
(a)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-3-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
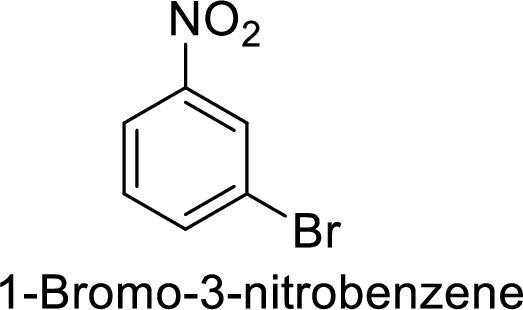
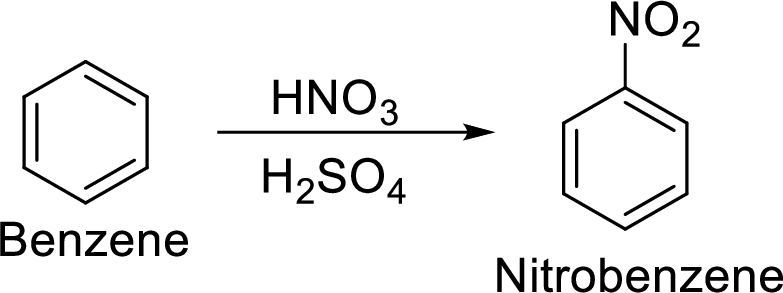
Step 1: Nitration of benzene ring by the reaction of benzene with nitrating mixture.
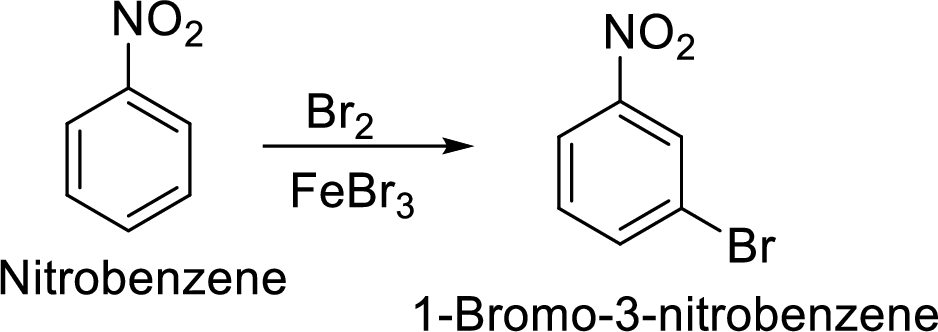
Step 2: Halogenation of nitrobenzene by the reaction of nitrobenzene with bromine in the presence of Lewis acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-4-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
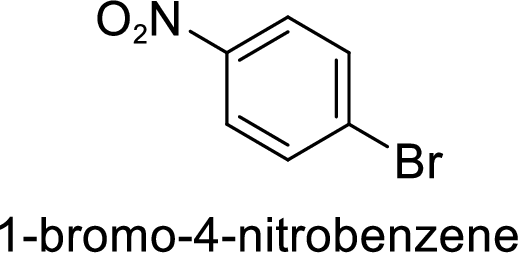
Step 1: Halogenation of benzene by the reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of Lewis acid.
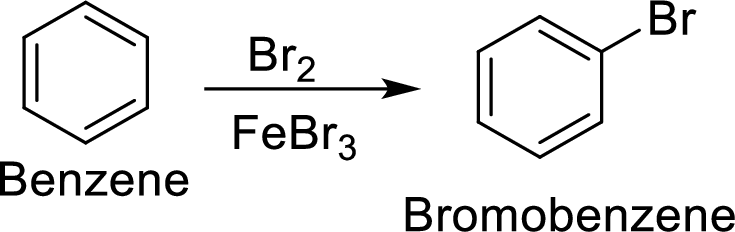
Step 2: Nitration of bromobenzene by the reaction of bromobenzene with nitrating mixture.
