
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134605173
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 25P
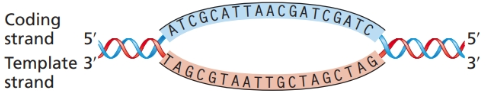
The accompanying illustration shows a portion of a gene undergoing transcription. The template and coding strands for the gene are labeled, and a segment of DNA sequence is given. For this gene segment:
a. Superimpose a drawing of RNA polymerase as it nears the end of transcription of the DNA sequence.
b. Indicate the direction in which RNA polymerase moves as it transcribes this gene.
c. Write the polarity and sequence of the RNA transcript from the DNA sequence given.
d. Identify the direction in which the promoter for this gene is located.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Given the template DNA sequence:
3’ - TAC - CAG - GTT - ACC - ATC - 5’
A.) What will be the mRNA requence corresponding to the template DNA sequence?
B.) What is the amino acid sequence in letter A? ( e.g. Arg, Phe, etc.)
C.) If the coding sequence of the dsDNA will "serve" as the template for transcription, what is the corresponding mRNA sequence?
D.) With the mRNA transcript in letter C, what will be the amino acid sequence? ( e.g. Arg, Phe, etc.)
f you made a change in the promoter sequence in the DNA that inactivates the promoter, what would happen at the RNA level?
A-Nothing, because the RNA would be made as usual
B-Transcription factors would be unable to bind and the RNA polymerase would not be recruited to the DNA, so no RNA would be made.
C-The mutation of the DNA would be carried through to the RNA sequence.
D-The DNA helicase would not be able to recognize and bind the DNA, so the RNA would not be made.
EXPLAIN WHY THE ANSWER YOU CHOOSE IS CORRECT
Complete the table below
6. Below are several DNA sequences that are mutated compared with the wild-type sequence: 3’-T A C T G A C T GA C G A T C-5’. Envision that each is a section of a DNA molecule that has separated in preparation for transcription, so you are only seeing the template strand. Construct the complementary DNA sequences (indicating 5’ and 3’ ends) for each mutated DNA sequence, then transcribe (indicating 5’ and 3’ ends) the template strands, and translate the mRNA molecules using the genetic code, recording the resulting amino acid sequence (indicating the N and C termini). What type of mutation is each?6.a. Mutated DNA Template Strand #1: 3’-T A C T G T C T G A C G A T C-5’Complementary DNA sequence:mRNA sequence transcribed from template:Amino acid sequence of peptide:Type of mutation:
6.b. Mutated DNA Template Strand #2: 3’-T A C G G A C T G A C G A T C-5’Complementary DNA sequence:mRNA sequence transcribed from template:Amino acid sequence of peptide:Type of…
Chapter 8 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1PCh. 8 - 8.2 In one to two sentences each, describe the...Ch. 8 - 8.3 Answer these questions concerning...Ch. 8 - 8.4 The diagram below shows a DNA duplex. The...Ch. 8 - The following is a portion of an mRNA sequence:...Ch. 8 - Compare and contrast the properties of DNA...Ch. 8 - The DNA sequences shown below are from the...Ch. 8 - Bacterial and eukaryotic gene transcripts can...Ch. 8 - Describe the two types of transcription...Ch. 8 - What is the role of enhancer sequences in...
Ch. 8 - Prob. 11PCh. 8 - Draw a bacterial promoter and label its consensus...Ch. 8 - For a eukaryotic gene whose transcription require...Ch. 8 - Three genes identified in the diagram as A, B and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 15PCh. 8 - 8.16 The segment of the bacterial gene involved in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17PCh. 8 - Prob. 18PCh. 8 - 8.19 A DNA fragment from the end of the mouse...Ch. 8 - 8.20 Wild-type E. coli grow best at but can grow...Ch. 8 - A mutant strain of Salmonella bacteria carries a...Ch. 8 - 8.22 The human wild-type allele and a certain...Ch. 8 - Prob. 23PCh. 8 - A full-length eukaryotic gene is inserted into a...Ch. 8 - The accompanying illustration shows a portion of a...Ch. 8 - DNA footprint protection (described in Research...Ch. 8 - Suppose you have a 1-kb segment of cloned DNA that...Ch. 8 - Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each...Ch. 8 - 8.29 The DNA sequence below gives the first base...Ch. 8 - 8.30 Genomic DNA from a mouse is isolated,...Ch. 8 - 8.31 A portion of a human gene is isolated from...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following is a portion of an mRNA sequence: 3’ –AUCGUCAUGCAGA-5’ a)During transcription, was the adenine at the left-hand side of the sequence the first or the last nucleotide used to build the portion of the mRNA shown? Explain how you know. b)Write out the sequence and polarity of the DNA duplex that encodes this mRNA segment. Label the template and coding DNA strands. c)Identify the direction in which the promoter region for this gene will be located.arrow_forwardYou are studying the rate of transcription of a particular eukaryotic gene. When the DNA located several thousand bases upstream from the gene is removed, the transcription rate of the gene decreases dramatically. How would you interpret these results?arrow_forwardThe following represent deoxyribonucleotide sequences in the template strand of DNA: Sequence 1: 5′-CTTTTTTGCCAT-3′ Sequence 2: 5′-ACATCAATAACT-3′ Sequence 3: 5′-TACAAGGGTTCT-3′ (a) For each strand, determine the mRNA sequence that would be derived from transcription. (b) Using Figure 12–7, determine the amino acid sequence that is encoded by these mRNAs. (c) For Sequence 1, what is the sequence of the partner DNA strand?arrow_forward
- A) Describe each step of the DNA REPLICATION in EUKARYOTIC organismsB) Describe each step of the TRANSCRIPTION in EUKARYOTIC organisms.C) Describe each step of the TRANSLATION. Please answer all if you can! thank youarrow_forwardYou are given the following mRNA sequence. You know that it contains some UTR sequence and the beginning of the coding sequence of a gene. 5’ ACGGUAUCUAUGGAUUCUGAGGUUGCUGCUUUGGUUAUU 3’ Part A: Write the amino acid sequence for this portion of the coding sequence. Part B: Write the double-stranded DNA sequence that corresponds to the mRNA above. Label 5’ and 3’ ends. Would transcription have occurred using the top or bottom strand as the template?arrow_forwardUse the Genetic Code below to help you answer the following questions. The nucleotide sequence of a hypothetical eukaryotic gene is: 3'- CCC CAT CAG TCA AGG GAA - 5' a. Provide the mRNA of the non-mutated gene. b. Provide the linear amino acid sequence of the non-mutated gene. üü c. Examine the mutated DNA sequence below. What would be the sequence of the mRNA? ü Mutated DNA sequence: 3' CCC CAC AGT CAA GGG AA 5' d. Provide the linear amino acid sequence of the mutated gene and identify the type of mutation. e. Comment on the consequences of this type of mutation?arrow_forward
- With regard to transcriptional termination in eukaryotes, which model suggests that RNA polymerase is physically removed from the DNA? a. Allosteric model b. Torpedo model c. Both models d. Neither modelarrow_forwardRefer to a genetic code table for the question. below is a portion of the template strand of a particular gene sequence. Which of the following would be the correct sequence of amino acids in the protein that this portion of the gene encodes? (Note that there are no entrance in this gene sequence, and this portion is found in the middle of the coding sequence, past the start codon, so you should transcribe and translate the entire portion of this sequence) template DNA : 3' - ACG GGT TCC TTT AAC GCG TAG -5' A) Thr-Gly-Ser-Phe-Asn-Ala B) Cys-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-Ile C) there is not enough information given to determine the amino acid sequence of this portion of the gene .arrow_forwardThe following diagram represents a transcription unit on a DNA molecule. a. Assume that this DNA molecule is from a bacterial cell. Draw the approximate locations of the promoter and terminator for this transcription unit. b. Assume that this DNA molecule is from a eukaryotic cell. Draw the approximate location of an RNA polymerase II promoter.arrow_forward
- Given the following DNA sequence of the template strand for a given gene: 5' TTTCCGTCTCAGGGCTGAAAATGTTTGCTCATCGAACGC3' Part A ) Write the mRNA that will be transcribed from the DNA sequence above (be sure to label the 5' and 3' ends). Part B ) Use the genetic code to write the peptide sequence translated in a cell from the mRNA in part A. Please use the 3 letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Part C: How would the peptide synthesized in a cell be different if the mRNA was translated in vitro (i.e. not in the cell)?arrow_forwardShown below is a portion of a wild-type DNA sequence that encodes the last amino acids of a protein that is 270 amino acids long. The first three bolded base pairs indicate the frame and include the coding region. 5^ ...GCTAAGTATTGCTCAAGATTAGGATGATAAATAACTGG 3^ 3^.. CGATTCATAACGAGTTCTAATCCTACTATTTATTGACC 5^ Which strand is the template strand for transcription of this gene? Briefly explain how you know. An insertion of one base pair causes the protein to decrease in length by seven amino acids. With respect to the sequence given above, where does this insertion occur? A change of one base pair leads to the protein increasing in the length by one amino acid. With respect to the sequence given above, which base pair would you change, and what would you change this base pair for the protein to increase in the length by one amino acid?arrow_forwardSickle cell anemia is a disease caused by a mutation at the genotypic level. A person with two copies of the gene has the disease, but a person with one copy of the gene does not have the disease. The diagram shows how this mutation affects an organism. Use the image to answer the question. Which conclusion can you draw based on the diagram? A. The mutation changed the amino acid sequence during the translation step. B. A mutation caused the information in DNA to change during the transcription step. C. A change in the DNA sequence can be carried over to the translation and transcription steps. D. The change that affected the translation and transcription steps does not affect the organism.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Bacterial Genomics and Metagenomics; Author: Quadram Institute;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_6IdVTAFXoU;License: Standard youtube license