
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
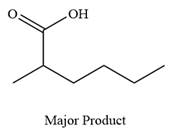
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
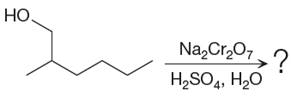
This is an example of an oxidation of a primary alcohol using sodium dichromate in aqueous acid. Chromic acid oxidizes a primary alcohol into corresponding carboxylic acid. The reaction is shown below:
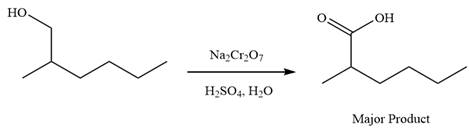
Thus, carboxylic acid is the major product of the reaction.
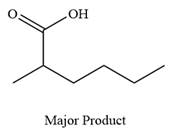
Chromic acid oxidizes a primary alcohol into corresponding carboxylic acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. Chromic acid is prepared by dissolving sodium dichromate in an acidic solution.
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
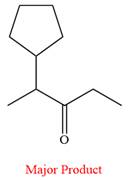
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
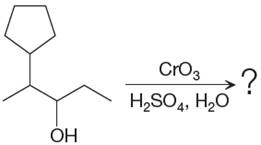
This is an example of an oxidation of a secondary alcohol using chromium trioxide in aqueous acid. Chromic acid oxidizes a secondary alcohol into corresponding ketone. The reaction is shown below:
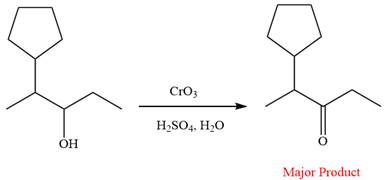
Thus, ketone is the major product of the reaction.
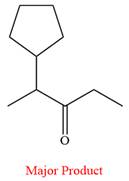
Chromic acid oxidizes a secondary alcohol into corresponding ketone.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. Chromic acid is prepared by dissolving sodium dichromate in an acidic solution. Oxidation of chromic acid requires an
Answer to Problem 19.56P
There is no product of the given reaction, as chromic acid cannot oxidize tertiary alcohols.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
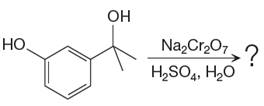
This is an example of an oxidation of a secondary alcohol using chromium trioxide in aqueous acid. Chromic acid oxidizes a secondary alcohol into corresponding ketone. Oxidation of chromic acid requires an
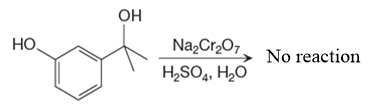
There is no product of the given reaction, as chromic acid cannot oxidize tertiary alcohols.
Chromic acid cannot oxidize tertiary alcohols as in tertiary alcohols carbon atom which is attached to the hydroxyl group does not have any hydrogen atom attached.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
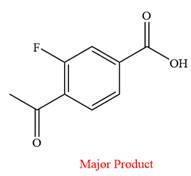
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
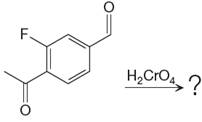
This is an example of an oxidation reaction using chromic acid. The reactant molecule has both an aldehyde and a ketone group. Chromic acid oxidizes an aldehyde group into carboxylic acid but is not a sufficiently strong oxidizing agent to oxidize ketones.
The reaction is shown below:
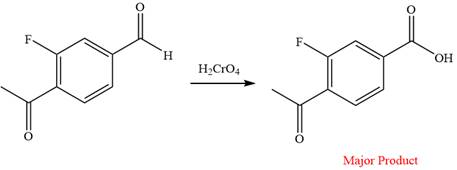
Thus, a carboxylic acid is the major product of the reaction.
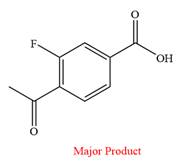
Chromic acid oxidizes an aldehyde to corresponding carboxylic acid but cannot oxidize a ketone.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Like chromic acid, potassium permanganate is also used as an oxidizing agent. When treated with a basic solution of potassium permanganate (
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
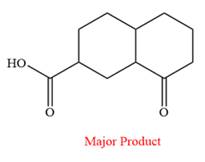
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
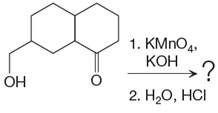
This is an example of an oxidation reaction using potassium permanganate. Like chromic acid, potassium permanganate is also used as an oxidizing agent. When treated with a basic solution of potassium permanganate (
The reaction is shown below:
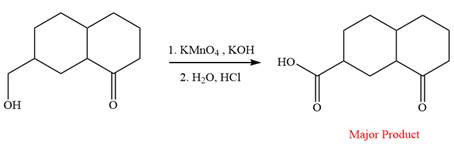
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is

When treated with a basic solution of potassium permanganate (
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a partial oxidizing agent. Oxidation of a primary alcohol by pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) stops at the aldehyde because the reaction takes place in a nonaqueous medium. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidizes a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
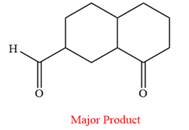
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
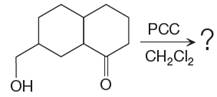
This is an example of an oxidation reaction using pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC). Like othe oxidizing agents, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidizes a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
The reaction is shown below:
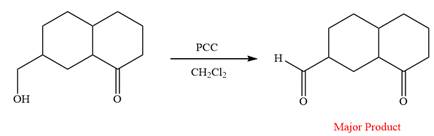
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is
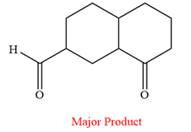
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidizes a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





