
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
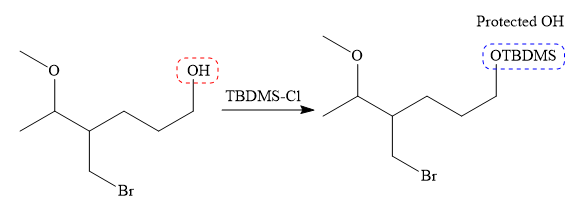
The protection of the alcoholic OH group is done by the treatment with silyl chloride (either
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
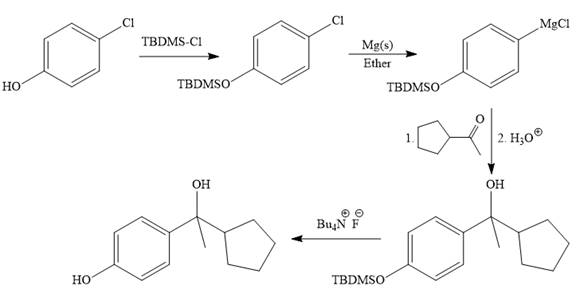
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
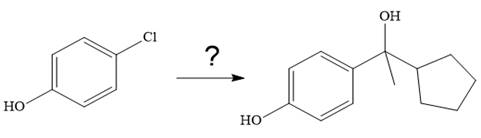
It is noticed that from the given starting material, a tertiary alcohol is synthesized. So the required step-up reaction carried out by using a Grignard reagent and corresponding ketone. This synthesis is given below:
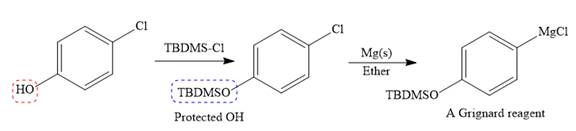
The given starting material is converted to corresponding Grignard reagent by the treatment with solid Mg metal in the ether as a solvent. But to avoid unwanted reactions of OH group with Mg metal this OH group protected first.
Then the Grignard reaction is carried out with the corresponding ketone to form the required tertiary alcohol.
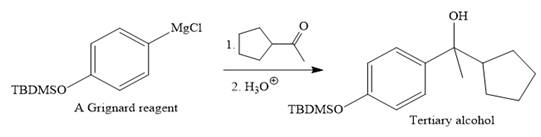
Finally, the deprotection of the OH group is done to produce the final required compound.
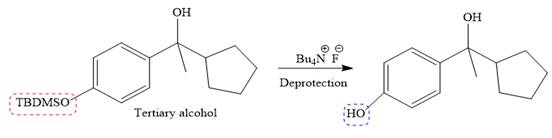
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The protection of the alcoholic OH group is done by the treatment with silyl chloride (either
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
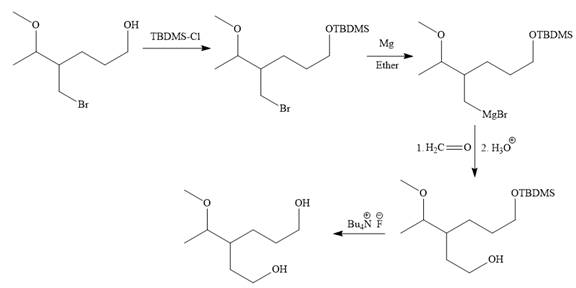
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
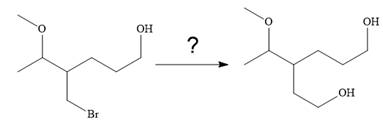
It is noticed that only the bromine atom of the starting material is replaced by the
Then the Br atom of the starting material subjected to Mg metal to form corresponding Grignard reagent.
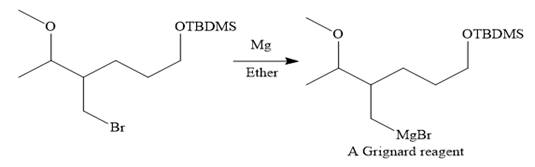
Above Grignard reagent is then treated with formaldehyde to carry out required step-up reaction via Grignard reaction. The acid workup step is needed for the Grignard reaction.
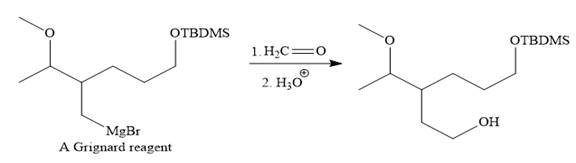
Finally, the deprotection of the protected OH group in the first step is carried out to form the final product.
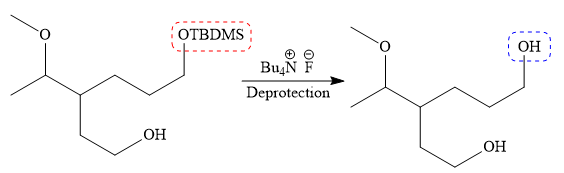
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide on treatment with solid magnesium metal corresponding Grignard reagent is formed. Grignard reagent on treatment with an aldehyde corresponding secondary alcohol is formed as the product during the workup step while ketone produces tertiary alcohol. The specialty of the Grignard reagent is when it treated with carbon dioxide (
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
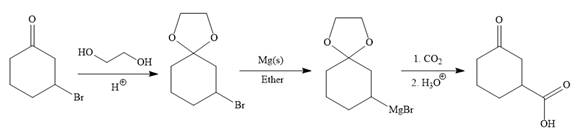
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
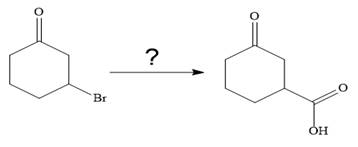
It is noticed that only a bromine atom of the starting material is replaced by a carboxylic acid group in the product. It is remembered that Grignard reagent when treated with carbon dioxide (
To carry out the required Grignard reaction the carbonyl group of the starting material is protected first to avoid an unwanted reaction.
