
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The molecule with the lowest potential energy needs to be drawn for the following condition:
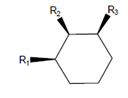
Here,
Concept Introduction: The molecule with lowest potential energy is most stable. In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, the stable conformation is when large groups are present in the equatorial positions. The equatorial positions in the chair conformation points away from the ring thus, there is less steric hinderance.
(b)
Interpretation: The molecule with the lowest potential energy needs to be drawn for the following condition:
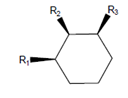
Here,
Concept Introduction: The molecule with lowest potential energy is most stable. In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, the stable conformation is when large groups are present in the equatorial positions. The equatorial positions in the chair conformation points away from the ring thus, there is less steric hinderance.
(c)
Interpretation: The molecule with the lowest potential energy needs to be drawn for the following condition:
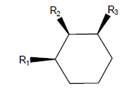
Here,
Concept Introduction: The molecule with lowest potential energy is most stable. In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, the stable conformation is when large groups are present in the equatorial positions. The equatorial positions in the chair conformation points away from the ring thus, there is less steric hinderance.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- What is the most stable chair conformation of the 4-methoxy-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane structure given below ?arrow_forwardWhat is the value in kJ/mol, of the lowest energy trnasition above? a.) 545 b.) 444 c.) 320 d.) 266arrow_forwardUsing your model, construct an energy diagram to show the variation in the free energy of the molecule as the FRONT ATOM is rotated CLOCKWISE from 0º to 360º in 60º increments. In your energy diagram, you should clearly show the relative energies of each conformer.arrow_forward
- .....Draw the Newman pr0jecti0ns 0f the three p0ssible staggered c0nf0rmati0ns 0f2,3-dimethylbutane, viewed thr0ugh the C2—C3 b0nd. What are the relativeenergies of each c0nf0rmati0n?arrow_forward(a) (S)-2-chlorobutane, draw any planes of symmetry.arrow_forwardWhich of the following Newman projections represents (2R,3R)-dibromobutane?arrow_forward
- The MOE results and a discussion pertaining to the conformation of Thioflavin T at low potential energies. At low energies, the conformation of ThT cannot be coplanar, that is, the dihedral angle cannot be 0. Why not?arrow_forwardDraw all the conformers of methyl cylobutane and also the corresponding energy profilearrow_forwardRank the following Newman projections in order of increasing energy.arrow_forward
- Which of the following molecules are chiral?I. cis-1,3-DibromocyclohexaneII.1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexaneIII.trans-1-Bromo-3-methylcyclohexaneIV.cis-1-Bromo-3-methylcyclohexanearrow_forwardFor the compounds given (A, B, C) 1. determine their relationship ( enantimers, idential/same compind, diatermeros, constitutional isomers) and give a short explanation whyarrow_forwardDraw the most stable chair conformation possible for this compound. Are there any 1,3-diaxial interactions in the most stable chair conformation ( H-H not included ) and please fill in the blank: From the biomolecules surveyed, the compound is a(n)___________arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