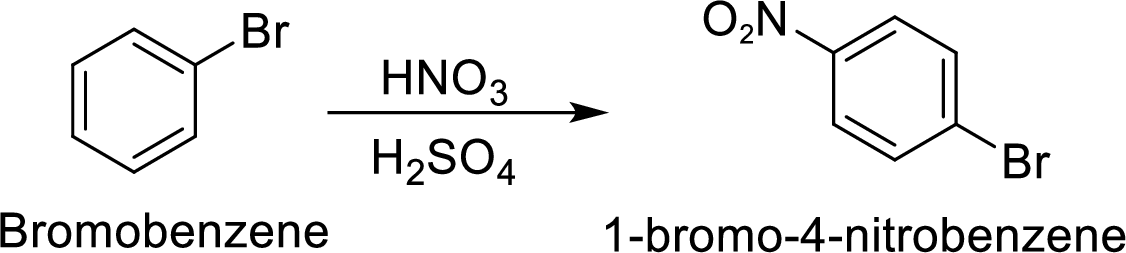
(c)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 2,4-6-trinitrotoluene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
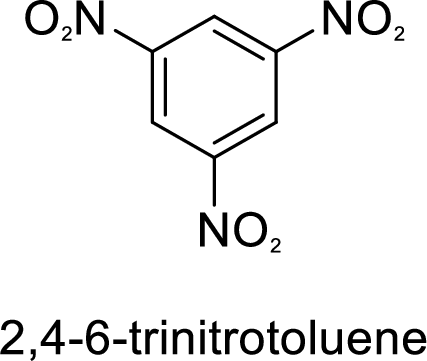
Methyl group in toluene is an activating and ortho-para directing group, so three times nitration of toluene gives the target compound.
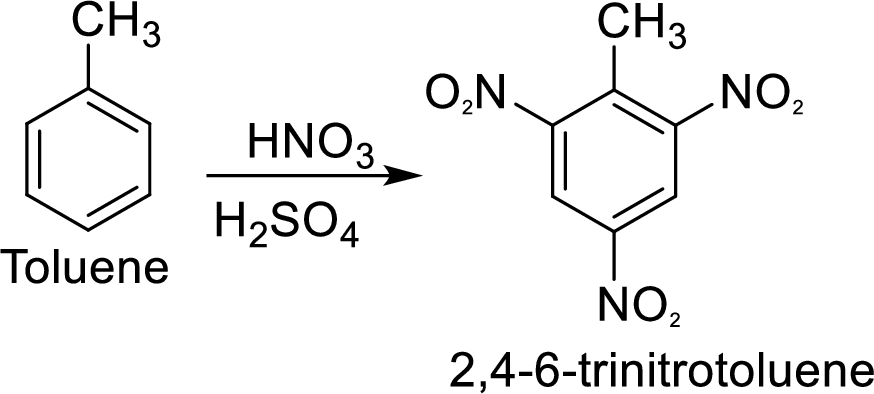
(d)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the m-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
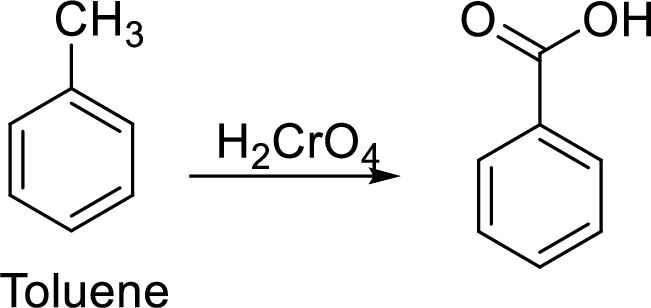
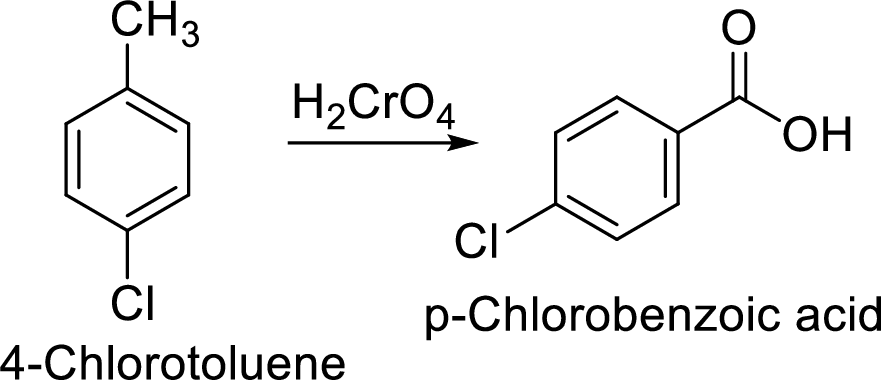
Step 1: Oxidation of toluene with chromic acid gives the benzoic acid.