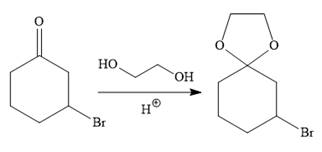
For the protection of ketone, it is treated with ethylene glycol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The protected form of the ketone is called ketal (a cyclic acetal).
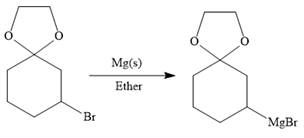
Above protected ketal then treated with Mg metal in the ether as a solvent to form the corresponding Grignard reagent.
The above Grignard reagent then treated with carbon dioxide to form the required product. Since acid workup step required in the Grignard reaction, the protected carbonyl group of the ketone is deprotected, too.
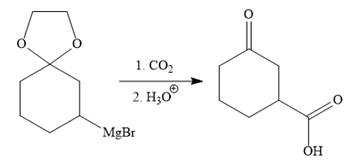
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The catalytic hydrogenation of the
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
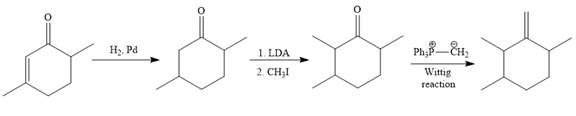
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is

To carry out the given synthesis following steps are carried out:
In the first step, the catalytic hydrogenation of the alkene group of the starting material is done as below:
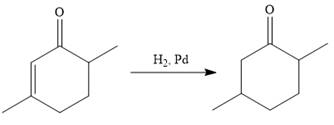
To reduce the only
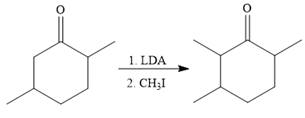
Finally, a Wittig reaction is carried out to produce the required product.
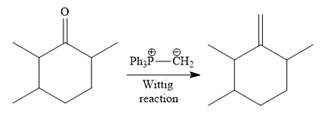
In the above Wittig reaction, the oxygen atom of the ketone is replaced by
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
(e)
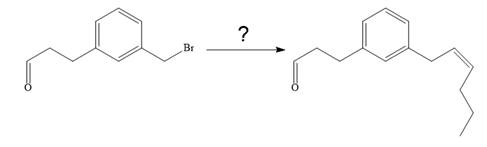
Interpretation:
It is to be shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The protection of the carbonyl group of the ketone and aldehyde is carried out by the treatment with ethylene glycol in the presence of acid as the catalyst. The protected form of the carbonyl group is called acetal. For deprotection, simply acidic conditions are required. Catalytic hydrogenation of an
Answer to Problem 19.79P
The given synthesis is carried out as:
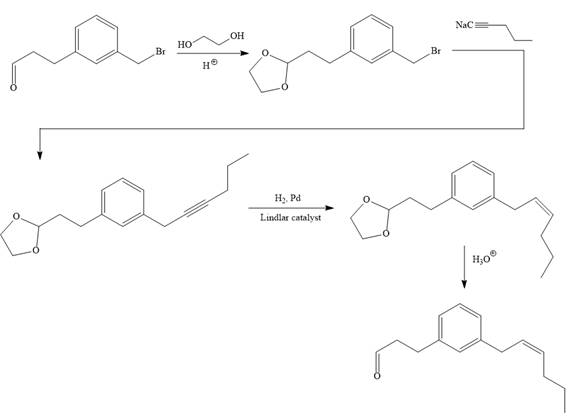
Explanation of Solution
The given synthesis is
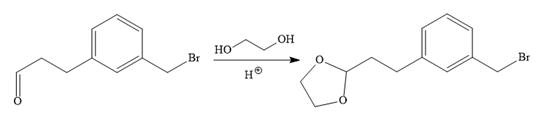
To carry out the given synthesis following steps are carried out:
In the first step, the protection of the carbonyl group of the given starting material is done by the treatment with ethylene glycol in the presence of an acid (e.g.
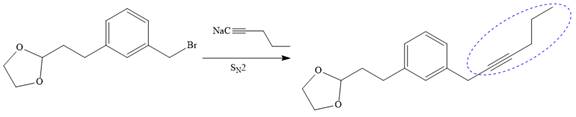
Now the required nucleophilic addition is done to insert required moiety in the product.
The triple bond of an above alkyne then subjected to catalytic hydrogenation with Lindlar catalyst to form the required cis alkene. Finally, a deprotection step carried out to produce the required product.
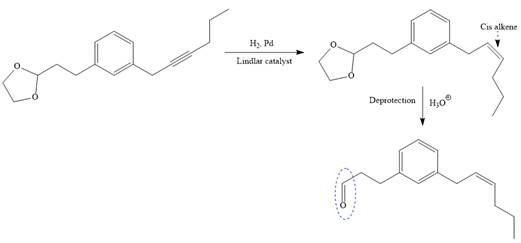
It is shown how to carry out the given synthesis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





