
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The overlap of orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
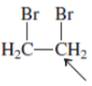
Concept Introduction: Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(b)
Interpretation: The overlap of orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
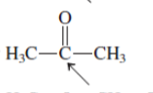
Concept Introduction: Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(c)
Interpretation: The overlap of orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
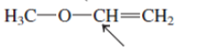
Concept Introduction: Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(d)
Interpretation: The overlap of orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
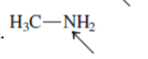
Concept Introduction: Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(e)
Interpretation: The overlap of orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
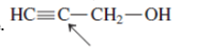
Concept Introduction: Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(f)
Interpretation: The overlap of orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
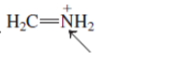
Concept Introduction: Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Which one has delocalized bonding ? a) ClO- b) NH4+ c) CH2=CHC(O)CH=CH2 d) CH2=CH(CH2)2CH=CH2 e) H2COarrow_forwardDraw and upload a model of 4 molecules of F2 and label the strongest interactions that are present between separate molecules.arrow_forwardDraw the structures of fluorene and fluorenone below. Label which one is polar and which one is non-polar overall below the name. On the structure you drew for the polar compound, label the atoms of the polar bond using d+ and d-arrow_forward
- Why do we need to find the most syabel structure possiblearrow_forwardWhat orbitals are used to form each highlighted bond? For multiple bonds, indicate the orbitals used in individual bonds.arrow_forwardUsing your model of butane (CH3CH2CH2CH3) , complete the following graph of the anglebetween the two Me groups vs. potential energy. a. Label each Newman projection of butane on the graph with the words staggered, eclipsed, gauche, and anti, as appropriate. (Note that some structures will have more than one label.) b. Draw a wedge and dash bond representation of butane in its lowest P.E. conformation.arrow_forward
- Identify each illustration as depicting a σ or π bond:(a) side-by-side overlap of a 4p and a 2p orbital(b) end-to-end overlap of a 4p and 4p orbital(c) end-to-end overlap of a 4p and a 2p orbitalarrow_forwardWhat is the dipole direction in H-D?arrow_forwardIdentify the type of configurational isomerism that exist for each double bond. E or Zarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



