
Concept explainers
To analyze:
In laboratory, the following dideoxy DNA sequencing gel is produced.
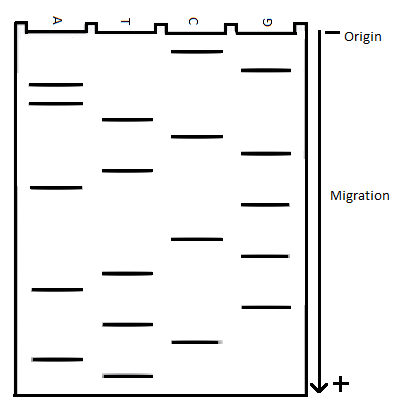
The double-stranded DNA sequence of this molecules to be determined.
The polarity of each strand is to be labeled.
Introduction:
DNA sequencing is the determination of a sequence of
Sanger sequencing is a method of sequencing a region of DNA that is up to
Sanger sequencing was first developed by Fred Sanger and his colleagues in
This process involved the formation of many copies of the template DNA strand.
Dideoxynucleotides inhibit the chain elongation process of DNA polymerases. They are also abbreviated as
The principle of Sanger sequencing is that sufficient time and material can produce at least one DNA sequence of every possible length with a tagged nucleotide at the end.
The tagged nucleotides get terminated because ddNTPs lack
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Pearson eText Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- The short DNA shown below is to be sequenced. Using your knowledge of how the Sanger method works, in the gel diagram, draw in the bands that will appear when DNA polymerase is added to the reaction along with the four different nucleotide mixtures indicated. Note that some of these mixtures are not what would normally be used in a sequencing reaction. Dideoxynucleatides (ddNTPs) are added in relatively small amounts. The asterisk represents a radioactive label. *5' - 3'-ОН 3' – -- ACGACGCAGGACATTAGAC-5' Nucleotide mixtures: A. DATP, DTTP, dCTP, DGTP, ddTTP (given) B. DATP, ATTP, dCTP, AGTP, ddATE C. dTTP, dGTP. ACTP, ddCTP, ddATP D. DATP, dCTP, dTTP, ddGTP A в с D | || ||arrow_forwardWhether done manually or automated, DNA sequencing gels are always made of polyacrylamide rather than agarose. Why can't agarose be used for a sequencing gel, as it is for other DNA gel electrophoresis?arrow_forwardA Sanger product of the sequencing of a template DNA is presented +ddTTP +ddATP +ddCTP +ddGTP Mononucleotide Pentanucleotide Trinucleotide Dinucleotide 11-nucleotide Hexanucleotide Octanucleotide Tetranucleotide 16-nucleotide Decanucleotide Nonanucleotide Heptanucleotide 17-nucleotide 15-nucleotide 13-nucleotide 12-nucleotide 18-nucleotide 20-nucleotide 14-nucleotide 19-nucleotide 21-nucleotide 1. Determine the sequence of template DNA 2. Determine the mRNA sequence from this template DNA 3. Determine the the sequence of protein product derived from that DNAarrow_forward
- What do you mean by amphoteric substance? Give examples of substance that is/are amphoteric. What is the purpose of the power supply in gel electrophoresis? Among the short and long strand of DNA, which moves the farthest in the gel and why? What is the purpose of buffer in agarose gel electrophoresis?arrow_forwardA piece of DNA is cut into four fragments as shown below. A solution containing the four fragments is placed in a single well at the top of an agarose gel. Using the information given below, draw (below the well) how you think the fragments will be aligned on the gel following electrophoresis. Label each fragment with its corresponding letter. Remember, each band on the gel will be the same width, equal to the width of the well at the top of the gel. These should all be in one lane. What is it about the chemistry of DNA that causes it to be uniformly negatively charged?arrow_forwardA piece of DNA is cut into four fragments as shown below. A solution containing the four fragments is placed in a single well at the top of an agarose gel. Using the information given below, draw (below the well) how you think the fragments will be aligned on the gel following electrophoresis. Label each fragment with its corresponding letter. Remember, each band on the gel will be the same width, equal to the width of the well at the top of the gel. These should all be in one lane. What if you had two different DNA fragments that were exactly the same length as measured in base-pairs. Would it be possible to distinguish them using this type of electrophoresis? How would they appear on a gel?arrow_forward
- The following gel was produced in manual DNA sequencing. What would the unknown DNA template be that this gel represents?arrow_forwardSanger DNA sequencing/ dideoxy sequencing was used as shown in the diagram below. The arrow indicates the direction for migration of the bands in the gel. What are the first 3 letters of this DNA sequence?arrow_forwardSimilarities between DNA agarose gels and SDS-PAGE are: Both methods use agarose gels. Both methods use electrical charge differences to separate molecules by size. Both methods determine the size of DNA fragments. All the given answers.arrow_forward
- A DNA fragment with 450 bp will be closer to the top (negative pole) of an electrophoresis gel than one with 2,500 bp.True or false?arrow_forwardA 13-nucleotide section of an autoradiogram from a Sanger sequencing experiment is depicted in the image below. Based on the band pattern observed here, write out the sequence of both the complementary strand generated during the experiment, and the template strand that is being analyzed. Be sure to clearly indicate the 5' and 3' ends of each. ddATP ddGTP ddCTP || | | ddTTP | 3' 5' Tyne a short answer in the space provided belowarrow_forwardThe sequences of several short single-stranded DNA molecules are shown below. Imagine each sequence as a typical double-stranded DNA molecule, with antiparallel strands held together by Watson-Crick base- pairs between the complementary bases. Which of these double-stranded molecules would have the highest melting temperature (Tm)? 5' ACTGAGTCTCTGACTAGTCT 3' 5' ACTTAGTCTATGACTAGTCT 3' 5' ACTTAATCTATGAATAGTCT 3' 5' ACTGCGTCTCCGACTAGTCT 3' 5' ACTGCGTCTCCGACGAGCCT 3'arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