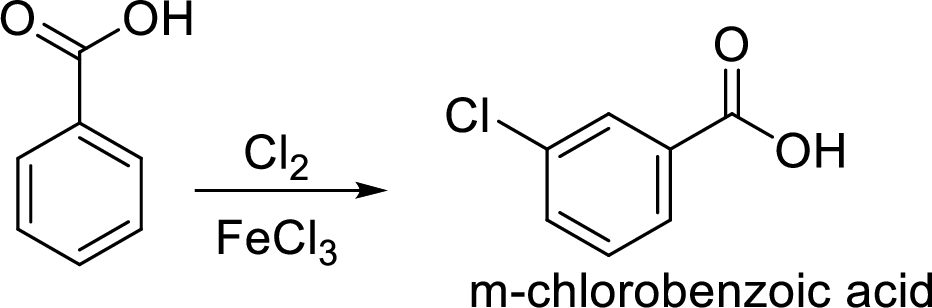
Step 2: Carboxyl group is a deactivating and meta directing group so the chlorination takes place at the meta position.
(e)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the p-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
Step 1: Halogenation of toluene by the reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
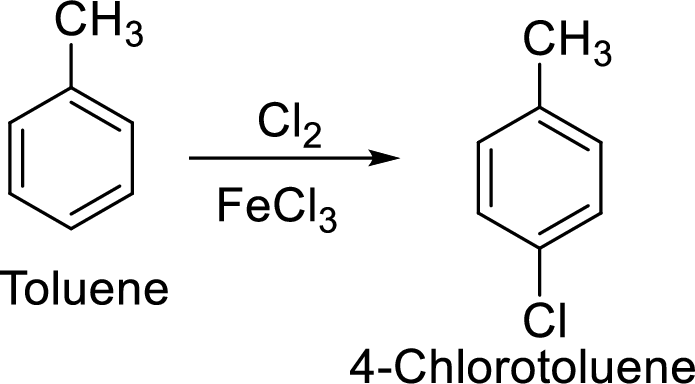
Step 2: Oxidation of 4-chlorotoluene by chromic acid gives the target compound.
