
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Base and monosaccharide used to form a given nucleoside needs to be identified and the name of the nucleoside needs to be stated.
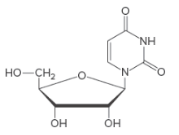
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA are
A
Only the base and the sugar portion of a nucleotide is called a nucleoside.
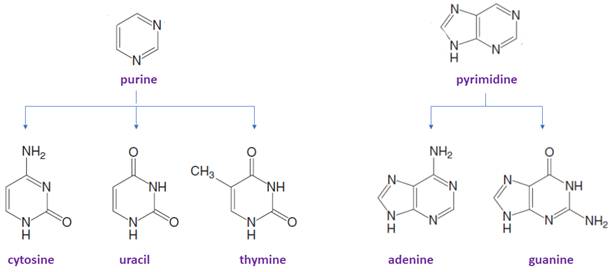
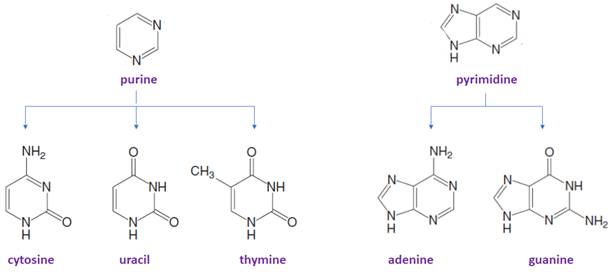
Bases in DNA/RNA:
There are only five common nitrogen-containing bases are present in DNA/RNA, which are derived either from pyrimidine or purine.
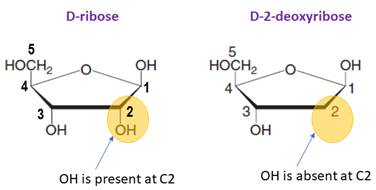
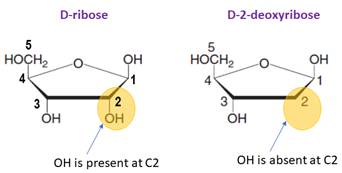
Sugar in DNA/RNA:
The monosaccharide in RNA is D-ribose.
In DNA, the monosaccharide is D-2-deoxyribose (lacks a hydroxylgroup at C2).
Naming Nucleosides:
The suffix −idine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a pyrimidine base.
The suffix -osine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a purine base.
The prefix deoxy- is used if hydroxyl group is missing at C-2 position of the sugar.
(b)
Interpretation:
Base and monosaccharide used to form a given nucleosideneed to be identified and the name of the nucleoside needs to be stated.
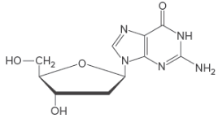
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA are linear
A nucleotide has three components; a five-membered sugar ring (monosaccharide), a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group.
Only the base and the sugar portion of a nucleotide is called a nucleoside.
Bases in DNA/RNA:
There are only five common nitrogen-containing bases are present in DNA/RNA, which are derived either from pyrimidine or purine.
Sugar in DNA/RNA:
The monosaccharide in RNA is D-ribose.
In DNA, the monosaccharide is D-2-deoxyribose (lacks a hydroxyl group at C2).
Naming Nucleosides:
The suffix −idine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a pyrimidine base.
The suffix -osine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a purine base.
The prefix deoxy- is used if hydroxyl group is missing at C-2 position of the sugar.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Give the name of the disaccharide that is presented:The name must be correct, the procedure with which the name is deduced must be displayedarrow_forwardDefine about Polysaccharides ?arrow_forwardComplete the following reaction for the acid hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose and label the two products. C12H22O11 + H2O ¡H+ sucrose waterarrow_forward
- Classify the following as monosaccharides or oligosaccharides.(i) Ribose (ii) Maltose(iii) Galactose (iv) Lactosearrow_forwardlabel the acetal and hemiketal moieties and peptride bonds. Indicate and name the bond that links the two saccharides in the disaccharide. Sketch the reaction of hydrolysis of the peptide, clearly drawing the reactants and products. Using one-letter codes, identify the dinucleotide sequence and state whether this is a DNA or RNA dinucleotide. Sketch the reaction of formation of the dinucleotide from its constituent nucleotides, clearly drawing reactants and products, and state which kind of reaction it is.arrow_forward`Of the choices listed below, which would be classified as a polysaccharide? glucose sucrose cellulose glycogen both cellulose and glycogenarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning




