
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The curved arrow to show electron movement in the first carbocation rearrangement should be drawn.
Concept introduction: Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
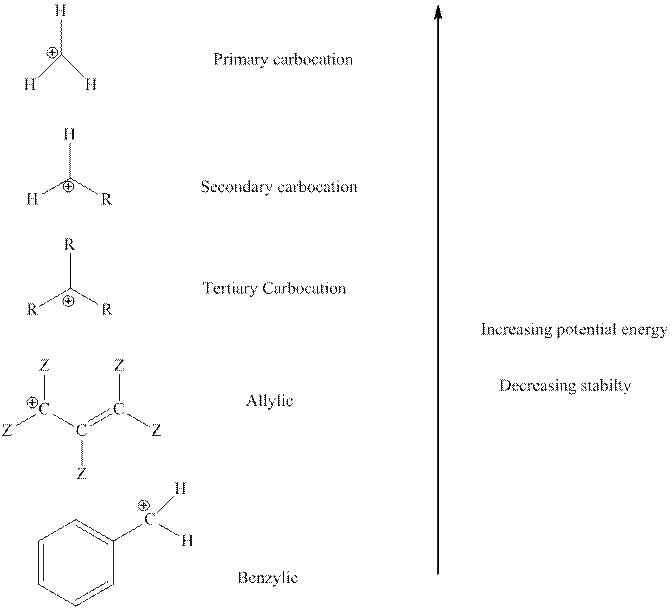
Some special carbocation may attain stability via ring explosion. This also occurs since five-membered rings are more stable than strained three or four-membered ring.
(b)
Interpretation: The curved arrow to show electron movement in the second carbocation rearrangement should be drawn.
Concept introduction: Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
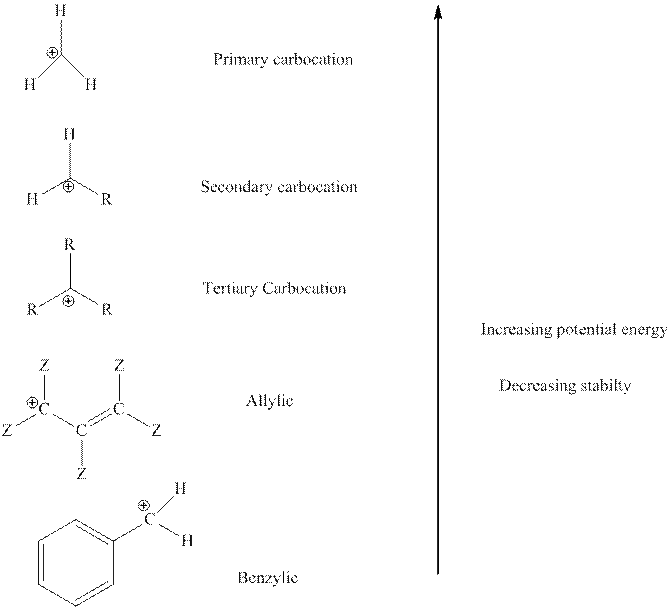
(c)
Interpretation: The force that drives this rearrangement should be illustrated.
Concept introduction: Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
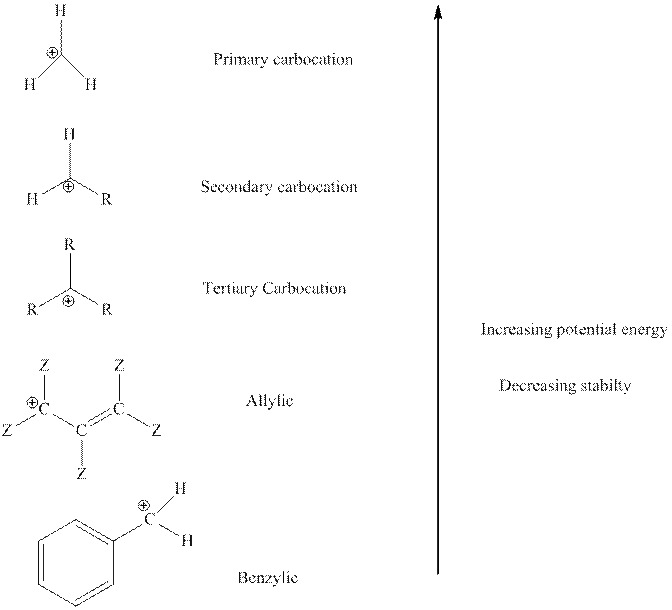
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- Honor Gross ma's Rule. A) For this question draw a curved arrow mechanism, start converting the Start matenal to Product A Only you Make Sure Pairs, and heteroatoms. also show the relevant resonance- Structure, and the conservation of Charge & mass B.) Then explain why product A. is a good major product. Then explain Product B is the minor product is H₂CO why and AIC137 CY why at all. draw all lone H3CO 4.5 A + not observed HCOarrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... i x + P C 1. NaOMe Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. Harrow_forwardWhat is the correct answer here? Answer key says D but it doesn't make sense to me because the final one (5) is tertiary allylic.arrow_forward
- Show the more stable carbocation that forms through a 1,2-shift. draw structure...arrow_forwardDraw both resonance structures of the most stable carbocation intermediate in the reaction shown. • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • Do not include anionic counter-ions, e.g., I, in your answer. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate resonance structures using the symbol from the drop-down menu. ☺. re HBr ChemDoodle Sn 11arrow_forward3. Answer the following questions based on the reaction scheme below. a. Use wedged and dashed lines to draw the (2S,4R)-2-iodo-4-methoxypentane configuration of 2-iodo-4-methoxypentane in labeled box. b. Draw the product(s) of the nucleophilic addition reaction shown. Make sure to use wedged and dashed lines to clearly show the resulting stereochemistry at each chiral center. Label each chiral center as R or S. If there is more than one possible product, draw one in each box - if not, leave one box blank. c. Write the correct chemical name of each product(s) in the labeled boxes. 2-iodo-4- methoxypentane + NaOCH 3 K[C6H1310] Product Name: Product Name: d. Are all the product(s) chiral? If your answer is 'yes' write 'yes' in the box below. If your answer is 'no', provide an explanation in 3 sentences or less in the box below.arrow_forward
- Working Backwards Tutorial. a. First, identify the reactions taking place. Look at the reagent over the arrows. What is the reaction used for? Does it have SN1 or SN2 conditions? b. Now look at the big molecule. Based on your answers to A, circle any portion of the molecule you suspect reacted under these conditions. Is it a stereocenter? c.Based on your answers to A and B, what will be the stereochemical outcome of this reaction?arrow_forwardComplete the following for the below reaction. i. draw the complete Molecular Orbital diagram with electron filling, nodes and phasing. ii. label each level with the number of bonding and antibonding interactions iii. label each level as bonding, nonbonding or antibonding, and HOMO & LUMO iv. Using the correct level, show how the cyclization occurs to give cyclohexadiene and indicate whether the product is cis or trans. heatarrow_forwardI. For each molecule below 1) Show the radical cation that would form, including all non-bonding electrons, if the molecule were subjected to electron impact mass spectrometry 2) Show the electron pushing mechanism for a. an a-cleavage reaction of the radical cation drawn in part 1) for molecule A. b. a McLafferty rearrangement of the radical cation drawn in part 1) for molecule B. 3) Show both products of the mechanism in part 2) A B Jön OH Electron Impact Mass Spec Electron Impact Mass Specarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