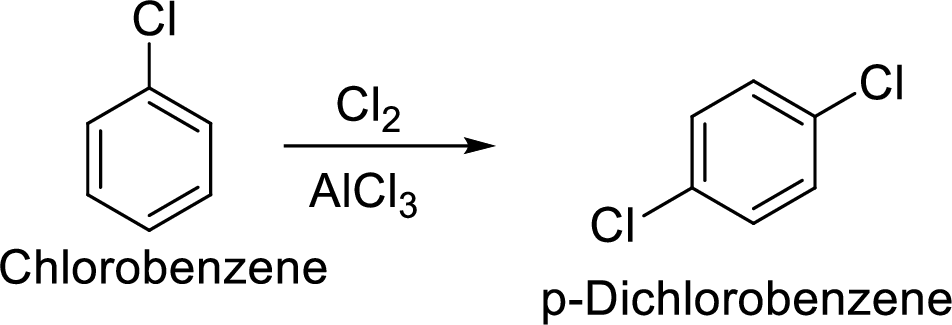
(f)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the p-dichlorobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
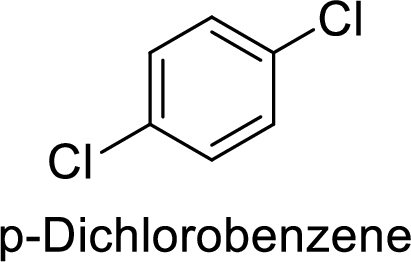
Step 1: Halogenation of benzene by the reaction of benzene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
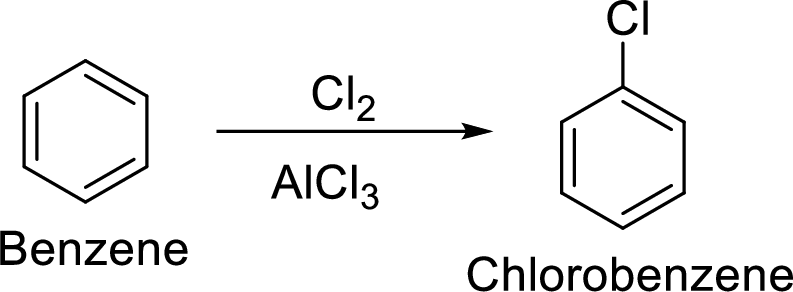
Step 2: Second halogenation of chlorobenzene by the reaction of chlorobenzene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
(g)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-4-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
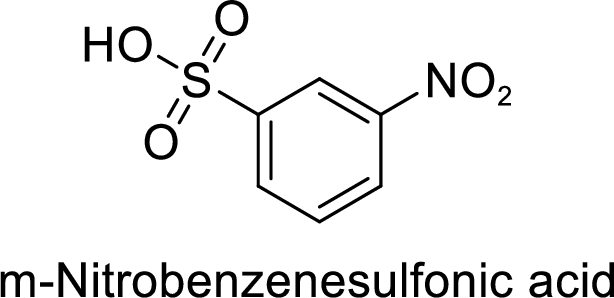
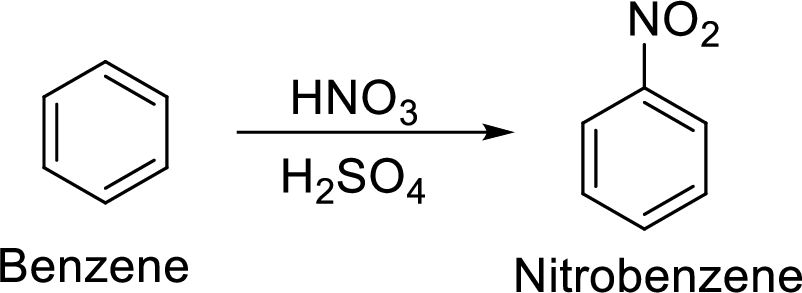
Step 1: Nitration of benzene by the reaction of benzene with nitrating mixture.
