
Two masses are attached to a wall by linear springs (Fig. P28.51). Force balances based on Newton's second law can be written as
where
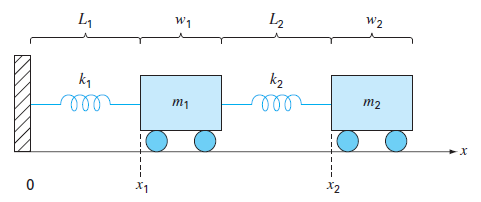
FIGURE P28.51
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
- 1. In general, the internal energy U depends on both temperature and volume, U=U(TV). The volume dependence comes from the potential energy due to the interactions among the particles. For free particles, there are no interactions, thus, the internal energy U should be independent of the volume, i.e., = 0. Verify this result for ideal gas pV = RT. au avarrow_forwardis a mass hanging by a spring under the influence of gravity. The force due to gravity, Fg, is acting in the negative-y direction. The dynamic variable is y. On the left, the system is shown without spring deflection. On the right, at the beginning of an experiment, the mass is pushed upward (positive-y direction) by an amount y₁. The gravitational constant g, is 9.81 m/s². DO C.D Frontly у Your tasks: No Deflection m k Fg = mg Initial Condition y m k Write down an expression for the total energy If as the sum Write down an expression for the total energy H Fg = mg Figure 3: System schematic for Problem 4. Yi & X Write down, in terms of the variables given, the total potential energy stored in the system when it is held in the initial condition, relative to the system with no deflection. as the sum of potential and kinetic energy in terms of y, y, yi C After the system is released, it will start to move. Write down an expression for the kinetic energy of the system, T, in terms of…arrow_forwardA physics lab consists of a large ball attached to a wire. Students hold on to one end of the wire, then whirl the ball around in circles and count the number of rotations per second. One group finds these numbers: ball mass= 320 gram, wire length= 1.3m, number of rotations/sec=2.5. The wire is made of steel with a diameter of 1mm and a Young's modulus of 20x10^10 N/m^2.How much does the wire stretch due to the tension on it? Should the students correct their data for the wire stretching?arrow_forward
- True or false Statics mechanics allows us to represent distributed loads as a concentrated force located at the centroid of the distributed load.arrow_forwardProblem #2: A velocity distribution is given as V = Please calculate the work flux (Iv) associated with molecular motions. -bx8,-byô, + bz8, where b is a constant and b‡0.arrow_forwardShow the solution paper below. 2.2 A spring-mass system has a natural period of 0.21 sec. What will be the new period if the spring constant is (a) increased by 50 percent and (b) decreased by 50 percent? Ans. a) 0.1715 sec; b) 0.2970 secarrow_forward
- 1. F3 The lateral-direction equations of motion of an aircraft in steady, straight and level flight are v=-0.243v-136.25r+9.80-0.7595 +4.825 p+0.0557r=-0.195v-1.695p+0.913r+16.535 +6.995 0.0152p+ 0.106v+0.039p-0.624r +0.3195-6.43% O=P (a) 4 € Consider the state-space representation of the equations of motion given by. Xlat Alat Alat + Blatulat ' and where and with F4 % Ylat 5 = Clat Xlat + Dlat lat Xlat = (V, p, r, $)T Ylat = (Y1, Y2, 3), Y₁ =B=V/VR, Determine the matrices Alat Blat, Clat, and Dlat- 10 F5 ^ Y2 = r, 6 1) F6 H y3 = (ay) eg 7 PrtScn F7 = V +136.25r. W * 8 Home F8 ( 9 End F9 ) PgUp 0arrow_forwardQ\. The first law of thermodynamics involves three main components, if we know the behavior of two components, estimate the behavior of the third component. ( Conclusion ) : a. If heat is added to the system, then the internal energy of the system increases. ..... .. b. If heat leaves the system, then the internal energy of the system decreases .... c. If the work is done by the system, then the internal energy of the system decreases ... ....... d. If the work is done on the system, then the internal energy of the system increases.. .......arrow_forward1. In the laboratory, when you hanged 100 grams at the end of the spring it stretched 10 cm. You pulled the 100-gram mass 6 cm from its equilibrium position and let it go at t = 0. Find an equation for the position of the mass as a function of time t. 2. The scale of a spring balance found in an old Physics lab reads from 0 to 15.0 kg is 12.0 cm long. To know its other specifications, a package was suspended from it and it was found to oscillate vertically with a frequency of 2.00 Hz. Calculate the spring constant of the balance? (b) How much does the package weigh?arrow_forward
- A cart at rest starts to move from its initial position by an external force F. Find its acceleration in m/s^2 when it has moved 0.1 m when m=20 kg, F=100 N, k=1000 N/m. O 0.1 www 0.025 0.25 None of abovearrow_forwardThe following table lists temperatures and specific volumes of water vapor at two pressures: p = 1.5 MPa v(m³/kg) p = 1.0 MPa T ("C) v(m³/kg) T ("C) 200 0.2060 200 0.1325 240 280 0.2275 0.2480 240 280 0.1483 0.1627 Data encountered in solving problems often do not fall exactly on the grid of values provided by property tables, and linear interpolation between adjacent table entries becomes necessary. Using the data provided here, estimate i. the specific volume at T= 240 °Č, p = 1.25 MPa, in m/kg ii. the temperature at p = 1.5 MPa, v = 0.1555 m/kg, in °C ii. the specific volume at T = 220 °C, p = 1.4 MPa, in m'/kgarrow_forward1.75m 1.5 m 2.75m Given: G/0 Find: 2.25m 6 o B 2.0m . h = 2.05 meters • Tension = 85 Newtons 26 1.5m W Magnitude of internal axial force (Newtons) Axial Force Bending moment V Shear forcearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





