
Concept explainers
The conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl acetate occurs via the following two-step mechanism.
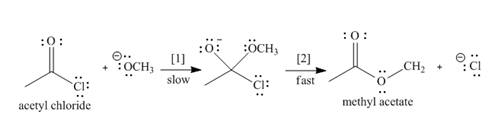
a. Add curved arrows to show the movement of the electrons in each step.
b. Write the rate equation for this reaction, assuming the first step is rate-determining.
c. If the concentration of
d. If the concentrations of both
e. Classify the conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl acetate as an addition, elimination, or substitution.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Inorganic Chemistry
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
- Monensin (1) is a potent antibiotic. JACS 1980, 102, 2118-2120. 1. Use arrows provided a pathway from (1) to (2) when we add a mild base sodium bicarbonate followed by iodine (I2). 2. What was a similar reaction between Br2 and an alkene? What did we name the intermediate?arrow_forwardIn the reaction from compound 10 to compound 11, why the C=C bond is retained and is not hydrogenated? f) LiAlH4, Et2O, 08C; g) Ac2O, py, DMAP, CH2Cl2, RT, 77% over 2 steps;arrow_forwarda.) What was the product of the first step (reaction involving HCl)? b.)What was the product of the second step (reaction involving NaOH)? If something else formed as the product of the first reaction, use that alternative structure as the reactant for this second reaction. c.)How would you change the reaction conditions (either step 1 or step 2) to ensure you obtained the planned final product as the major product.arrow_forward
- What would be the missing steps and intermediates for the following reaction?arrow_forwardWhat is the CCl4 do on the first step of the reaction?arrow_forwardReaction of (CH3)3CH with Cl2 forms two products: (CH3)2CHCH2Cl (63%) and (CH3)3CCl (37%). Why is the major product formed by cleavage of the stronger 1° C–H bond?arrow_forward
- An SN1 reaction is shown in the box; the reaction energy profile diagram for this reaction is shown below. Identify the location for Compound I on the reaction profile. A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5arrow_forwardPlease explain why reagent 1 cannot be (Br2, FeBr3) 1. Identify reagent 1, and draw the mechanism & product in this step. 2. Identify reagnet 2 (answer given in the picture), and draw the mechanism & product in this step. 3. Explain why Reagent 3 is Zn(Hg), HCl ? draw the mechanism of what happen to the compound when Reagent 3 is Zn(Hg), HCl is added.arrow_forwardAcid-catalyzed water removal reaction of neopentyl alcohol, (CH3) 3CCH2OH, produces 2-methyl-2-butene as the main product. Design a mechanism that shows all the steps in the formation of this product.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