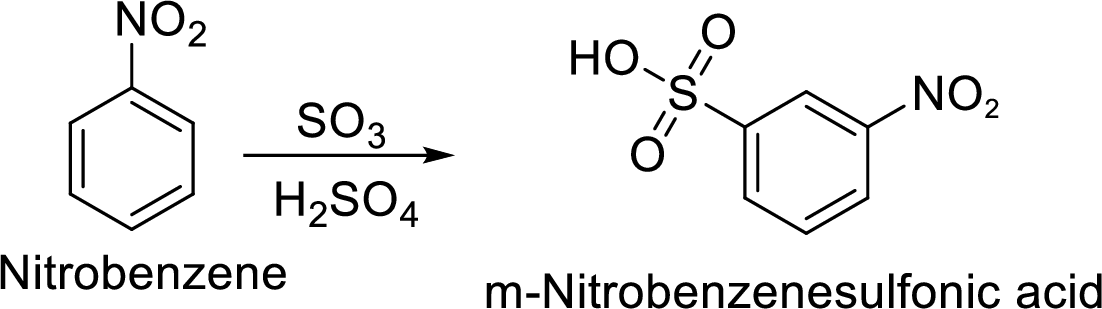
Step 2: Sulfonation of nitrobenzene by the reaction with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Starting with benzene, toluene, or phenol as the only sources of aromatic rings, show how to synthesize the following. Assume in all syntheses that mixtures of ortho-para products can be separated into the desired isomer. Q.)m-Nitrobenzenesulfonic acidarrow_forwardCompound A, C3H7Br, does not react with cold dilute potassium permanganate solution. Upon treatment with potassium hydroxide in ethanol, A gives only product B, C3H6. Unlike A, B decolourises potassium permanganate solution. Ozonolysis of Bgives C, C2H4O, and D, CH2O. Suggest the structural formulae of A, B, C and D.Write the equations for all the reactions involved.arrow_forwardDescribe the ozonolysis of alkenes one mole of a hydrocarbon(A) reacts with one mole of beomine giving a dibromo compound C5H10Br2.Substance A on treatment with cold dilute kMnO4 solution forms a compound C5C12O2(C5H12O2) on ozonolysis A,gives equimolar quantities of propanone and ethanol.Deduce the structure of substance A.arrow_forward
- Starting with benzene, toluene, or phenol as the only sources of aromatic rings, show how to synthesize the following. Assume in all syntheses that mixtures of ortho-para products can be separated into the desired isomer. Q.) p-Dichlorobenzenearrow_forwardThe sex attractant of the housefly has the formula C23H46. When treated with warm potassium permanganate, this pheromone gives two products: CH3(CH2)12COOH and CH3(CH2)7COOH. Suggest a structure for this sex attractant. Explainwhich part of the structure is uncertainarrow_forward1,2,3,4,5-Pentafluoro-6-nitrobenzene reacts readily with sodium methoxide in methanol at room temperature to yield two major products, each having the molecular formula C7H3F4NO3. Suggest reasonable structures for these two compounds.arrow_forward
- An optically active monoterpene (compound A) with molecular formula C10H18O undergoes catalytic hydrogenation to form an optically inactive compound with molecular formula C10H20O (compound B). When compound B is heated with acid, followed by reaction with O3 and then with dimethyl sulfide, one of the products obtained is 4-methylcyclohexanone. Give possible structures for compounds A and B.arrow_forwardWolff-Kishner reduction of compound W gave compound A. Treatment of A with m-chloroperbenzoic acid gave B which on reduction with LiAH4 gave C. Oxidation of compound C with chromic acid gave D (C9H14O). Suggest the structures for A, B, C, and D.arrow_forwardCompound A(C10H12O)gives off oxygen on treatment with sodium metal and also decolorizes Br2 in CCl4 to give organic compound B. Compound A on treatment with I2 in NaOH gives iodoform and salt C which after acidification gives a white solid D(C7H6O2). Using knowledge of organic chemistry identify structures A,B,C and Darrow_forward
- Using benzene and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents, suggest efficient syntheses of (a) Isobutylbenzene, C6H5CH2CH(CH3)2 (b) (2,2-Dimethylpropyl)benzene, C6H5CH2C(CH3)3arrow_forwardCompound A has molecular formula C4H10, and gives two monochlorides, B and C, on photochemical chlorination. Treatment of either of these monochlorides with potassium tert-butoxide gives the same alkene (C4H8) as the product, but B leads to just one isomer of the alkene, D, where C gives D and another isomer of the alkene, E. Treatment of monochlorides B and C with aqueous ethanol gives products F and G, respectively, both of which are of molecular formula C4H10O. What are the names of compounds A-G?arrow_forwardStarting with benzene, toluene, or phenol as the only sources of aromatic rings, show how to synthesize the following. Assume in all syntheses that mixtures of ortho-para products can be separated into the desired isomer. Q.) m-Chlorobenzoic acidarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,

