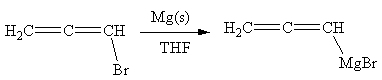
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
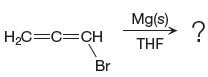
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Br bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. An alkyl bromide can be converted to a Grignard reagent (RMgBr) simply by treating it with solid magnesium in an ether solvent such as tetrahydrofuran (THF). So the C-Br bond will become C-Mg bond. Therefore, the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:

The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
(c)
Interpretation:
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the alkyl halide reactant, the C atom bonded to the halogen atom bears a partial positive charge and is relatively electron poor. By contrast, that C atom has to become electron rich in the organometallic compound produced. An alkyl bromide can be converted to a Grignard reagent (RMgBr) simply by treating it with solid magnesium in an ether solvent such as tetrahydrofuran (THF).
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is shown below:
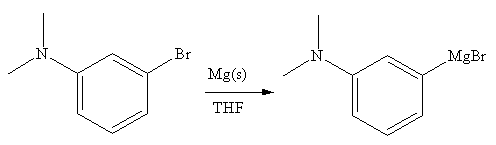
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
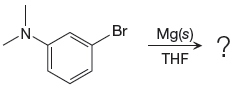
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Br bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. An alkyl bromide can be converted to a Grignard reagent (RMgBr) simply by treating it with solid magnesium in an ether solvent such as tetrahydrofuran (THF). So the C-Br bond will become C-Mg bond. Therefore, the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:

The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
(d)
Interpretation:
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the alkyl halide reactant, the C atom bonded to the halogen atom bears a partial positive charge and is relatively electron poor. By contrast, that C atom has to become electron rich in the organometallic compound produced. An alkyl bromide can be converted to a Grignard reagent (RMgX) simply by treating it with solid magnesium in an ether solvent.
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is shown below:
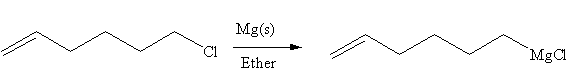
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
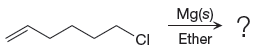
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Cl bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. An alkyl chloride can be converted to a Grignard reagent (RMgBr) simply by treating it with solid magnesium in an ether. So the C-Cl bond will become C-Mg bond. Therefore, the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:
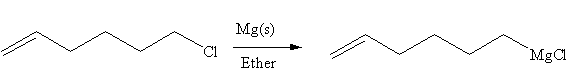
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
(e)
Interpretation:
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the alkyl halide reactant, the C atom bonded to the halogen atom bears a partial positive charge and is relatively electron poor. By contrast, that C atom has to become electron rich in the organometallic compound produced. A lithium dialkylcuprate is synthesized from the corresponding alkyllithium reagent by treating it with copper(I) iodide, CuI.
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
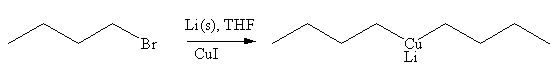
The given reaction is
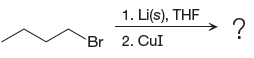
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Br bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. Lithium dialkylcuprate is synthesized from the corresponding alkyllithium reagent by treating it with copper(I) iodide, CuI. So the C-Br bond will become C-CuLi bond. Therefore, the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:

The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
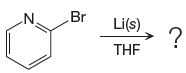
(f)
Interpretation:
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the alkyl halide reactant, the C atom bonded to the halogen atom bears a partial positive charge and is relatively electron poor. By contrast, that C atom has to become electron rich in the organometallic compound produced. An alkyllithium reagent (RLi) can be synthesized from an alkyl bromide by treating it with solid lithium in ether solvent such as THF.
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is shown below:
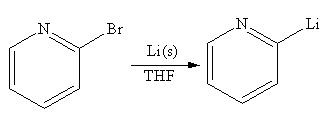
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Br bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. An alkyllithium reagent (RLi) can be synthesized from an alkyl bromide by treating it with solid lithium in ether solvent such as THF. So the C-Br bond will become C-Li bond. Therefore the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:

The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
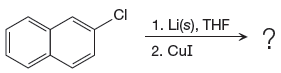
(g)
Interpretation:
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
To form a bond between two carbons of like charge, a separate reaction that first reverses the charge (or polarity) at one of the carbons is carried out. Thus, one carbon atom would become electron rich while the other would remain electron poor. This general idea of reversing a charge at a particular atom is called umpolung. In the alkyl halide reactant, the C atom bonded to the halogen atom bears a partial positive charge and is relatively electron poor. By contrast, that C atom has to become electron rich in the organometallic compound produced. A lithium dialkylcuprate is synthesized from the corresponding alkyllithium reagent by treating it with copper(I) iodide, CuI.
Answer to Problem 19.41P
The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is shown below:
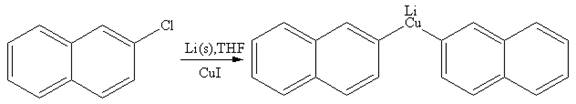
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
In the above reaction, the C atom of the C-Cl bond is electron-poor. When the C-Br bond is bonded to the metal, the carbon will become electron-rich. A lithium dialkylcuprate is synthesized from the corresponding alkyllithium reagent by treating it with copper(I) iodide, CuI. Therefore, the organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is as shown below:

The organometallic compound that would be produced by the given reaction is drawn by converting the electron-poor carbon of C-Br bond to an electron-rich carbon.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Draw the product of the attached reaction sequence, includingstereochemistry.arrow_forwardWhich reaction intermediate (A or B) is more likely to form in the epoxide ring opening reaction? Reactions prefer to react through lower energy intermediates. How might you justify one structure being lower in energy than the other? Draw structures as part of your explanation why.arrow_forwardWhen a single compound contains both a nucleophile and a leaving group, an intramolecular reaction may occur. With this in mind, draw the product of the following reactionarrow_forward
- Solution please. Should correct Draw out the complete mechanism of the Aldol condensation reaction given reaction below . Include all relevant electrons and arrows showing electron movement.arrow_forwarddetermine and draw the intermediate X; this is not an SN2 reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the enolate intermediate that cannot be formed in the aldol reaction with the starting compounds?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
